- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄69013 > M37549G1FP 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO24 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M37549G1FP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO24 |
| 封裝: | 5.30 X 10.10 MM, 0.80 MM PITCH, PLASTIC, SSOP-24 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 4/86頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1375K |
| 代理商: | M37549G1FP |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)當(dāng)前第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)
Rev.2.02
Mar 31, 2009
Page 10 of 81
REJ03B0202-0202
7549 Group
[Processor status register (PS)]
The processor status register is an 8-bit register consisting of flags
which indicate the status of the processor after an arithmetic
operation. Branch operations can be performed by testing the
Carry (C) flag, Zero (Z) flag, Overflow (V) flag, or the Negative
(N) flag. In decimal mode, the Z, V, N flags are not valid.
After reset, the Interrupt disable (I) flag is set to “1”, but all other
flags are undefined. Since the Index X mode (T) and Decimal
mode (D) flags directly affect arithmetic operations, they should
be initialized in the beginning of a program.
Bit 0: Carry flag (C)
The C flag contains a carry or borrow generated by the
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) immediately after an arithmetic
operation. It can also be changed by a shift or rotate instruction.
Bit 1: Zero flag (Z)
The Z flag is set if the result of an immediate arithmetic
operation or a data transfer is “0”, and cleared if the result is
anything other than “0”.
Bit 2: Interrupt disable flag (I)
The I flag disables all interrupts except for the interrupt
generated by the BRK instruction. Interrupts are disabled
when the I flag is “1”.
When an interrupt occurs, this flag is automatically set to “1”
to prevent other interrupts from interfering until the current
interrupt is serviced.
Bit 3: Decimal mode flag (D)
The D flag determines whether additions and subtractions are
executed in binary or decimal. Binary arithmetic is executed when
this flag is “0”; decimal arithmetic is executed when it is “1”.
Decimal correction is automatic in decimal mode. Only the
ADC and SBC instructions can be used for decimal arithmetic.
Bit 4: Break flag (B)
The B flag is used to indicate that the current interrupt was
generated by the BRK instruction. The BRK flag in the
processor status register is always “0”. When the BRK
instruction is used to generate an interrupt, the processor
status register is pushed onto the stack with the break flag set
to “1”. The saved processor status is the only place where the
break flag is ever set.
Bit 5: Index X mode flag (T)
When the T flag is “0”, arithmetic operations are performed
between accumulator and memory, e.g. the results of an
operation between two memory locations is stored in the
accumulator. When the T flag is “1”, direct arithmetic
operations and direct data transfers are enabled between
memory locations, i.e. between memory and memory,
memory and I/O, and I/O and I/O. In this case, the result of
an arithmetic operation performed on data in memory
location 1 and memory location 2 is stored in memory
location 1. The address of memory location 1 is specified by
index register X, and the address of memory location 2 is
specified by normal addressing modes.
Bit 6: Overflow flag (V)
The V flag is used during the addition or subtraction of one
byte of signed data. It is set if the result exceeds +127 to -
128. When the BIT instruction is executed, bit 6 of the
memory location operated on by the BIT instruction is stored
in the overflow flag.
Bit 7: Negative flag (N)
The N flag is set if the result of an arithmetic operation or
data transfer is negative. When the BIT instruction is
executed, bit 7 of the memory location operated on by the
BIT instruction is stored in the negative flag.
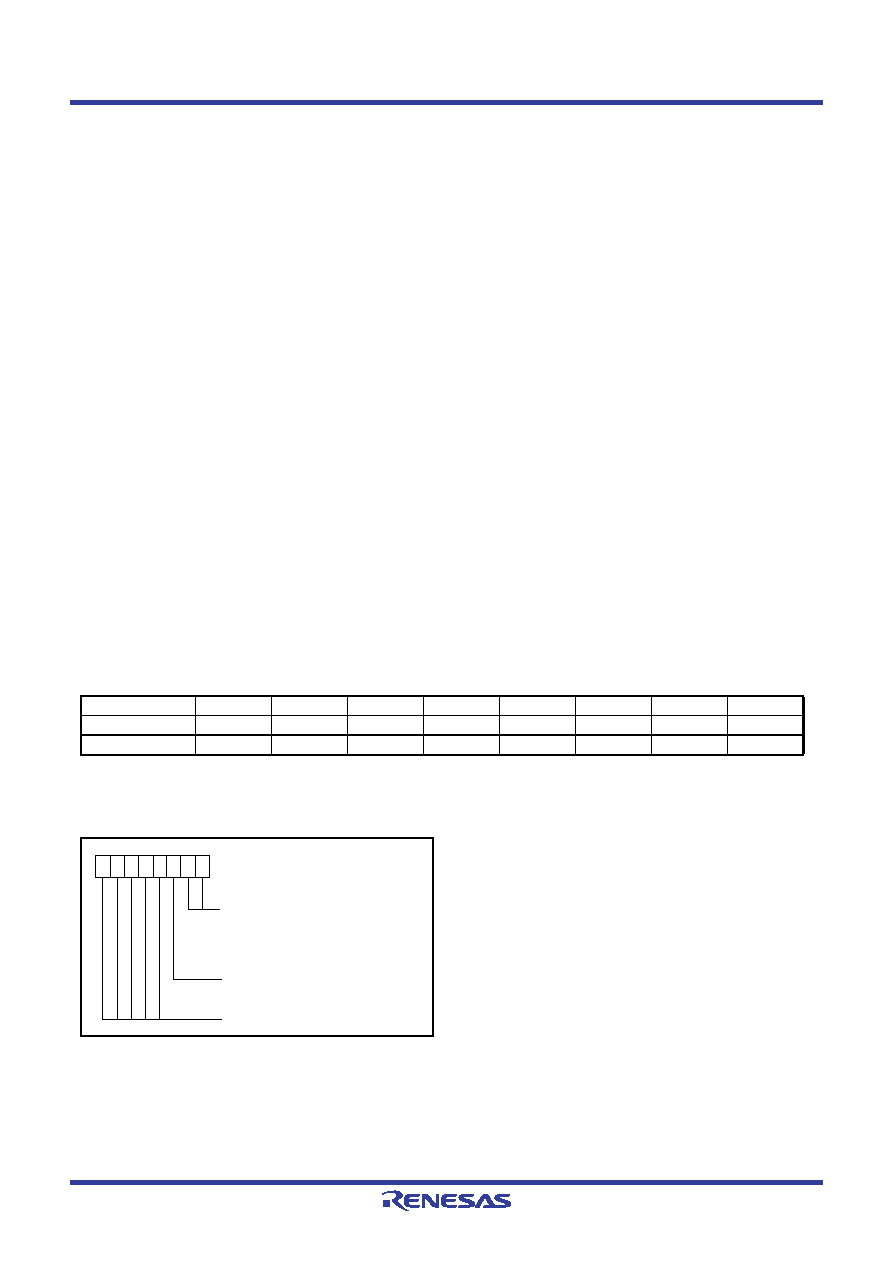
[CPU mode register] CPUM
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit.
This register is allocated at address 003B16.
Fig 7.
Structure of CPU mode register
The processor mode bits can be written only once after releasing reset.
Always set them to “002”. After written, rewriting any data to these
bits is disabled because they are locked. (Emulator MCU is excluded.)
Also, the stack page selection bit (bit 2) is not locked.
In order to prevent error-writing to the processor mode bits (at
program runaway), write the CPU mode register at the start of
the program that runs after releasing reset.
Table 5
Set and clear instructions of each bit of processor status register
C flag
Z flag
I flag
D flag
B flag
T flag
V flag
N flag
Set instruction
SEC
SEI
SED
SET
Clear instruction
CLC
CLI
CLD
CLT
CLV
CPU mode register
(CPUM: address 003B16, initial value: 0016)
Processor mode bits
b1b0
0 0 :
Single-chip mode
0 1 :
Not available
1 0 :
Not available
1 1 :
Not available
Stack page selection bit
0 : 0
page
1 : 1
page
Disable (returns “0” when read
)
b7
b0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M37560M8-XXXFP | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M37560EFDFP | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M37560MFD-XXXFP | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M37560EFFP | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M37560M8-XXXGP | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M37549G1-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37549G2FP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37549G2-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37549G3FP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37549G3-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。