- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄199495 > TSPC860SRMZPU50D4 (E2V TECHNOLOGIES PLC) 32-BIT, 50 MHz, RISC PROCESSOR, PBGA357 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TSPC860SRMZPU50D4 |
| 廠商: | E2V TECHNOLOGIES PLC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 32-BIT, 50 MHz, RISC PROCESSOR, PBGA357 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, BGA-357 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 89/90頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 2351K |
| 代理商: | TSPC860SRMZPU50D4 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)當(dāng)前第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)
9
TSPC860
2129A–HIREL–08/02
System Bus Signals
The TSPC860 system bus consists of all signals that interface with the external bus.
Many of these signals perform different functions, depending on how the user assigns
them. The following input and output signals are identified by their abbreviation. Each
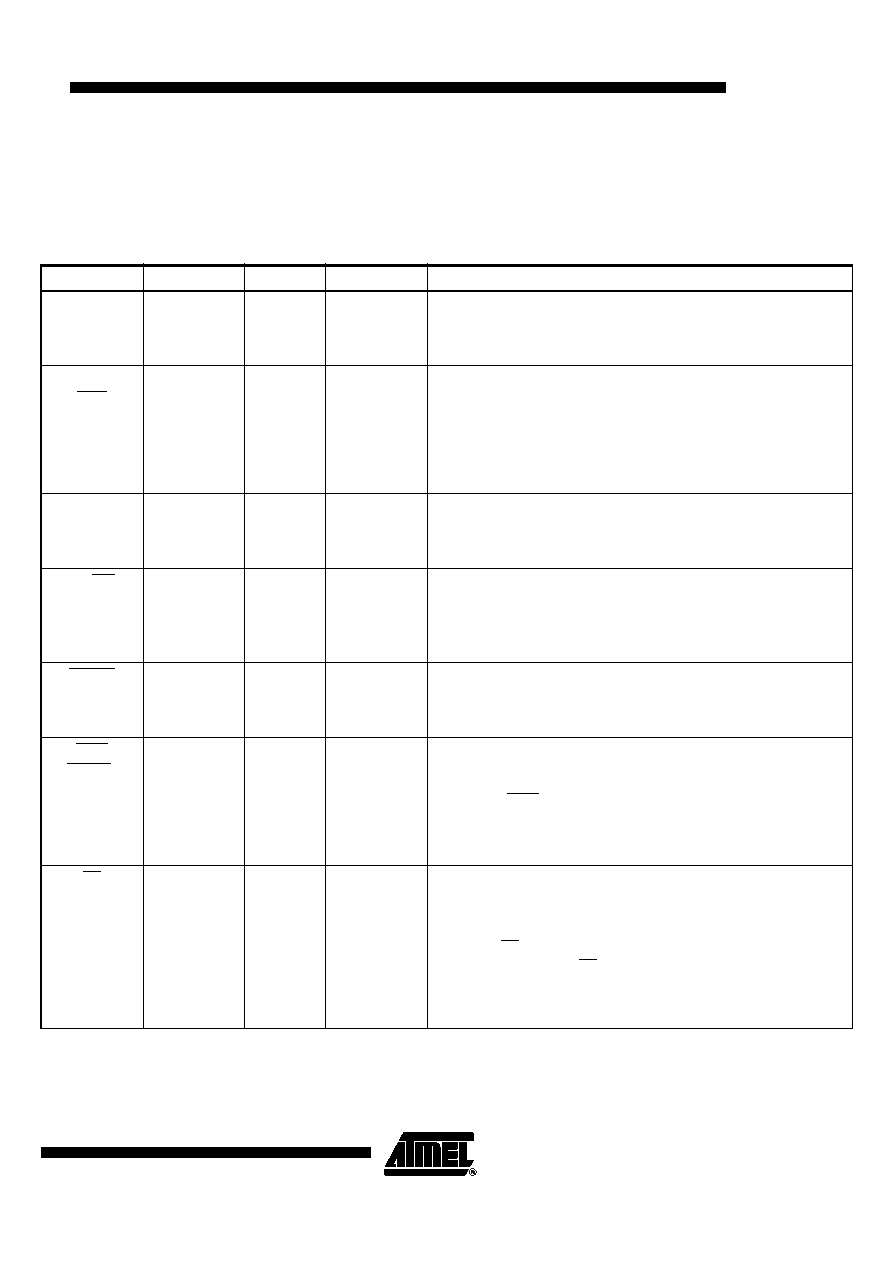
Table 1. Signal Descriptions
Name
Reset
Number
Type
Description
A(0-31)
Hi-Z
See
Bidirectional
Three-state
Address Bus — Provides the address for the current bus cycle. A0 is
the most-significant signal. The bus is output when an internal
master starts a transaction on the external bus. The bus is input
when an external master starts a transaction on the bus.
TSIZ0
REG
Hi-Z
B9
Bidirectional
Three-state
Transfer Size 0 — When accessing a slave in the external bus, used
(together with TSIZ1) by the bus master to indicate the number of
operand bytes waiting to be transferred in the current bus cycle.
TSIZ0 is an input when an external master starts a bus transaction.
Register — When an internal master initiates an access to a slave
controlled by the PCMCIA interface, REG is output to indicate which
space in the PCMCIA card is accessed.
TSIZ1
Hi-Z
C9
Bidirectional
Three-state
Transfer Size 1 — Used (with TSIZ0) by the bus master to indicate
the number of operand bytes waiting to be transferred in the current
bus cycle. The TSPC860 drives TSIZ1 when it is bus master. TSIZ1
is input when an external master starts a bus transaction.
RD/WR
Hi-Z
B2
Bidirectional
Three-state
Read/Write — Driven by the bus master to indicate the direction of
the bus’s data transfer. A logic one indicates a read from a slave
device and a logic zero indicates a write to a slave device.
The TSPC860 drives this signal when it is bus master. Input when an
external master initiates a transaction on the bus.
BURST
Hi-Z
F1
Bidirectional
Three-state
Burst Transaction — Driven by the bus master to indicate that the
current initiated transfer is a burst. The TSPC860 drives this signal
when it is bus master. This signal is input when an external master
initiates a transaction on the bus.
BDIP
GPL_B5
See Section
D2
Bidirectional
Three-state
Burst Data in Progress — When accessing a slave device in the
external bus, the master on the bus asserts this signal to indicate
that the data beat in front of the current one is the one requested by
the master. BDIP is negated before the expected last data beat of
the burst transfer.
General-Purpose Line B5-Used by the memory controller when
UPMB takes control of the slave access.
TS
Hi-Z
F3
Bidirectional
Active Pull-up
Transfer Start — Asserted by the bus master to indicate the start of a
bus cycle that transfers data to or from a slave device.
Driven by the master only when it has gained the ownership of the
bus. Every master should negate this signal before the bus
relinquish. TS requires the use of an external pull-up resistor.
The TSPC860 samples TS when it is not the external bus master to
allow the memory controller/PCMCIA interface to control the
accessed slave device. It indicates that an external synchronous
master initiated a transaction.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TSPD11CGVRA0 | PUSHBUTTON SWITCH, SPST, MOMENTARY, 0.02A, 20VDC, THROUGH HOLE-RIGHT ANGLE |
| 2-1437573-9 | PUSHBUTTON SWITCH, SPDT, MOMENTARY, 0.02A, 20VDC, SURFACE MOUNT-RIGHT ANGLE |
| 3-1437573-4 | PUSHBUTTON SWITCH, SPST, MOMENTARY, 0.02A, 20VDC, THROUGH HOLE-RIGHT ANGLE |
| TSPF5400AS21 | 5 mm, 1 ELEMENT, INFRARED LED, 870 nm |
| TSS11DGRA | SLIDE SWITCH, SPDT, LATCHED, 0.02A, 20VDC, THROUGH HOLE-RIGHT ANGLE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TSPC860SRMZQU66D | 制造商:e2v technologies 功能描述:MPU RISC 32BIT 66MHZ 3.3V 357BGA - Trays |
| TSPC860SRVZQU66D | 制造商:e2v technologies 功能描述:TSPC860SRVZQU66D - Trays |
| TSPC860XRMZPU66D | 制造商:ATMEL 制造商全稱:ATMEL Corporation 功能描述:Integrated Communication Processor |
| TSPC860XRMZQU66D | 制造商:ATMEL 制造商全稱:ATMEL Corporation 功能描述:Integrated Communication Processor |
| TSPC860XRVZPU66D | 制造商:ATMEL 制造商全稱:ATMEL Corporation 功能描述:Integrated Communication Processor |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。