- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄69032 > MCM16Y1BACFT16 (MOTOROLA INC) 16-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP160 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MCM16Y1BACFT16 |
| 廠商: | MOTOROLA INC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 16-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP160 |
| 封裝: | QFP-160 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 81/138頁 |
| 文件大小: | 784K |
| 代理商: | MCM16Y1BACFT16 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁當(dāng)前第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁
MC68HC16Y1
MOTOROLA
MC68HC16Y1TS/D
47
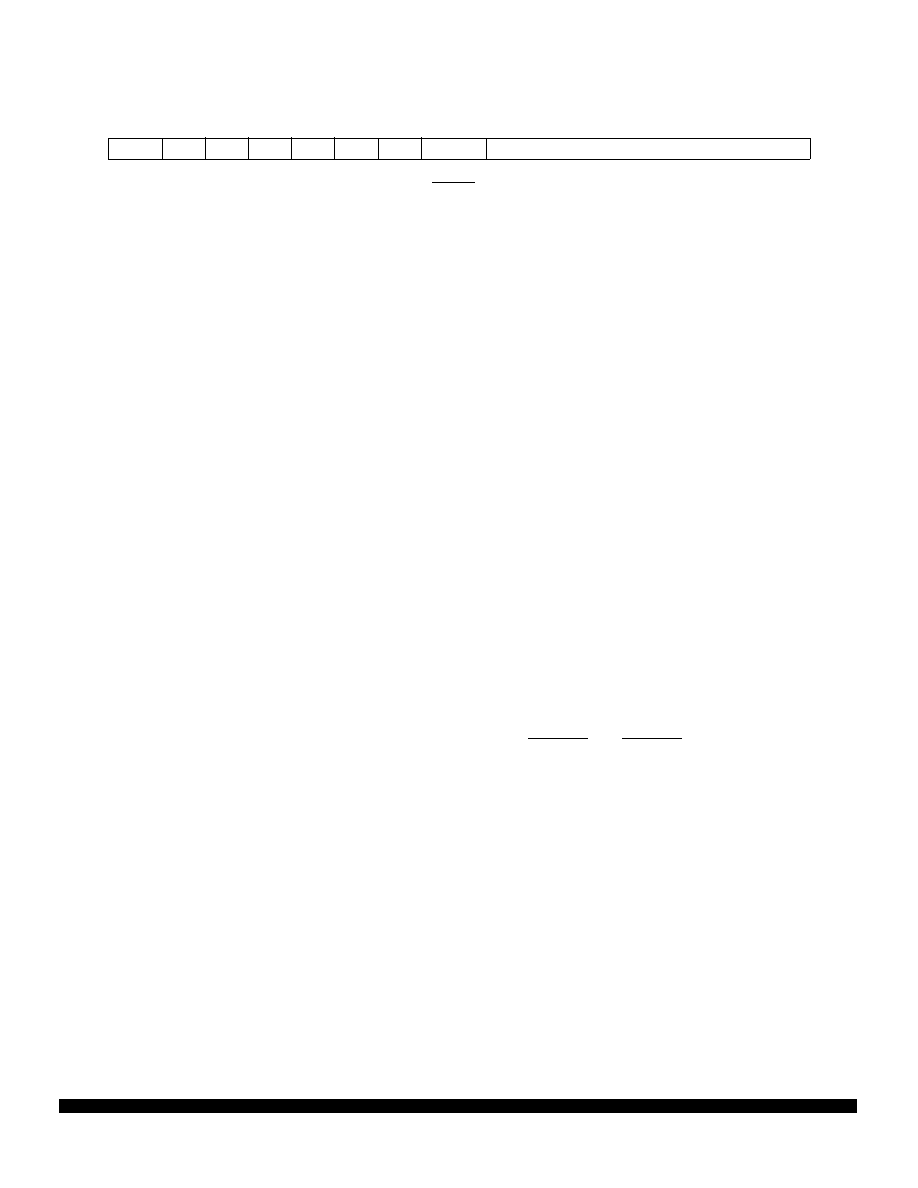
PITR contains the count value for the periodic timer. A zero value turns off the periodic timer. This reg-
ister can be read or written at any time.
PTP — Periodic Timer Prescaler Control
1 = Periodic timer clock prescaled by a value of 512
0 = Periodic timer clock not prescaled
The reset state of PTP is the complement of the state of the MODCLK signal during reset.
PITM[7:0] — Periodic Interrupt Timing Modulus Field
This is an 8-bit timing modulus. The period of the timer can be calculated as follows:
PIT Period = [(PITM)(Prescale)(4)]/EXTAL
where
PIT Period = Periodic interrupt timer period
PITM = Periodic interrupt timer register modulus (PITR[7:0])
EXTAL = Crystal frequency
Prescale = 512 or 1 depending on the state of the PTP bit in the PITR
3.5 External Bus Interface
The external bus interface (EBI) transfers information between the internal MCU bus and external de-
vices when the MC68HC16Y1 is operating in expanded modes. In fully expanded mode, the external
bus has 24 address lines and 16 data lines. In partially expanded mode, the external bus has 24 ad-
dress lines and 8 data lines. Because the CPU16 in the MC68HC16Y1 drives only 20 of the 24 IMB
address lines, ADDR[23:20] follow the output state of ADDR19.
The EBI provides dynamic sizing between 8-bit and 16-bit data accesses. It supports byte, word, and
long-word transfers. Ports are accessed through the use of asynchronous cycles controlled by the data
transfer (SIZ1 and SIZ0) and data size acknowledge pins (DSACK1 and DSACK0). In fully expanded
mode, both 8-bit and 16-bit data ports can be accessed; in partially expanded mode, only 8-bit ports
can be accessed. Multiple bus cycles may be required for a transfer to an 8-bit port.
Port width is the maximum number of bits accepted or provided during a bus transfer. External devices
must follow the handshake protocol described below. Control signals indicate the beginning of the cycle,
the address space, the size of the transfer, and the type of cycle. The selected device controls the length
of the cycle. Strobe signals, one for the address bus and another for the data bus, indicate the validity
of an address and provide timing information for data. The EBI operates in an asynchronous mode for
any port width.
To add flexibility and minimize the necessity for external logic, MCU chip select logic can be synchro-
nized with EBI transfers. Chip select logic can also provide internally-generated bus control signals for
these accesses. See 3.9 Chip Selects for more information.
3.5.1 Bus Control Signals
The CPU initiates a bus cycle by driving the address, size, function code, and read/write outputs. At the
beginning of the cycle, size signals SIZ0 and SIZ1 are driven along with the function code signals. The
PITR — Periodic Interrupt Timer Register
$YFFA24
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
PTP
PITM
RESET:
0
MODCLK
0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MCM16Y1BGCFT16 | 16-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP160 |
| M68HC16Y1CFC | 16-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP16 |
| MCV14AI/SL | 8-BIT, FLASH, 20 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO14 |
| MCV14ATI/SL | 8-BIT, FLASH, 20 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO14 |
| MCV14AI/P | 8-BIT, FLASH, 20 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP14 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MCM16Z2BCFC16 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Symbols and Operators, CPU16 Register Mnemonics |
| MCM16Z2BCFC16B1 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Symbols and Operators, CPU16 Register Mnemonics |
| MCM16Z2BCFC20 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Symbols and Operators, CPU16 Register Mnemonics |
| MCM16Z2BCFC20B1 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:M68HC16Z Series users manual |
| MCM16Z2BCFC25 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:M68HC16Z Series users manual |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。