- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359354 > VDP3130Y (MICRONAS SEMICONDUCTOR HOLDING AG) Video Processor Family PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | VDP3130Y |
| 廠商: | MICRONAS SEMICONDUCTOR HOLDING AG |
| 英文描述: | Video Processor Family |
| 中文描述: | 視頻處理器系列 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 28/76頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1770K |
| 代理商: | VDP3130Y |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁當前第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁
VDP 313xY
ADVANCE INFORMATION
28
Micronas
2.12.5.EHT Compensation
The vertical waveform can be scaled according the
average beam current. This is used to compensate the
effects of electric high tension changes due to beam
current variations. EHT compensation for East/West
deflection is done with an offset corresponding to the
average beam current.
2.12.6.Protection Circuitry
–
Picture tube and drive stage protection is provided
through the following measures:
–
Vertical flyback protection input: this pin searches
for a negative edge in every field, otherwise the
RGB drive signals are blanked.
–
Drive shutoff during flyback: this feature can be
selected by software.
–
Safety input pin: this input has two thresholds.
Between zero and the lower threshold, normal func-
tioning takes place. Between the lower and the
higher threshold, the RGB signals are blanked.
Above the higher threshold, the RGB signals are
blanked and the horizontal drive is shut off. Both
thresholds have a small hysteresis.
–
The main oscillator and the horizontal drive circuitry
are run from a separate (standby) power supply and
are already active while the TV set is powering up.
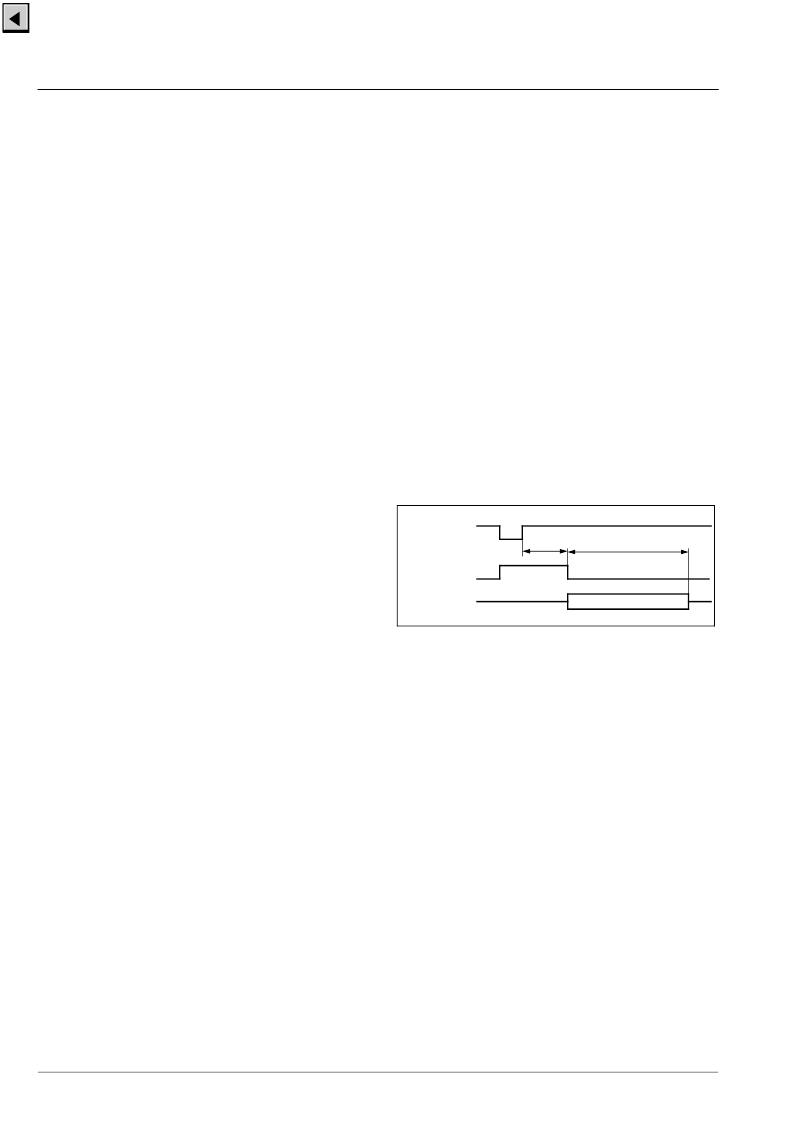
2.13.Reset and Power On
Reset of most VDP 313xY functions is performed by
the RESQ pin. When this pin becomes active all inter-
nal registers and counters are lost. When the RESQ
pin is released, the internal reset is still active for 4
μ
s.
After that time, the initialization of all required registers
is performed by the internal Fast Processor.
The VDP 313xY has clock and voltage supervision cir-
cuits to generate a stable HOUT signal. The voltage
supervision activates an internal reset signal when the
supply for the digital circuits (VSUP
D
) goes below
~2.5 V for more than 50 ns. This reset signal is
extended by 50
μ
s after VSUP
D
is back again.
After power on or reset the HOUT generation is
switched to a freerunning mode with a fix duty cycle of
50 %. For normal operation the EHPLL bit has to be
set first. During the switch the actual period of HOUT
can vary by up to 1
μ
s.
Fig. 2
–
26:
External Reset
4
μ
s
approx. 60
μ
s
Reset
Initialization
Internal
Reset
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| VDP31XXB | Video Processor Family |
| VDP3108PR | Consumer IC |
| VDSGLD_38.88 | TRANS PREBIASED PNP 200MW SOT23 |
| VDSL5100I | TVS 400W 43V UNIDIRECT SMA |
| VDSL5100 | TVS 400W 40V BIDIRECT SMA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| VDP3131Y | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Video Processor Family |
| VDP3132Y | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Video Processor Family |
| VDP3133Y | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Video Processor Family |
| VDP3134Y | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Video Processor Family |
| VDP313XY | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Video Processor Family |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。