- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄3985 > XCS30-4VQ100C (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 5V C-TEMP 100-VQFP PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XCS30-4VQ100C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 20/83頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 5V C-TEMP 100-VQFP |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 90 |
| 系列: | Spartan® |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 576 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 1368 |
| RAM 位總計: | 18432 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 77 |
| 門數(shù): | 30000 |
| 電源電壓: | 4.75 V ~ 5.25 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 100-TQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 100-VQFP(14x14) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁當(dāng)前第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁
Spartan and Spartan-XL FPGA Families Data Sheet
DS060 (v2.0) March 1, 2013
27
Product Specification
R
Product Obsolete/Under Obsolescence
Master Serial Mode
The Master serial mode uses an internal oscillator to gener-
ate a Configuration Clock (CCLK) for driving potential slave
devices
and
the
Xilinx
serial-configuration
PROM
(SPROM). The CCLK speed is selectable as either 1 MHz
(default) or 8 MHz. Configuration always starts at the default
slow frequency, then can switch to the higher frequency dur-
ing the first frame. Frequency tolerance is –50% to +25%.
In Master Serial mode, the CCLK output of the device drives
a Xilinx SPROM that feeds the FPGA DIN input. Each rising
edge of the CCLK output increments the Serial PROM inter-
nal address counter. The next data bit is put on the SPROM
data output, connected to the FPGA DIN pin. The FPGA
accepts this data on the subsequent rising CCLK edge.
When used in a daisy-chain configuration the Master Serial
FPGA is placed as the first device in the chain and is
referred to as the lead FPGA. The lead FPGA presents the
preamble data, and all data that overflows the lead device,
on its DOUT pin. There is an internal pipeline delay of 1.5
CCLK periods, which means that DOUT changes on the
falling CCLK edge, and the next FPGA in the daisy chain
accepts data on the subsequent rising CCLK edge. See the
timing diagram in Figure 24.
In the bitstream generation software, the user can specify
Fast Configuration Rate, which, starting several bits into the
first frame, increases the CCLK frequency by a factor of
eight. For actual timing values please refer to the specifica-
tion section. Be sure that the serial PROM and slaves are
fast enough to support this data rate. Earlier families such
as the XC3000 series do not support the Fast Configuration
Rate option.
The SPROM CE input can be driven from either LDC or
DONE. Using LDC avoids potential contention on the DIN
pin, if this pin is configured as user I/O, but LDC is then
restricted to be a permanently High user output after config-
uration. Using DONE can also avoid contention on DIN, pro-
vided the Early DONE option is invoked.
Figure 25 shows a full master/slave system. The leftmost
device is in Master Serial mode, all other devices in the
chain are in Slave Serial mode.
Slave Serial Mode
In Slave Serial mode, the FPGA receives serial configura-
tion data on the rising edge of CCLK and, after loading its
configuration, passes additional data out, resynchronized
on the next falling edge of CCLK.
In this mode, an external signal drives the CCLK input of the
FPGA (most often from a Master Serial device). The serial
configuration bitstream must be available at the DIN input of
the lead FPGA a short setup time before each rising CCLK
edge.
The lead FPGA then presents the preamble data—and all
data that overflows the lead device—on its DOUT pin. There
is an internal delay of 0.5 CCLK periods, which means that
DOUT changes on the falling CCLK edge, and the next
FPGA in the daisy chain accepts data on the subsequent
rising CCLK edge.
Figure 25 shows a full master/slave system. A Spartan/XL
device in Slave Serial mode should be connected as shown
in the third device from the left.
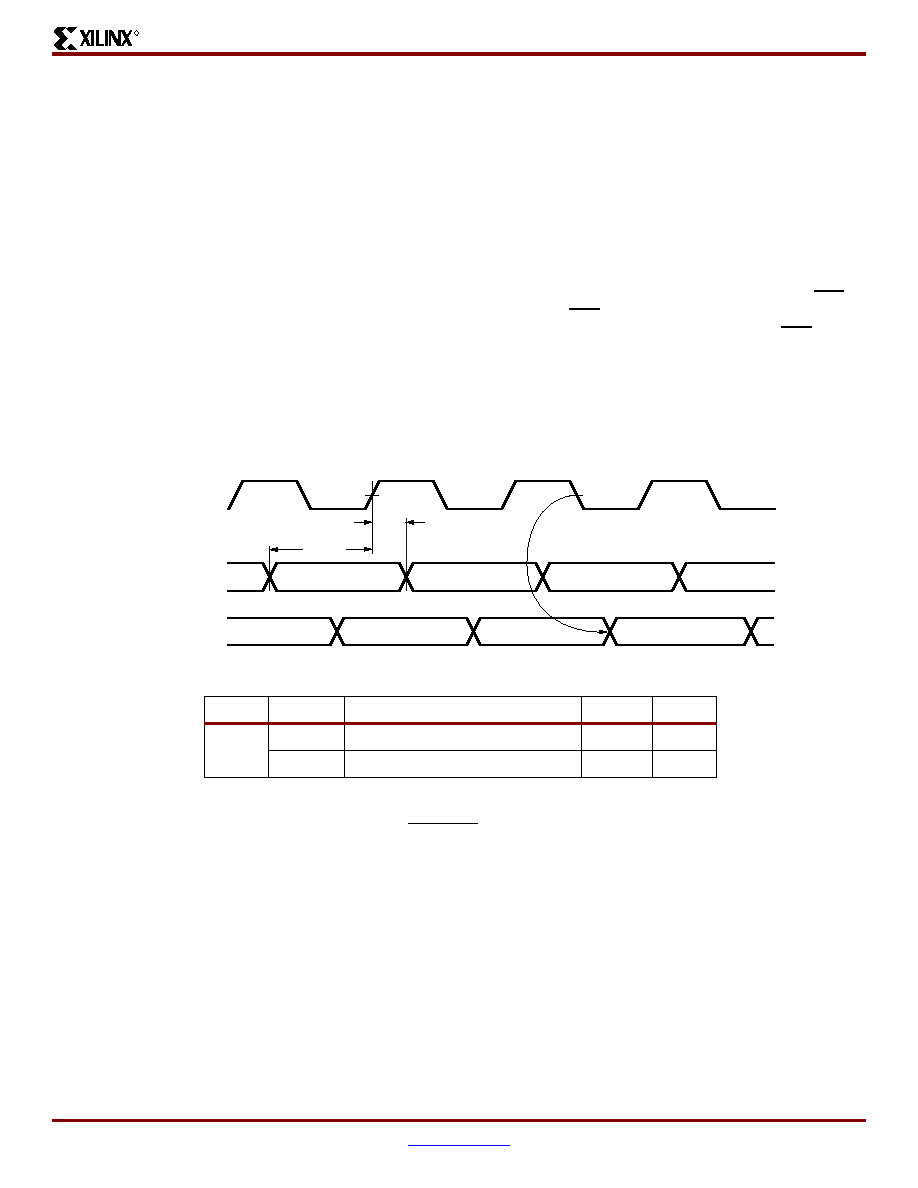
Figure 24: Master Serial Mode Programming Switching Characteristics
Serial Data In
CCLK
(Output)
Serial DOUT
(Output)
TDSCK
n
n + 1
n + 2
n – 3
n – 2
n – 1
n
TCKDS
DS060_24_080400
Notes:
1.
At power-up, VCC must rise from 2.0V to VCC min in less than 25 ms, otherwise
delay configuration by pulling PROGRAM Low until VCC is valid.
2.
Master Serial mode timing is based on testing in slave mode.
Symbol
Description
Min
Units
CCLK
TDSCK
DIN setup
20
ns
TCKDS
DIN hold
0
ns
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 1-1734248-9 | CONN FPC/ZIP 19POS 1MM VERT SMD |
| KMPC860ENVR66D4 | IC MPU POWERQUICC 66MHZ 357-PBGA |
| AMC31DTEH | CONN EDGECARD 62POS .100 EYELET |
| KMPC860ENCZQ66D4 | IC MPU POWERQUICC 66MHZ 357-PBGA |
| IDT7015L17G | IC SRAM 72KBIT 17NS 68PGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCS30-4VQ100I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS30-4VQ144C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS30-4VQ144I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS30-4VQ208C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS30-4VQ208I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。