- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄361880 > WM8191 (Wolfson Microelectronics) TVS BI-DIR 6.0V 400W SMA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | WM8191 |
| 廠商: | Wolfson Microelectronics |
| 英文描述: | TVS BI-DIR 6.0V 400W SMA |
| 中文描述: | 14位6MSPS獨(dú)聯(lián)體/防治荒漠化公約模擬前端/數(shù)字轉(zhuǎn)換器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 17/27頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 355K |
| 代理商: | WM8191 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁當(dāng)前第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁
Advanced Information
WM8191
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 3.1 April 2001
17
STB
DNA
RNW
OP[13:6]
Address
Data
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Driven by WM8191
Normal Output Data
Driven Externally
Driven by WM8191
Normal Output Data
Figure 16 Parallel Interface Register Write
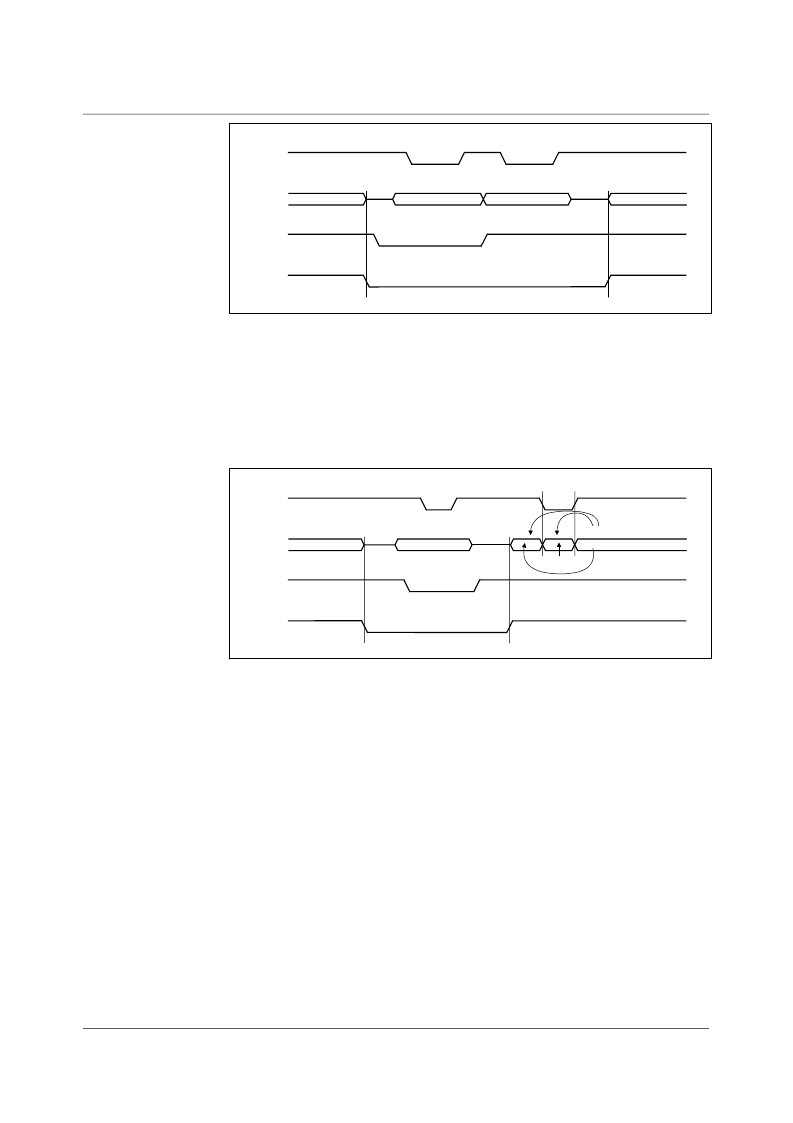
PARALLEL INTERFACE: REGISTER READ-BACK
Figure 17 shows register read-back in parallel mode. Read-back is initiated by writing the 6-bit
address (a5, 1, a3, a2, a1, a0) into OP[11:6] by pulsing the STB pin low. Note that a4 = 1 and pins
RNW and DNA are low. When RNW and DNA are high and STB is strobed again, the contents (d7,
d6, d5, d4, d3, d2, d1, d0) of the corresponding register (a5, 0, a3, a2, a1, a0) will be output on
OP[13:6], LSB on pin OP[6]. Until STB is pulsed low, the current contents of the ADC (shown as
Normal Output Data) will be present on OP[13:6]. Note that the register data becomes available on
the output data pins so OEB should be held low when read-back data is expected.
STB
DNA
RNW
OP[13:6]
Address
Hi-Z
Driven by WM8191
Driven Externally
Hi-Z
Normal Output Data
Read Data
Driven by WM8191
Normal Output Data
Figure 17 Parallel Interface Register Read-back
TIMING REQUIREMENTS
To use this device a master clock (MCLK) of up to 12MHz and a per-pixel synchronisation clock
(VSMP) of up to 6MHz are required. These clocks drive a timing control block, which produces
internal signals to control the sampling of the video signal. MCLK to VSMP ratios and maximum
sample rates for the various modes are shown in Table 5.
PROGRAMMABLE VSMP DETECT CIRCUIT
The VSMP input is used to determine the sampling point and frequency of the WM8191. Under
normal operation a pulse of 1 MCLK period should be applied to VSMP at the desired sampling
frequency (as shown in the Operating Mode Timing Diagrams) and the input sample will be taken on
the first rising MCLK edge after VSMP has gone low. However, in certain applications such a signal
may not be readily available. The programmable VSMP detect circuit in the WM8191 allows the
sampling point to be derived from any signal of the correct frequency, such as a CCD shift register
clock, when applied to the VSMP pin.
When enabled, by setting the VSMPDET control bit, the circuit detects either a rising or falling edge
(determined by POSNNEG control bit) on the VSMP input pin and generates an internal VSMP pulse.
This pulse can optionally be delayed by a number of MCLK periods, specified by the VDEL[2:0] bits.
Figure 18 shows the internal VSMP pulses that can be generated by this circuit for a typical clock
input signal. The internal VSMP pulse is then applied to the timing control block in place of the
normal VSMP pulse provided from the input pin. The sampling point then occurs on the first rising
MCLK edge after this internal VSMP pulse, as shown in the Operating Mode Timing Diagrams.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| WM8192 | TVS UNIDIRECT 400W 6.5V SMA |
| WM8196 | (8+8)BIT OUTPUT 16-BIT CIS/CCD AFE/DIGITISER |
| WM8199 | 20MSPS 16-bit CCD Digitiser |
| WM8199CDR | TVS BIDIRECT 400W 60V SMA |
| WM8199CDS | TVS UNIDIRECT 400W 64V SMA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| WM8192 | 制造商:WOLFSON 制造商全稱:WOLFSON 功能描述:(8+8) Bit Output 16-bit CIS/CCD AFE/Digitiser |
| WM8195 | 制造商:WOLFSON 制造商全稱:WOLFSON 功能描述:14-bit 12MSPS CIS/CCD Analogue Front End/Digitiser |
| WM8195_05 | 制造商:WOLFSON 制造商全稱:WOLFSON 功能描述:14-bit 12MSPS CIS/CCD Analogue Front End/Digitiser |
| WM8195SCFT/RV | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 14Bit 12MSPS 3C AFE RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
| WM8195SCFT/V | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 14Bit 12MSPS 3Ch AFE RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。