- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄368349 > PT7D6555 -40V Single P-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a TSOP-6 (Micro 6) package PDF資料下載
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)當(dāng)前第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary Data Sheet
PT7D6555
Extended PCM Interface Controller
11
PT0105(08/02)
Ver:0
Packet Handlers
The PT7D6555 is an important building block for networks
based on either central, decentral or mixed signaling and packet
data handling architectures. Its flexibility allows for the modi-
fication of the packet handling architecture according to the
changing needs.
Thus it may be useful to add central packet handling groups to
a network originally based on decentral signaling and packet
handling. This may be the case if growing data packet traffic
exceeds the initial capacity of the network. The result is a
mixed architecture.
On the other hand, increasing packet handling demand on a
few dedicated subscriber lines calls for solutions which back
up the capacity at these few decentral line cards.
In both of these cases and several other applications, the
PT7D6555 is a powerful device for solving the problem of
packet handling. In most applications it is used together with
the PT7A6527.
Decentralized and mixed packet handling has already been
covered in the line card chapter. In the following, the central-
ized signaling/packet handlers built up with the PT7D6555
will be described.
Central packet handling is used if many subscribers with a
generally low demand for packet switching are to be connected
to a system. Concentrating the packet servers for multiple us-
ers eliminates the need to provide a packet server channel for
every user. The overall number of packet server channels can
thus be reduced.
In such a central packet-handling group, the PT7D6555 per-
forms the switching and concentrator function. It connects a
variable number of PCM highways to the packet handler inter-
nal highway. HDLC controllers are also connected to this in-
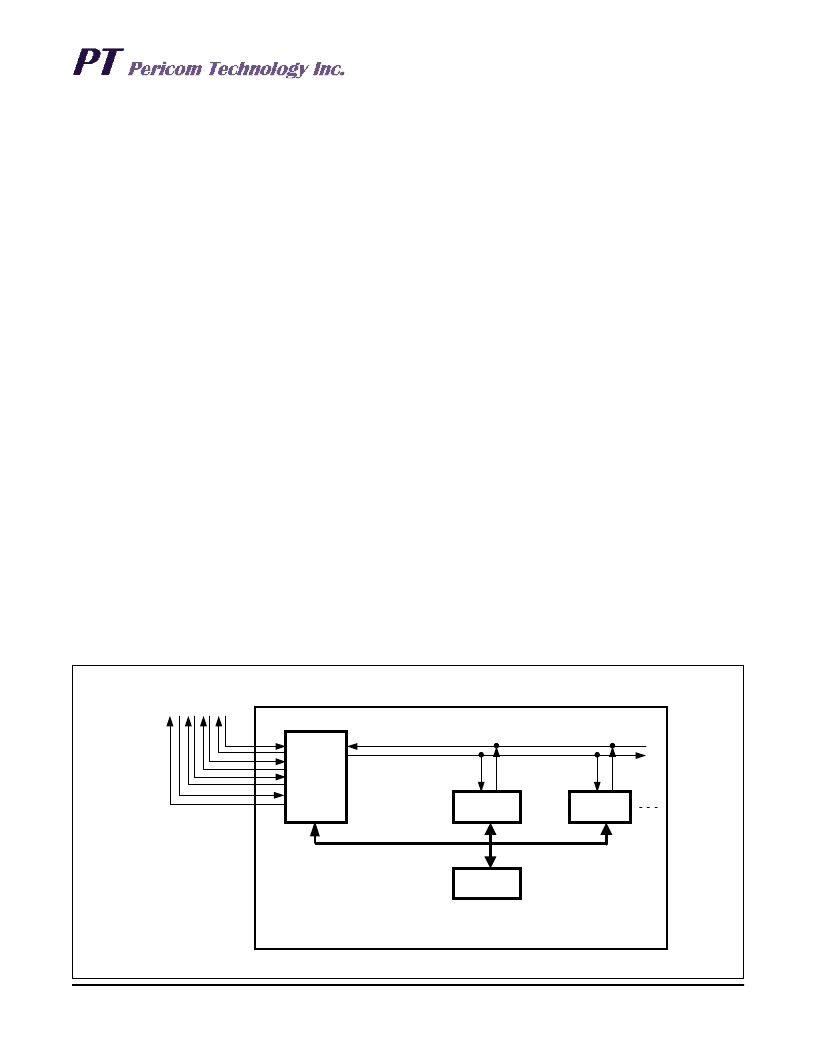
ternal highway as illustrated in figure 6.
This figure shows one PT7D6555 connecting four PCM high-
ways to one packet handler internal highway. These highways
are accessed by the PT7A6527, which are 4 channel HDLC
controller and handle the packets. If more than four PCM high-
ways shall be connected to the centralized packet handler,
further PT7D6555 are necessary. Such a configuration is shown
in figure 7, where 8 highways are switched to one packet han-
dler internal highway. In this case the two PT7D6555 are con-
nected in parallel at the packet handlers internal side.
The data rate of the packet handler internal highway can be up
to 4.096 Mbit/s. If this capacity is not sufficient, other packet
handler internal highways may be added as depicted in figure
8.
In some applications an additional collision resolution signal
is required for the HDLC controllers. This information can be
demultiplexed from the PCM highways to a third line for each
packet handler internal highway (refer to figure 9). The appli-
cations apply equally to centralized signaling as well as to
data packet handlers.
Figure 6. Centralized Packet Handler with a Single Internal Highway Connected to 4 PCM Highways
PT7D6555
PT7A6527
PT7A6527
μP
Centralized Packet Handler Unit
Packet Handler Internal Highway
PCMHighway
A B C D
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PT7M7803RT | μP Supervisor Circuits? |
| PT7V2727 | 3.3v/5.0v operating voltage |
| PT7V2727W | 3.3v/5.0v operating voltage |
| PT7V3727W | 3.3v/5.0v operating voltage |
| PT7V4027W | 3.3V operating voltage |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PT7FFSDGY | 制造商:Hubbell Wiring Device-Kellems 功能描述:FLUSH FRPT, 1 SERV, FURN FEED, GY |
| PT7FFSDI | 制造商:Hubbell Wiring Device-Kellems 功能描述:FLUSH FRPT, 1 SERV, FURN FEED, IV |
| PT7FSD | 制造商:Hubbell Wiring Device-Kellems 功能描述:THRU-FLOOR FITTING, 3 FLUSH FRPT |
| PT7FSDBLA | 制造商:Hubbell Wiring Device-Kellems 功能描述:FLUSH FRPT, W/20A DUP/TELE/DATA,BK |
| PT7FSDBRA | 制造商:Hubbell Wiring Device-Kellems 功能描述:FLUSH FRPT, W/20A DUP/TELE/DATA,BR |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。