- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4254 > XC3S1500-5FGG676C (Xilinx Inc)SPARTAN-3A FPGA 1.5M 676-FBGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XC3S1500-5FGG676C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 214/272頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | SPARTAN-3A FPGA 1.5M 676-FBGA |
| 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊: | Extended Spartan 3A FPGA Family |
| 標(biāo)準包裝: | 40 |
| 系列: | Spartan®-3 |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 3328 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 29952 |
| RAM 位總計: | 589824 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 487 |
| 門數(shù): | 1500000 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.14 V ~ 1.26 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 676-BGA |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 676-FBGA(27x27) |
| 配用: | NANO-SPARTAN-ND - KIT NANOBOARD AND SPARTAN3 DC 807-1001-ND - DAUGHTER CARD XILINX SPARTAN 3 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁當(dāng)前第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁第221頁第222頁第223頁第224頁第225頁第226頁第227頁第228頁第229頁第230頁第231頁第232頁第233頁第234頁第235頁第236頁第237頁第238頁第239頁第240頁第241頁第242頁第243頁第244頁第245頁第246頁第247頁第248頁第249頁第250頁第251頁第252頁第253頁第254頁第255頁第256頁第257頁第258頁第259頁第260頁第261頁第262頁第263頁第264頁第265頁第266頁第267頁第268頁第269頁第270頁第271頁第272頁
Spartan-3 FPGA Family: Functional Description
DS099 (v3.1) June 27, 2013
Product Specification
46
Configuration
Spartan-3 devices are configured by loading application specific configuration data into the internal configuration memory.
Configuration is carried out using a subset of the device pins, some of which are "Dedicated" to one function only, while
others, indicated by the term "Dual-Purpose", can be re-used as general-purpose User I/Os once configuration is complete.
Depending on the system design, several configuration modes are supported, selectable via mode pins. The mode pins M0,
M1, and M2 are Dedicated pins. The mode pin settings are shown in Table 26.
The HSWAP_EN input pin defines whether the I/O pins that are not actively used during configuration have pull-up resistors
during configuration. By default, HSWAP_EN is tied High (via an internal pull-up resistor if left floating) which shuts off the
pull-up resistors on the user I/O pins during configuration. When HSWAP_EN is tied Low, user I/Os have pull-ups during
configuration. The Dedicated configuration pins (CCLK, DONE, PROG_B, M2, M1, M0, HSWAP_EN) and the JTAG pins
(TDI, TMS, TCK, and TDO) always have a pull-up resistor to VCCAUX during configuration, regardless of the value on the
HSWAP_EN pin. Similarly, the dual-purpose INIT_B pin has an internal pull-up resistor to VCCO_4 or VCCO_BOTTOM,
depending on the package style.
Depending on the chosen configuration mode, the FPGA either generates a CCLK output, or CCLK is an input accepting an
externally generated clock.
A persist option is available which can be used to force the configuration pins to retain their configuration function even after
device configuration is complete. If the persist option is not selected then the configuration pins with the exception of CCLK,
PROG_B, and DONE can be used as user I/O in normal operation. The persist option does not apply to the boundary-scan
related pins. The persist feature is valuable in applications that readback configuration data after entering the User mode.
Table 27 lists the total number of bits required to configure each FPGA as well as the PROMs suitable for storing those bits.
See DS123: Platform Flash In-System Programmable Configuration PROMs data sheet for more information.
The maximum bitstream length that Spartan-3 FPGAs support in serial daisy-chains is 4,294,967,264 bits (4 Gbits), roughly
equivalent to a daisy-chain with 323 XC3S5000 FPGAs. This is a limit only for serial daisy-chains where configuration data
is passed via the FPGA’s DOUT pin. There is no such limit for JTAG chains.
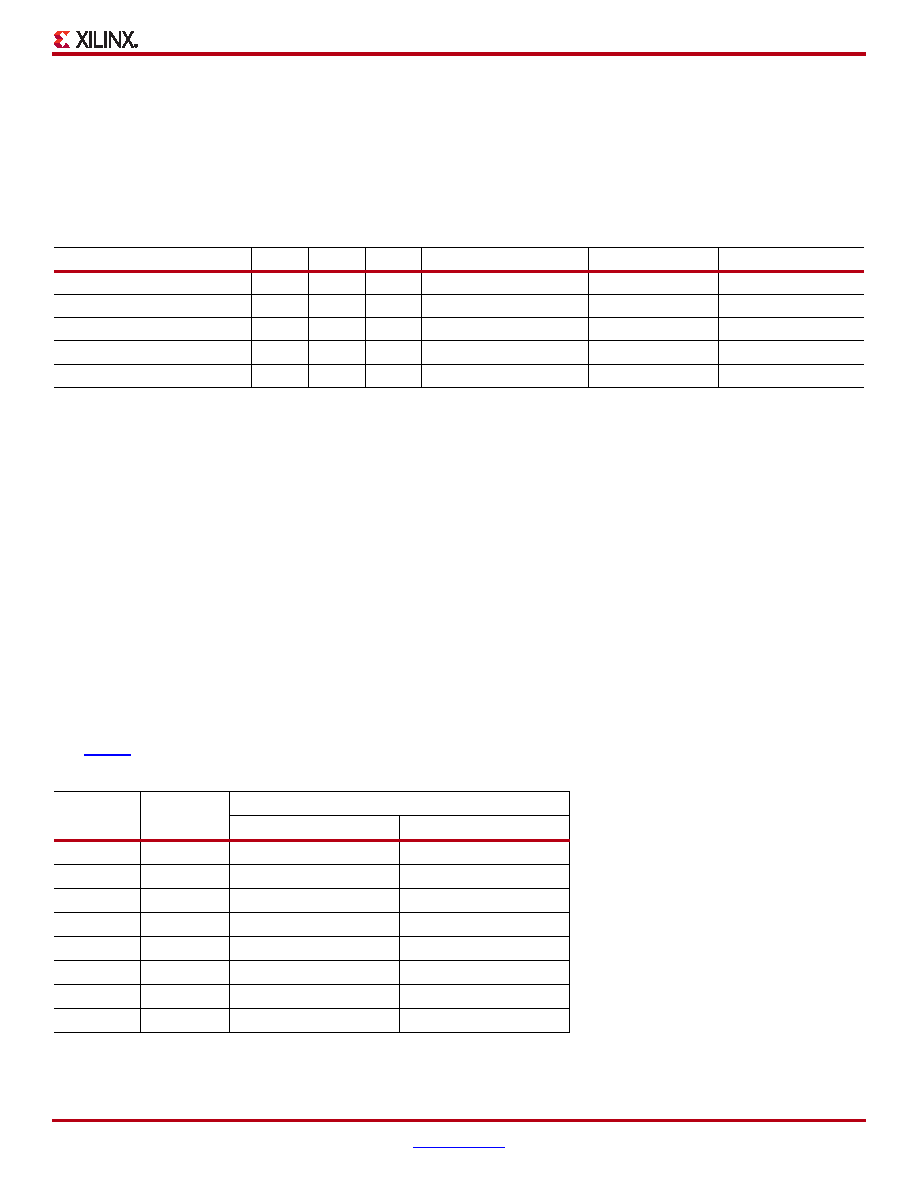
Table 26: Spartan-3 FPGAs Configuration Mode Pin Settings
Configuration Mode(1)
M0
M1
M2
Synchronizing Clock
Data Width
Serial DOUT(2)
Master Serial
0
CCLK Output
1
Yes
Slave Serial
1
CCLK Input
1
Yes
Master Parallel
1
0
CCLK Output
8
No
Slave Parallel
0
1
CCLK Input
8
No
JTAG
101
TCK Input
1
No
Notes:
1.
The voltage levels on the M0, M1, and M2 pins select the configuration mode.
2.
The daisy chain is possible only in the Serial modes when DOUT is used.
Table 27: Spartan-3 FPGA Configuration Data
Device
File Sizes
Xilinx Platform Flash PROM
Serial Configuration
Parallel Configuration
XC3S50
439,264
XCF01S
XCF08P
XC3S200
1,047,616
XCF01S
XCF08P
XC3S400
1,699,136
XCF02S
XCF08P
XC3S1000
3,223,488
XCF04S
XCF08P
XC3S1500
5,214,784
XCF08P
XC3S2000
7,673,024
XCF08P
XC3S4000
11,316,864
XCF16P
XC3S5000
13,271,936
XCF16P
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 25AA640XT-I/ST | IC EEPROM 64KBIT 1MHZ 8TSSOP |
| 24LC128-E/P | IC EEPROM 128KBIT 400KHZ 8DIP |
| XC2V250-4FG256I | IC FPGA VIRTEX-II 256FGBGA |
| 25LC320/P | IC EEPROM 32KBIT 2MHZ 8DIP |
| XC2V250-5FGG256C | IC FPGA VIRTEX-II 250K 256-FBGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XC3S1500-5FT256C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-3 FPGA |
| XC3S1500-5FT256I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-3 FPGA |
| XC3S1500-5PQ208C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-3 FPGA |
| XC3S1500-5PQ208I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-3 FPGA |
| XC3S1500-5PQG208C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-3 FPGA Family: Complete Data Sheet |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。