- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359235 > MT90883 (Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.) TDM to Packet Processors PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MT90883 |
| 廠商: | Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. |
| 英文描述: | TDM to Packet Processors |
| 中文描述: | TDM到分組處理器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 74/97頁 |
| 文件大小: | 702K |
| 代理商: | MT90883 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁當(dāng)前第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁
MT90880/1/2/3
Data Sheet
74
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
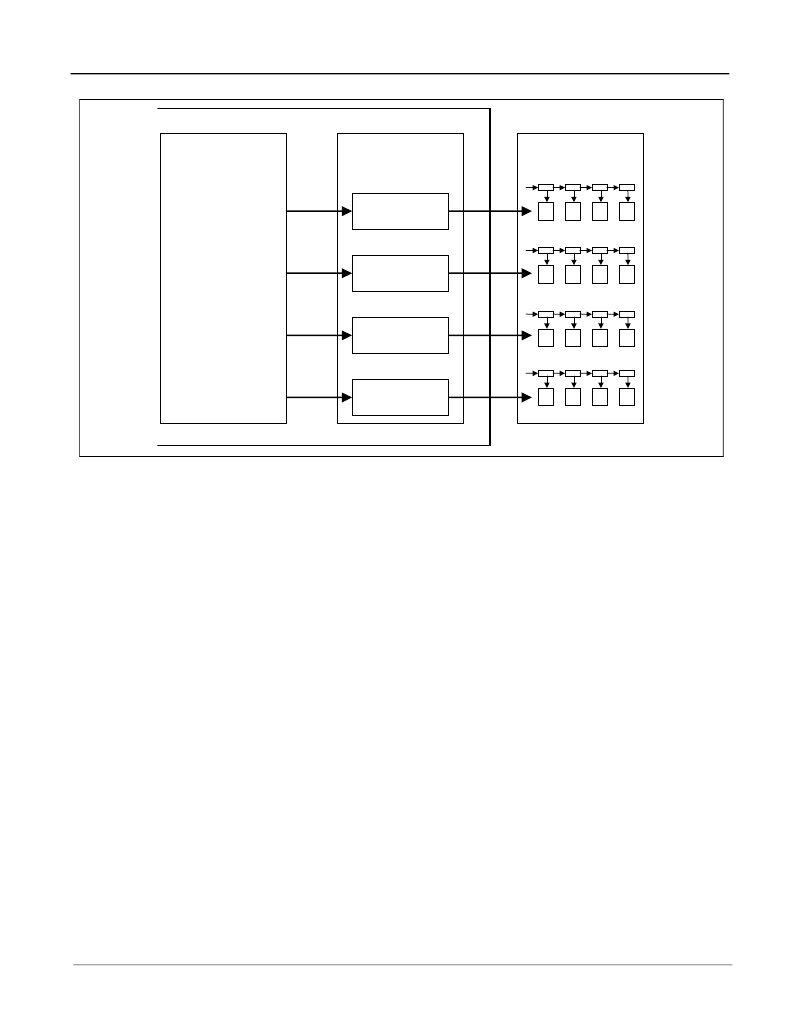
Figure 35 - DMA Operation from CPU Packet Queues
Queue Priority
While the CPU queues have no inherent priority levels associated with them, in that the CPU can choose to
service which queue it wants to first, there is a priority level associated with the DMA transfer into system
memory. The MT90880 uses a prioritised round robin methodology to determine which queue gets serviced
first, with L2P queue 3 having the highest priority and L2P queue 0 the lowest priority. Therefore the DMA will
only transfer packets in a given queue if all the higher priority queues are empty.
However, this is only true if there is room in the corresponding data structure in system memory for the DMA to
transfer into. If there are no empty data buffers for a particular queue then that queue will be stalled, irrespective
of its priority. The DMA engine will then continue to service the lower priority queues. Therefore the CPU can
also control the priority by how fast it processes each queue.
6.12 Board Level Test Features
6.12.1 JTAG Support
The JTAG port is used to access the boundary scan logic for board level production testing. A NAND tree test
mode is also provided on the MT9088x family. The MT9088x JTAG interface conforms to the IEEE standard
1149.1 (reference 4, Table 2). This standard specifies a design-for-testability technique called "Boundary-Scan
Test" (BST). An external Test Access Port (TAP) Controller controls the operation of the boundary scan circuitry.
Details of the contents of the scan register are contained in the BSDL file.
MT90880
Ring/List 0
Ring/List 1
Ring/List 2
Ring/List 3
Descriptor lists in
System Memory
CPU queues
L2P queue 0
L2P queue 1
L2P queue 2
L2P queue 3
Packet Classification
Search the incoming
packets for a match and
forward to the
appropriate queue
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT91600 | Programmable SLIC |
| MT91600AN | Programmable SLIC |
| MT91600AN1 | Programmable SLIC |
| MT91600ANR | Programmable SLIC |
| MT91600ANR1 | Programmable SLIC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MT90883A | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:TDM to Packet Processors |
| MT90883A/IG | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:TDM to Packet Processors |
| MT90883BP1N | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:TDM to Packet Processors |
| MT90883IG | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:TDM to Packet Processors |
| MT9088IG | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:TDM to Packet Processors |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。