- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369873 > LV8572AMX Real-Time Clock PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | LV8572AMX |
| 英文描述: | Real-Time Clock |
| 中文描述: | 實時時鐘 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 14/24頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 353K |
| 代理商: | LV8572AMX |
Functional Description
(Continued)
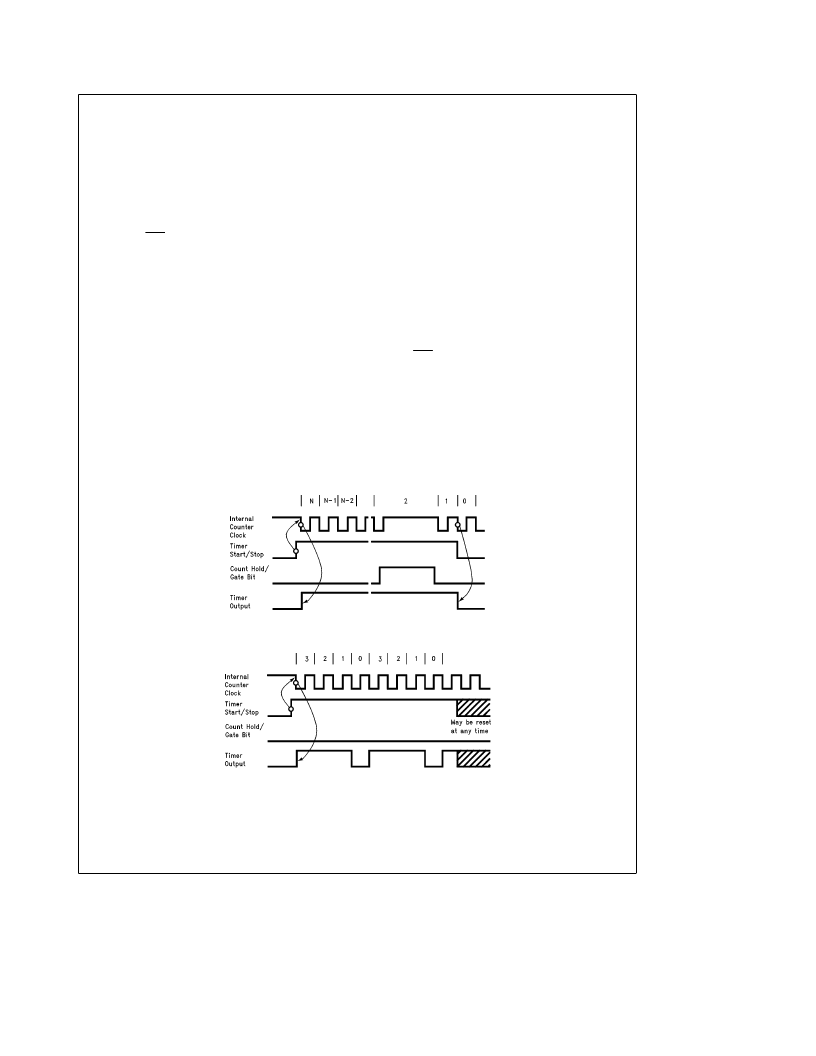
input data registers are loaded into the timer. The output will
stay high until the counter reaches zero. At zero the output
is reset. The result is an output pulse whose duration is
equal to the input clock period times the count value (N)
loaded into the input data register. This is shown inFigure 8.
Pulse Width
e
Clock Period
c
N
An interrupt is generated when the zero count is reached.
This can be used for one-time interrupts that are set to oc-
cur a certain amount of time in the future. In this mode the
Timer Start/Stop bit (TSS) is automatically reset upon zero
detection. This removes the need to reset TSS before start-
ing another operation.
The count down operation may be temporarily suspended
either under software control by setting the Count Hold/
Gate bit in the timer register high, or in hardware by setting
the G0 or G1 pin high.
The above discussion assumes that the MFO output is pro-
grammed to be non-inverting outputs (active high). If the
polarity of the output waveform is wrong for the application
the polarity can be reversed by configuring the Output Mode
Register. The drive configuration can also be programmed
to be push pull or open drain.
MODE 1: RATE GENERATOR
When operating in this mode the timer will operate continu-
ously. Before the timer is started its output is low. When the
timer is started the input data register contents are loaded
into the counter on the negative clock edge and the output
is set high (again assuming the Output Mode Register is
programmed active high). The timer will then count down to
zero. Once the zero count is reached the output goes low
for one clock period of the timer clock. Then on the next
clock the counter is reloaded automatically and the count-
down repeats itself. The output, shown in Figure 9, is a
waveform whose pulse width and period is determined by N,
the input register value, and the input clock period:
Period
e
(N
a
1) (Clock Period)
Pulse Width
e
Clock Period
Again, the output polarity is controllable as in mode 0. If
enabled, an interrupt is generated whenever the zero count
is reached. This can be used to generate a periodic inter-
rupt.
MODE 2: SQUARE WAVE GENERATOR
This mode is also cyclic but in this case a square wave
rather than a pulse is generated. The output square wave
period is determined by the value loaded into the timer input
register. This period and the duty cycle are:
Period
e
2(N
a
1) (Clock Period)
When the timer is stopped the output will be low, and when
the Start/Stop bit is set high the timer’s counter will be load-
ed on the next clock falling transition and the output will be
set high.
Duty Cycle
e
0.5
The output will be toggled after the zero count is detected
and the counter will then be reloaded, and the cycle will
continue. Thus, every N
a
1 counts the output gets toggled,
as shown inFigure 10. Like the other modes the timer oper-
ation can be suspended by setting the count hold/gate bit
(CHG) in the Timer Control Register. An interrupt will be
generated every falling edge of the timer output, if enabled.
TL/F/11416–12
FIGURE 8. Typical Waveforms for Timer Mode 0
(MFO Output Programmed Active High)
TL/F/11416–13
FIGURE 9. Timing Waveforms for Timer Mode 1
(MFO Output Programmed Active High)
14
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LV8572AVX | Real-Time Clock |
| LV8800C | Optoelectronic |
| LVA12D | Analog IC |
| LVA12S | Analog IC |
| LVA15D | Analog IC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LV8572AN | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| LV8572AVX | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Real-Time Clock |
| LV8573A | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:LV8573A Low Voltage Real Time Clock (RTC) |
| LV8573AM | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:LV8573A Low Voltage Real Time Clock (RTC) |
| LV8573AN | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:LV8573A Low Voltage Real Time Clock (RTC) |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。