- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371773 > HC05V7GRS 68HC05V7 General Release Specification PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HC05V7GRS |
| 英文描述: | 68HC05V7 General Release Specification |
| 中文描述: | 68HC05V7一般版本規(guī)范 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 78/170頁 |
| 文件大小: | 980K |
| 代理商: | HC05V7GRS |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁當(dāng)前第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁
MOTOROLA
Page 64
SECTION 9: PARALLEL I/O
MC68HC05V7 Specification Rev. 1.0
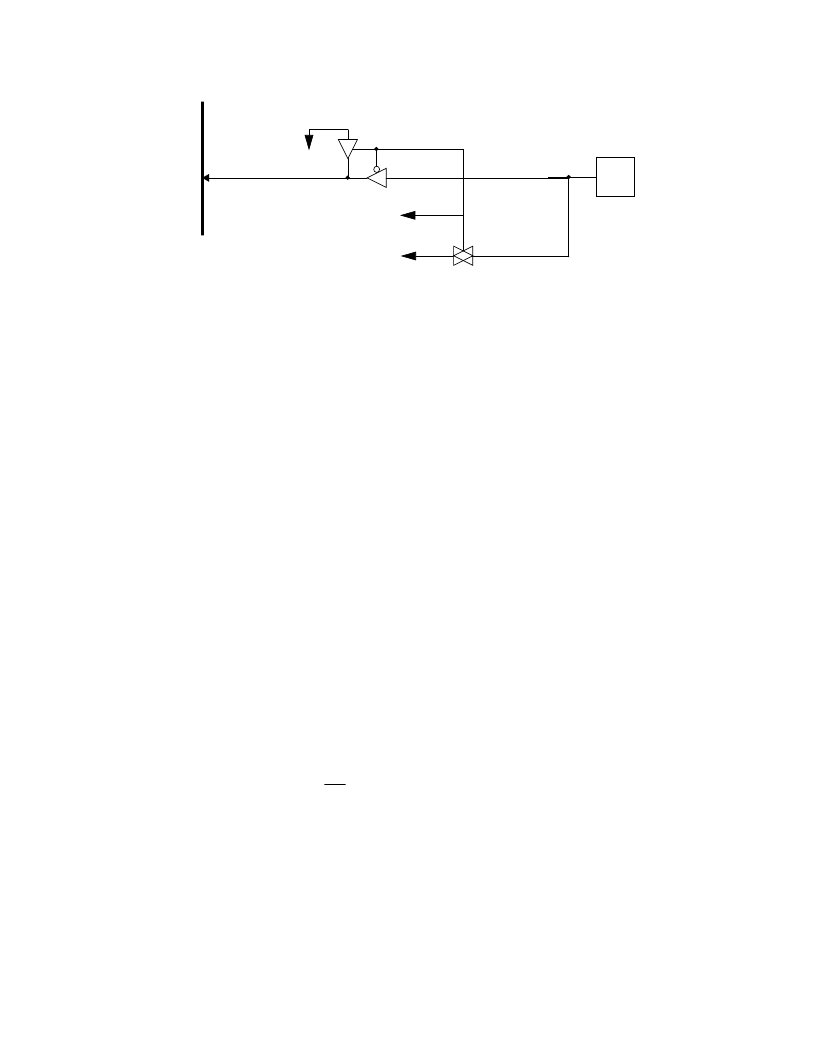
Figure 9-3: Port D and Port E Circuitry
9.4
PORT F
Port F is a 4-bit bidirectional port which shares all of its pins with the SPI subsystem. If the
SPI is enabled, Port F3-1 are disabled as regular I/O pins. PF0 can still function as an
output if the DDR bit is set. Each Port F pin is controlled by the corresponding bits in a data
direction register and a data register. The Port F Data Register is located at address $002C.
The Port F Data Direction Register (DDRF) is located at address $002E. Reset clears the
DDRF register. The Port F Data Register is unaffected by reset. Port F is shared with the
SPI.
9.4.1
PORT F DATA REGISTER
Each Port F I/O pin has a corresponding bit in the Port F Data Register. When a Port F pin
is programmed as an output the state of the corresponding data register bit determines the
state of the output pin. When a Port F pin is programmed as an input, any read of the Port
F Data Register will return the logic state of the corresponding I/O pin. The Port F data
register may be read even if the SPI subsystem is enabled. The Port F data register is
unaffected by reset.
9.4.2
PORT F DATA DIRECTION REGISTER
Each Port F I/O pin may be programmed as an input by clearing the corresponding bit in
the DDRF, or programmed as an output by setting the corresponding bit in the DDRF. The
DDRF can be accessed at address $002E. If the SPI subsystem is enabled (SPE bit is set),
the DDRF bit corresponding to PF0 will determine the function of the PF0 pin. If DDRF0 is
cleared, the PF0 pin functions as a SS (slave select) input to the SPI. If DDRF0 is set, then
PF0 can serve as a normal output pin. When the SPI subsystem is enabled, the DDRF3-1
bits are set or cleared according to the required pin function. The DDRF is cleared by reset.
Read $0003/2B
Input
Pin
Internal HC05
Data Bus
V
SS
To A/D Sampling Circuitry
To A/D Channel Select Logic
F
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
n
.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HC05 | Bipolar Transistor; Transistor Polarity:Dual P Channel; Power Dissipation:20W; DC Current Gain Min (hfe):25; Collector Current:1A; DC Current Gain Max (hfe):200; Power (Ptot):20W |
| HC1-5502A-7 | Subscriber Line Interface Circuit |
| HC4P-5502A-7 | Subscriber Line Interface Circuit |
| HC1062A | Low Voltage Telephone Speech Transmission Circuit / High/Low Level Mute |
| HC1198 | Peripheral IC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HC060WE1DS038B | 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:EC7174-000 |
| HC060YW1DS038B | 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:EC7207-000 |
| HC06B05000J0G | 制造商:FCI 功能描述:OEM ITEM 505-5BNF-SPRING CLAMP SYSTEM |
| HC08 | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
| HC08100 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Breake Away Header .025(0.64mm) Square Posts |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。