- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370847 > M37560ME-XXXFP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M37560ME-XXXFP |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片8位CMOS微機(jī) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 21/65頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 955K |
| 代理商: | M37560ME-XXXFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁當(dāng)前第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁
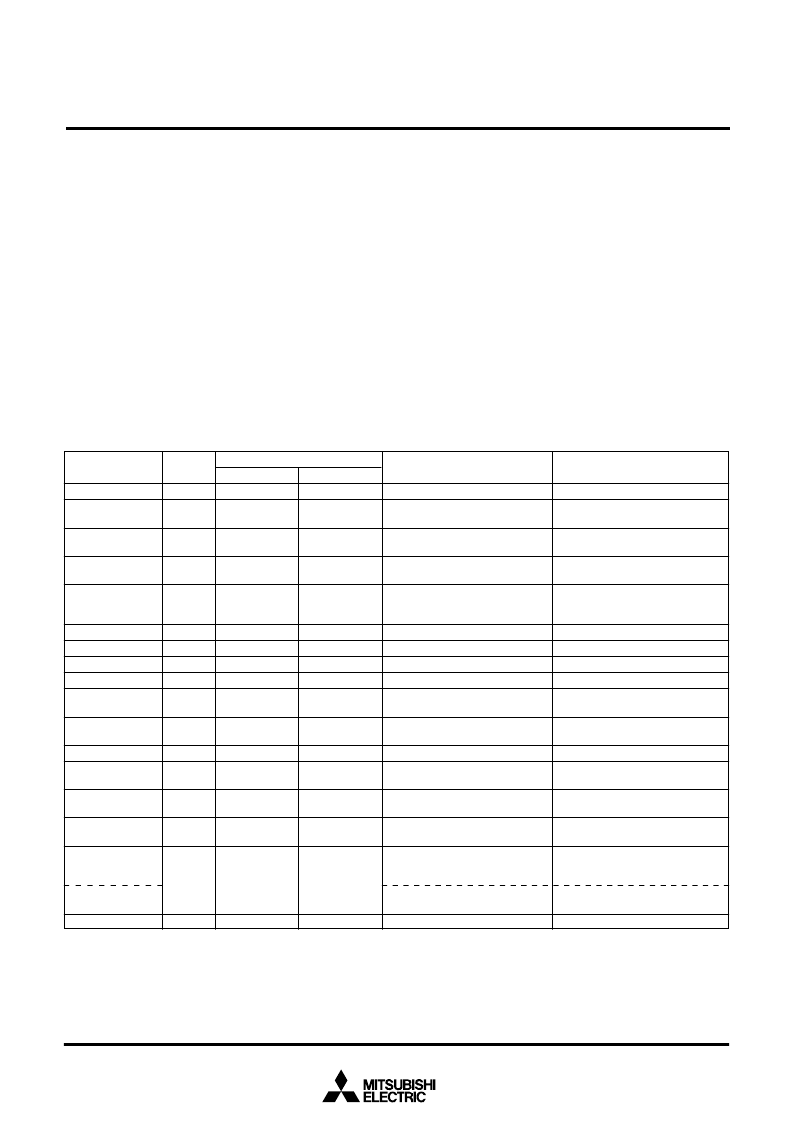
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
21
INTERRUPTS
I
nterrupts occur by seventeen sources: seven external, nine inter-
nal, and one software.
Interrupt Control
Each interrupt is controlled by an interrupt request bit, an interrupt
enable bit, and the interrupt disable flag except for the software in-
terrupt set by the BRK instruction. An interrupt occurs if the corre-
sponding interrupt request and enable bits are
“
1
”
and the inter-
rupt disable flag is
“
0
”
.
Interrupt enable bits can be set or cleared by software.
Interrupt request bits can be cleared by software, but cannot be
set by software.
The BRK instruction cannot be disabled with any flag or bit. The I
flag disables all interrupts except the BRK instruction interrupt.
When several interrupts occur at the same time, the interrupts are
received according to priority.
Interrupt Operation
By acceptance of an interrupt, the following operations are auto-
matically performed:
1. The contents of the program counter and the processor status
register are automatically pushed onto the stack.
2. The interrupt disable flag is set and the corresponding interrupt
request bit is cleared.
3. The interrupt jump destination address is read from the vector
table into the program counter.
Notes1:
Vector addresses contain interrupt jump destination addresses.
2:
Reset function in the same way as an interrupt with the highest priority.
Table 8 Interrupt vector addresses and priority
Remarks
Interrupt Request
Generating Conditions
At reset
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT
0
input
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT
1
input
At completion of serial I/O1 data
reception
At completion of serial I/O1
transmit shift or when transmis-
sion buffer is empty
At timer X underflow
At timer Y underflow
At timer 2 underflow
At timer 3 underflow
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of CNTR
0
input
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of CNTR
1
input
At timer 1 underflow
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT
2
input
At completion of serial I/O2 data
transmission or reception
At falling of conjunction of input
level for port P2 (at input mode)
At falling edge of ADT input
Interrupt Source
Low
FFFC
16
FFFA
16
High
FFFD
16
FFFB
16
Priority
Vector Addresses
(Note 1)
Reset
(Note 2)
INT
0
INT
1
Serial I/O1
reception
Serial I/O1
transmission
Timer X
Timer Y
Timer 2
Timer 3
CNTR
0
CNTR
1
Timer 1
INT
2
Serial I/O2
Key input
(Key-on wake-up)
ADT
A-D conversion
BRK instruction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
FFF9
16
FFF7
16
FFF5
16
FFF3
16
FFF1
16
FFEF
16
FFED
16
FFEB
16
FFE9
16
FFE7
16
FFE5
16
FFE3
16
FFE1
16
FFDF
16
FFDD
16
FFF8
16
FFF6
16
FFF4
16
FFF2
16
FFF0
16
FFEE
16
FFEC
16
FFEA
16
FFE8
16
FFE6
16
FFE4
16
FFE2
16
FFE0
16
FFDE
16
FFDC
16
At completion of A-D conversion
At BRK instruction execution
Non-maskable
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
Valid when serial I/O1 is selected
Valid when serial I/O1 is selected
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
Valid when serial I/O2 is selected
External interrupt
(valid at falling)
Valid when ADT interrupt is selected
External interrupt
(valid at falling)
Valid when A-D interrupt is selected
Non-maskable software interrupt
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M37560ME-XXXGP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37560MF-XXXFP | CAP 68UF 100VDC FILM POWER |
| M37630E4FP | Connector |
| M37630M4T-XXXFP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37630M4T-XXXFS | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M37560ME-XXXGP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37560MF | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37560MF-324GP | 制造商:Renesas Electronics Corporation 功能描述: |
| M37560MF-330GP | 制造商:Renesas Electronics Corporation 功能描述: |
| M37560MFA-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。