- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄69008 > M30218MFCFP 16-BIT, FLASH, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M30218MFCFP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 16-BIT, FLASH, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, QFP-100 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 40/161頁 |
| 文件大小: | 2043K |
| 代理商: | M30218MFCFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁當(dāng)前第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁
Under
development
Tentative Specifications REV.A1
Specifications in this manual are tentative and subject to change.
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M30218 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
134
Pull-down
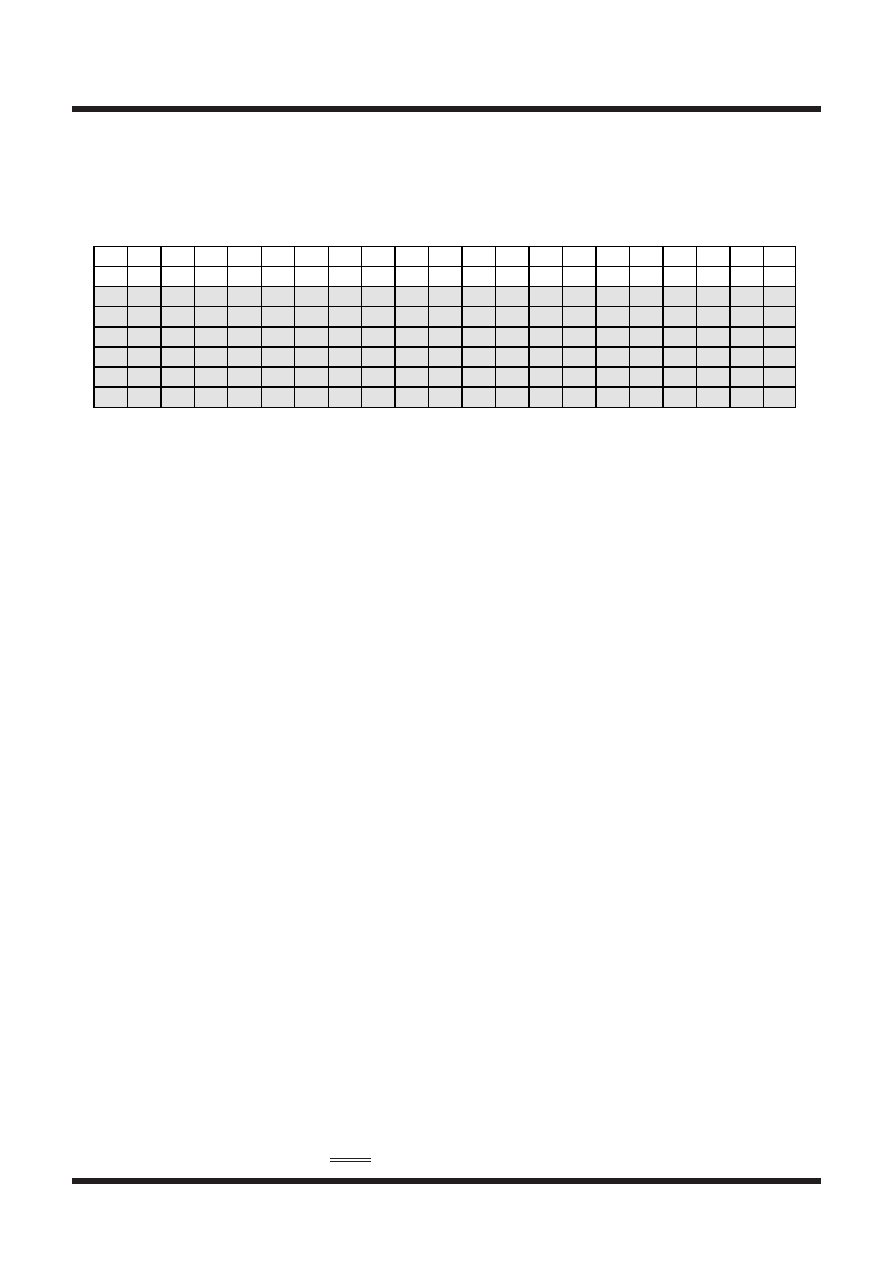
MASK OPTION OF PULL-DOWN RESISTOR (object product: mask ROM version)
Whether built-in pull-down resistors are connected or not to high-breakdown voltage ports P20 to P27, P30
to P37,and P40 to P43 can be specified in ordering mask ROM. The option type can be specified from
among 7 types; A to G.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
P20
P21
P22
P23
P24
P25
P26
P27
P30
P31
P32
P33
P34
P35
P36
P37
P40
P41
P42
0
00
0
P43
0
1
0
00
0
1
11
00
0
1
11
00
0
1
11
00
0
1
11
0
1
11
1
Note 1: The electrical characteristics of high-breakdown voltage ports P20 to P27, P30 to P37,and P40 to
P43’s built-in pull-down resistors are the same as that of high-breakdown voltage ports P00 to P07.
Note 2: The absolute maximum ratings of power dissipation may be exceed owing to the number of built-in
pull-down resistor. After calculating the power dissipation, specify the option type.
Note 3: The option types B to G cannot be specified because these types are currently under development.
Power Dissipation Calculating Method
(Fixed number depending on microcomputer’s standard)
VOH output fall voltage of high-breakdown port
2 V (max.); | Current value | = at 18 mA
Resistor value = 68 k
(min.)
Power dissipation of internal circuit (CPU, ROM, RAM etc.) = 5 V X 38 mA = 190 mW
(Fixed number depending on use condition)
Apply voltage to VEE pin: Vcc – 50 V
Timing number a; digit number b; segment number c
Ratio of Toff time corresponding Tdisp time: 1/16
Turn ON segment number during repeat cycle: d
All segment number during repeat cycle: e (= a X c)
Total number of built-in resistor: for digit; f, for segment; g
Digit pin current value h (mA)
Segment pin current value i (mA)
(1) Digit pin power dissipation
{h X b X (1–Toff / Tdisp) X voltage} / a
(2) Segment pin power dissipation
{i X d X (1–Toff / Tdisp) X voltage} / a
(3) Pull-down resistor power dissipation (digit)
{power dissipation per 1 digit X (b X f / b) X (1–Toff / Tdisp) } / a
(4) Pull-down resistor power dissipation (segment)
{power dissipation per 1 segment X (d X g / c) X (1–Toff / Tdisp) } / a
(5) Internal circuit power dissipation (CPU, ROM, RAM etc.) = 190 mW
(1) + (2)+ (3) + (4) + (5) = X mW
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M30220FCRP | 16-BIT, FLASH, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M30220MA-XXXGP | 16-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M30220MA-XXXRP | 16-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M30220FCRP | 16-BIT, FLASH, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M30220FCGP | 16-BIT, FLASH, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M3021E8F2-AXXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3021E8F4-AXXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3021E8F6-AXXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3021E8F8-AXXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M3021E8FA-AXXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。