- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄370960 > M38B57M6-126FP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SENSOR HALL EFFECT DIFF SPEED PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | M38B57M6-126FP |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SENSOR HALL EFFECT DIFF SPEED |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片8位CMOS微機 |
| 文件頁數: | 39/69頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1011K |
| 代理商: | M38B57M6-126FP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁當前第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁
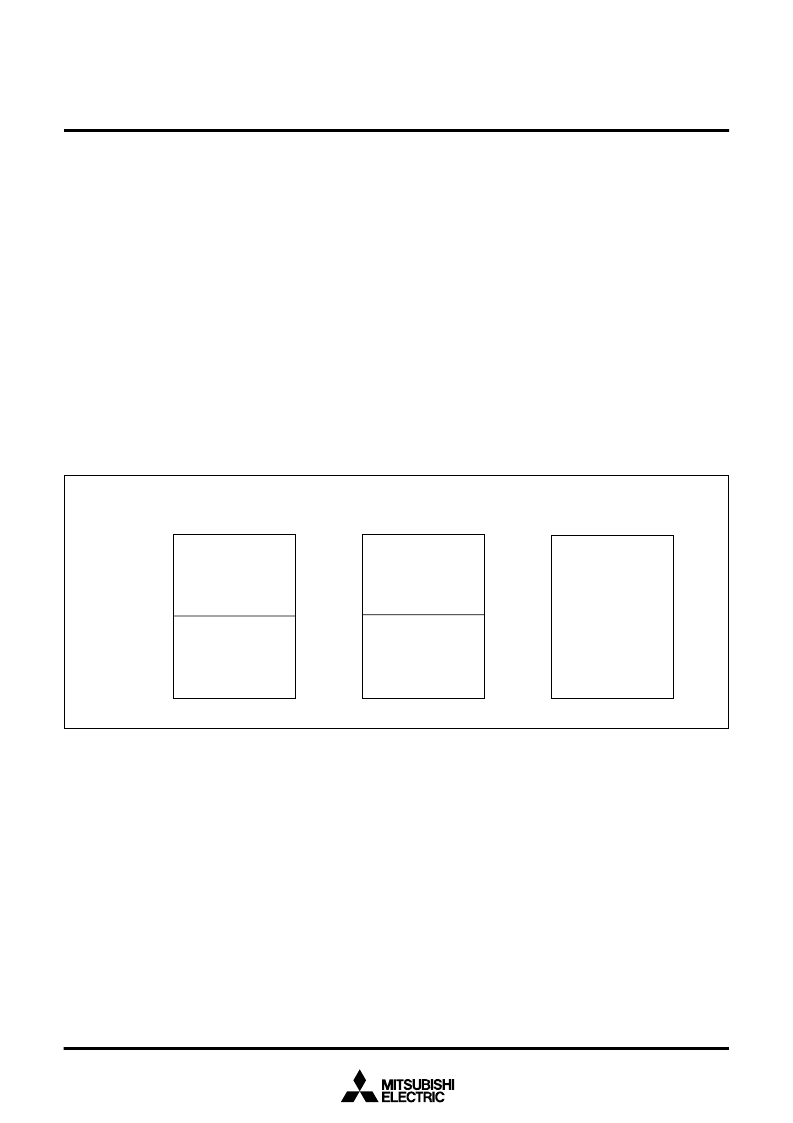
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
38B5 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
39
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This s not a final specification.
Some parametric imits are subject to change.
FLD automatic display RAM
The FLD automatic display RAM uses the 160 bytes of addresses
0F60
16
to 0FFF
16
. For FLD, the 3 modes of 16-timing ordinary mode,
16-timinggradation display mode and 32-timing mode are available
depending on the number of timings and the presence/absence of
gradation display.
The automatic display RAM in each mode is as follows:
(1) 16-timingOrdinary Mode
The 80 bytes of addresses 0FB0
16
to 0FFF
16
are used as a FLD
display data store area. Because addresses 0F60
16
to 0FAF
16
are not used as the automatic display RAM, they can be the ordi-
nary RAM or serial I/O automatic reverse RAM.
(2) 16-timingGradation Display Mode
The 160 bytes of addresses 0F60
16
to 0FFF
16
are used. The 80
bytes of addresses 0FB0
16
to 0FFF
16
are used as an FLD dis-
play data store area, while the 80 bytes of addresses 0F60
16
to
0FAF
16
are used as a gradation display control data store area.
(3) 32-timing Mode
The 160 bytes of addresses 0F60
16
to 0FFF
16
are used as an
FLD display data store area.
[FLD Data Pointer and FLD Data Pointer Reload Register]
FLDDP (0EF8
16
)
Both the FLD data pointer and FLD data pointer reload register are
8-bit registers assigned at address 0EF8
16
. When writing data to this
address, the data is written to the FLD data pointer reload register;
when reading data from this address, the value in the FLD data pointer
is read.
Fig. 42 FLD Automatic Display RAM Assignment
16-timingordinary mode
0FFF
16
0FB0
16
0F60
16
0FFF
16
0F60
16
0FFF
16
0FB0
16
0F60
16
16-timinggradation display mode
32-timing mode
1 to 32 timing display
data stored area
Gradation display
control data stored
area
1 to 16 timing display
data stored area
1 to 16 timing display
data stored area
Not used
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M38B57M6-147FP | SENSOR SST 5/8 HALL EFFECT |
| M38B57M6-150FP | SENSOR SST 5/8 HALL EFFECT |
| M38B57M6-154FP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38B57M6-166FP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38B5 | Single Chip 8 Bits Microcomputer(8位單片機) |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| M38B57M6127F | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:IC |
| M38B57M6140F | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:IC |
| M38B57M6141F | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:SUB ONLY IC |
| M38B57M6-147FP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38B57M6-150FP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。