- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369945 > P8XC591 (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) HiRel FPGA, Low-Power 1.0?? CMOS Technology PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | P8XC591 |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 英文描述: | HiRel FPGA, Low-Power 1.0?? CMOS Technology |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片8 - CAN控制器位微控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 78/160頁 |
| 文件大小: | 601K |
| 代理商: | P8XC591 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁當(dāng)前第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁
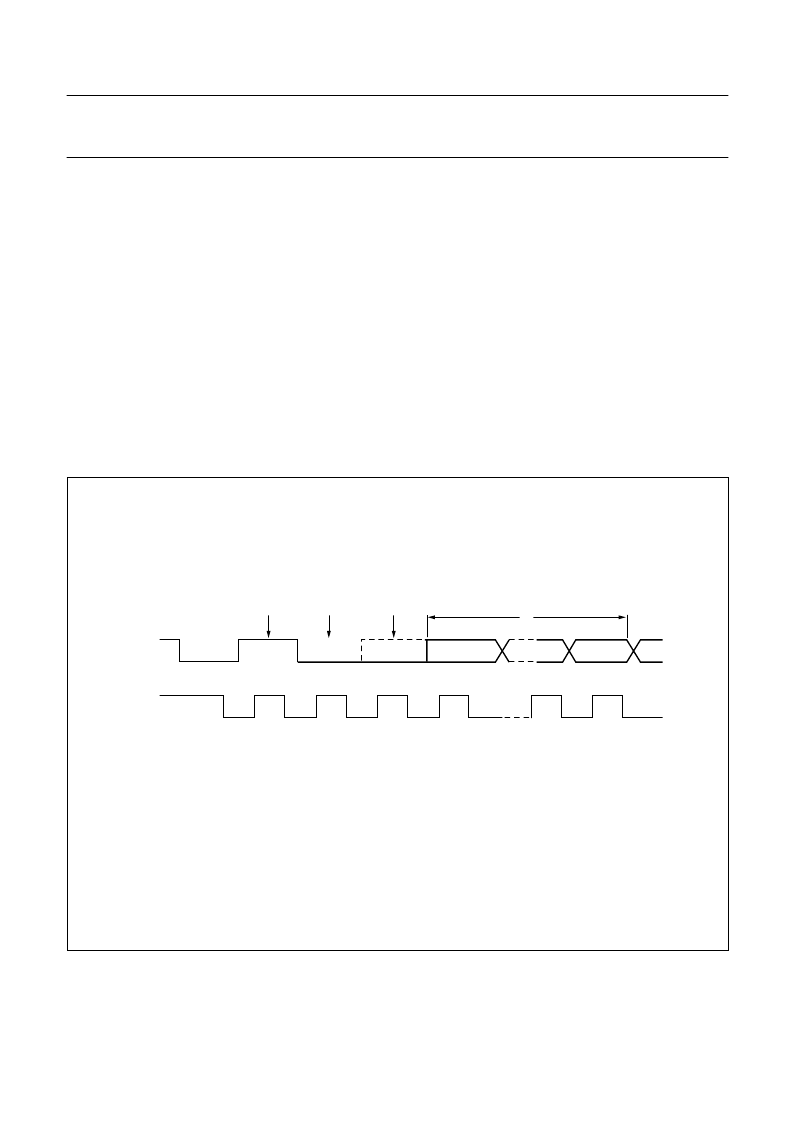
2000 Jul 26
78
Philips Semiconductors
Preliminary Specification
Single-chip 8-bit microcontroller with CAN controller
P8xC591
15.2.5
A
RBITRATION AND
S
YNCHRONIZATION
L
OGIC
Inthemastertransmittermode,thearbitrationlogicchecks
that every transmitted logic 1 actually appears as a logic 1
on the I
2
C bus. If another device on the bus overrules a
logic 1 and pulls the SDA line low, arbitration is lost, and
SIO1 immediately changes from master transmitter to
slave receiver. SIO1 will continue to output clock pulses
(on SCL) until transmission of the current serial byte is
complete.
Arbitration may also be lost in the master receiver mode.
Loss of arbitration in this mode can only occur while SIO1
is returning a not acknowledge: (logic 1) to the bus.
Arbitration is lost when another device on the bus pulls this
signal LOW. Since this can occur only at the end of a serial
byte, SIO1 generates no further clock pulses. Figure 33
shows the arbitration procedure.
The synchronization logic will synchronize the serial clock
generator with the clock pulses on the SCL line from
another device. If two or more master devices generate
clock pulses, the mark duration is determined by the
device that generates the shortest marks, and the space
duration is determined by the device that generates the
longest spaces. Figure 34 shows the synchronization
procedure.
A slave may stretch the space duration to slow down the
bus master. The space duration may also be stretched for
handshaking purposes. This can be done after each bit or
after a complete byte transfer. SIO1 will stretch the SCL
space duration after a byte has been transmitted or
received and the acknowledge bit has been transferred.
The serial interrupt flag (SI) is set, and the stretching
continues until the serial interrupt flag is cleared.
Fig.33 Arbitration Procedure.
handbook, full pagewidth
MHI034
SDA
SCL
1
2
3
4
8
9
ACK
(2)
(1)
(1)
(3)
(1) Another device transmits identical serial data.
(2) Another device overrules a logic 1 (dotted line) transmitted by SIO1 (master) by pulling the SDA line low. Arbitration is lost,
and SIO1 enters the slave receiver mode.
(3) SIO1 is in the slave receiver mode but still generates clock pulses until the current byte has been transmitted. SIO1 will not
generate clock pulses for the next byte. Data on SDA originates from the new master once it has won arbitration.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| P90CE201 | 16-bit microcontroller |
| P90CE201AEB | 16-bit microcontroller |
| P9217 | PbS photoconductive detector |
| P930 | CdS photoconductive cell |
| PA025XSB | This technical specification applies to 2.5inch color TFT-LCD panel. |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| P8XC592 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:8-bit microcontroller with on-chip CAN |
| P8XCE598 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:8-bit microcontroller with on-chip CAN |
| P8XCL580HFH | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Low voltage 8-bit microcontrollers with UART, I2C-bus and ADC |
| P8XCL580HFT | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Low voltage 8-bit microcontrollers with UART, I2C-bus and ADC |
| P8Z77 DELUXE | 制造商:Asus 功能描述:P8Z77-V Deluxe ATX Motherboard |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。