- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4176 > XC3130A-3PQ100C (Xilinx Inc)IC LOGIC CL ARRAY 3000GAT 100PQF PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XC3130A-3PQ100C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 67/76頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC LOGIC CL ARRAY 3000GAT 100PQF |
| 產(chǎn)品變化通告: | XC4000XL/E, XC9500XV, XC3100A Discontinuance 12/Apr/2010 |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 66 |
| 系列: | XC3000A/L |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 100 |
| RAM 位總計(jì): | 22176 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 80 |
| 門數(shù): | 2000 |
| 電源電壓: | 4.25 V ~ 5.25 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 100-BQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 100-QFP(14x20) |
| 其它名稱: | 122-1041 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)當(dāng)前第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)
R
November 9, 1998 (Version 3.1)
7-9
XC3000 Series Field Programmable Gate Arrays
7
Configurable Logic Block
The array of CLBs provides the functional elements from
which the user’s logic is constructed. The logic blocks are
arranged in a matrix within the perimeter of IOBs. For
example, the XC3020A has 64 such blocks arranged in 8
rows and 8 columns. The development system is used to
compile the configuration data which is to be loaded into
the internal configuration memory to define the operation
and interconnection of each block. User definition of CLBs
and their interconnecting networks may be done by auto-
matic translation from a schematic-capture logic diagram or
optionally by installing library or user macros.
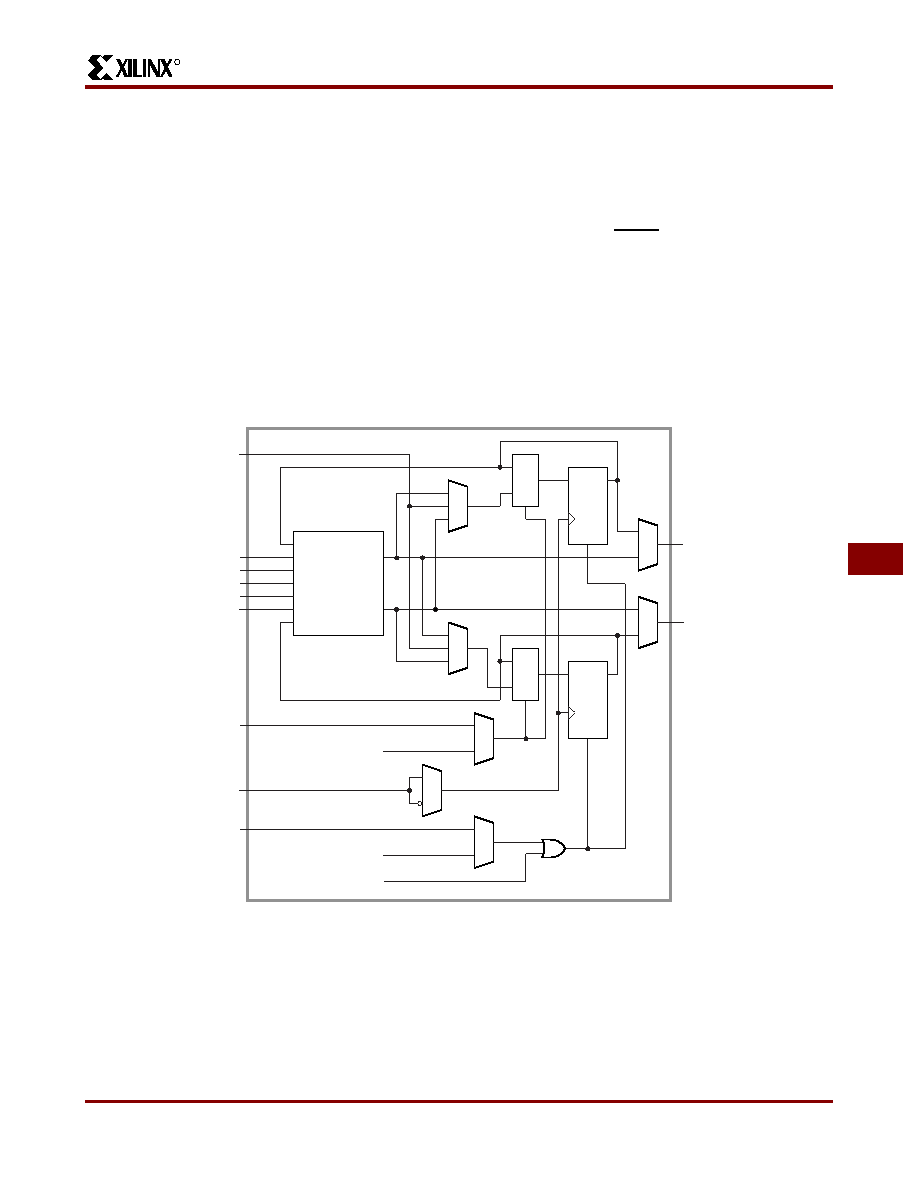
Each CLB has a combinatorial logic section, two flip-flops,
and an internal control section. See Figure 5. There are:
five logic inputs (A, B, C, D and E); a common clock input
(K); an asynchronous direct RESET input (RD); and an
enable clock (EC). All may be driven from the interconnect
resources adjacent to the blocks. Each CLB also has two
outputs (X and Y) which may drive interconnect networks.
Data input for either flip-flop within a CLB is supplied from
the function F or G outputs of the combinatorial logic, or the
block input, DI. Both flip-flops in each CLB share the asyn-
chronous RD which, when enabled and High, is dominant
over clocked inputs. All flip-flops are reset by the
active-Low chip input, RESET, or during the configuration
process. The flip-flops share the enable clock (EC) which,
when Low, recirculates the flip-flops’ present states and
inhibits response to the data-in or combinatorial function
inputs on a CLB. The user may enable these control inputs
and select their sources. The user may also select the
clock net input (K), as well as its active sense within each
CLB. This programmable inversion eliminates the need to
route both phases of a clock signal throughout the device.
Q
COMBINATORIAL
FUNCTION
LOGIC
VARIABLES
D
RD
G
F
DIN
F
G
QX
QY
DIN
F
G
QY
QX
F
Q
D
RD
ENABLE CLOCK
CLOCK
DIRECT
RESET
1 (ENABLE)
A
B
C
D
E
DI
EC
K
RD
Y
X
X3032
0 (INHIBIT)
(GLOBAL RESET)
CLB OUTPUTS
DATA IN
0
1
0
1
MUX
Figure 5: Configurable Logic Block.
Each CLB includes a combinatorial logic section, two flip-flops and a program memory controlled multiplexer selection of
function. It has the following:
-
five logic variable inputs A, B, C, D, and E
-
a direct data in DI
-
an enable clock EC
-
a clock (invertible) K
-
an asynchronous direct RESET RD
-
two outputs X and Y
Product Obsolete or Under Obsolescence
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XC3130A-3PC84C | IC LOGIC CL ARRAY 3000GAT 84PLCC |
| RCB108DHBR | CONN EDGECARD 216PS R/A .050 DIP |
| XC3120A-3PC68C | IC LOGIC CL ARRAY 2000GAT 68PLCC |
| ASC49DRYN-S93 | CONN EDGECARD 98POS DIP .100 SLD |
| XC3090A-7PC84C | IC LOGIC CL ARRAY 9000GAT 84PLCC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XC3130A-3PQ100C0262 | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述: |
| XC3130A-3PQ100I | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述: |
| XC3130A-3VQ100C | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述: |
| XC3130A-3VQ100I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Arrays (XC3000A/L, XC3100A/L) |
| XC3130A-3VQ64C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Arrays (XC3000A/L, XC3100A/L) |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。