- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄1895 > AD9983AKSTZ-170 (Analog Devices Inc)IC DISPLAY 8BIT 170MSPS 80LQFP PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | AD9983AKSTZ-170 |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices Inc |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 7/44頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC DISPLAY 8BIT 170MSPS 80LQFP |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 應(yīng)用: | 視頻 |
| 接口: | 模擬 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.7 V ~ 3.47 V |
| 封裝/外殼: | 80-LQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 80-LQFP(14x14) |
| 包裝: | 管件 |
| 安裝類(lèi)型: | 表面貼裝 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)當(dāng)前第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)
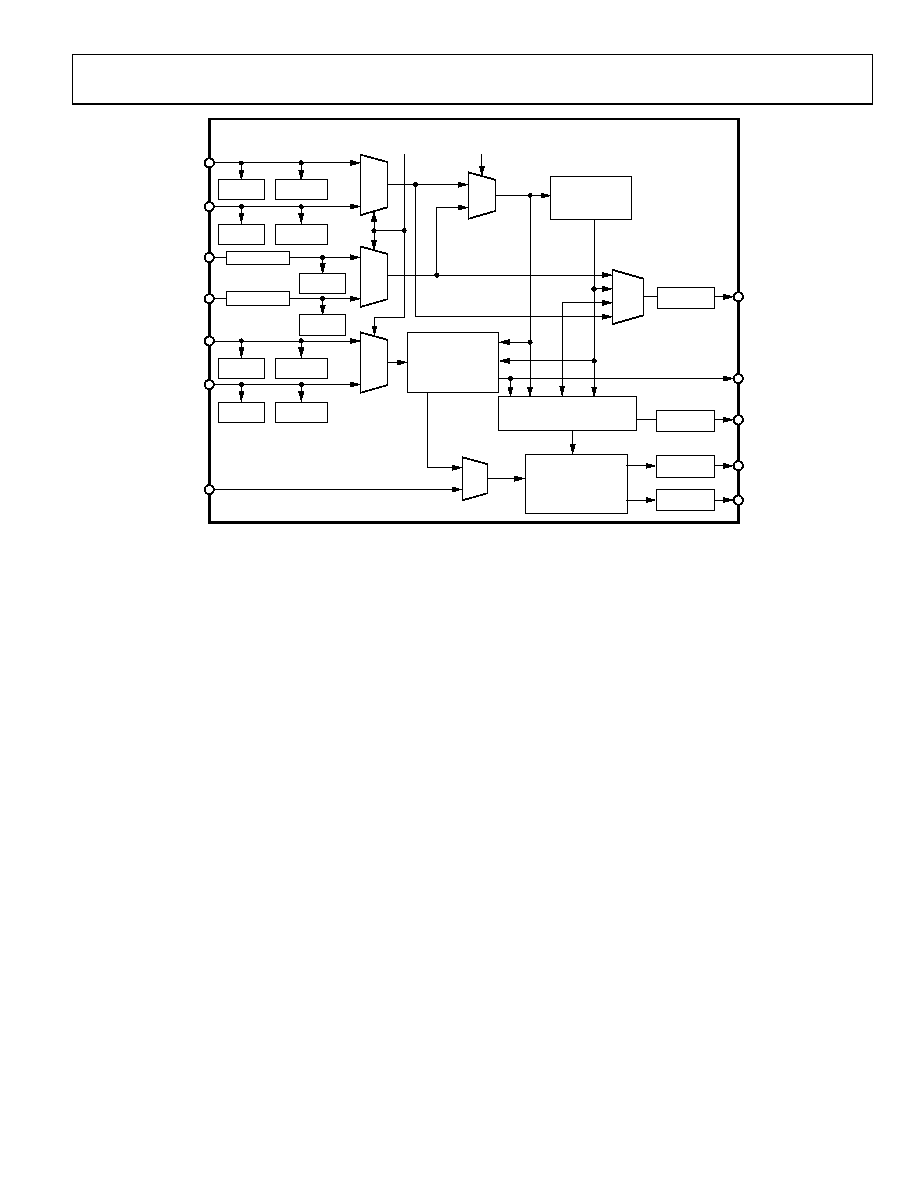
AD9983A
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 44
AD9983A
SOGOUT
HSYNC
COAST
DATACK
SOGIN0
EXTCK/COAST
VSYNC1
MUX
VSYNC0
HSYNC1
HSYNC0
HSOUT
VSOUT/A0
SOGIN1
HSYNC
SELECT
FILTERED
HSYNC
ACTIVITY
DETECT
ACTIVITY
DETECT
ACTIVITY
DETECT
ACTIVITY
DETECT
ACTIVITY
DETECT
ACTIVITY
DETECT
POLARITY
DETECT
POLARITY
DETECT
POLARITY
DETECT
POLARITY
DETECT
SYNC SLICER
PLL CLOCK
GENERATOR
O/E FIELD
CHANNEL
SELECT
HSYNC FILTER
AND
REGENERATOR
REGENERATED
HSYNC
SET
POLARITY
SYNC
PROCESSOR
AND
VSYNC FILTER
HSYNC/VSYNC
COUNTER
REG 0x26, 0x27
0
64
75
-01
3
SET
POLARITY
SET
POLARITY
SET
POLARITY
Figure 8. Sync Processing Block Diagram
SYNC PROCESSING
The inputs of the sync processing section of the AD9983A are
combinations of digital Hsyncs and Vsyncs, analog sync-on-
green, or sync-on-Y signals, and an optional external coast
signal. From these signals it generates a precise, jitter-free clock
from its PLL; an odd/even field signal; HSOUT and VSOUT
signals; a count of Hsyncs per Vsync; and a programmable
SOGOUT. The main sync processing blocks are the sync slicer,
sync separator, Hsync filter, Hsync regenerator, Vsync filter, and
coast generator.
The sync slicer extracts the sync signal from the green
graphics or luminance video signal that is connected to the
SOGINx input and outputs a digital composite sync.
The sync separator’s task is to extract Vsync from the
composite sync signal, which can come from either the sync
slicer or the HSYNCx inputs.
The Hsync filter is used to eliminate any extraneous pulses
from the HSYNCx or SOGINx inputs, outputting a clean,
low jitter signal that is appropriate for mode detection and
clock generation.
The Hsync regenerator is used to recreate a clean, although
not low jitter, Hsync signal that can be used for mode
detection and counting Hsyncs per Vsync.
The Vsync filter is used to eliminate spurious Vsyncs,
maintain a stable timing relationship between the Vsync and
Hsync output signals, and generate the odd/even field output.
The coast generator creates a robust coast signal that
allows the PLL to maintain its frequency in the absence of
Hsync pulses.
Sync Slicer
The purpose of the sync slicer is to extract the sync signal from
the green graphics or luminance video signal that is connected
to the SOG input. The sync signal is extracted in a two step
process. First, the SOG input is clamped to its negative peak,
(typically 0.3 V below the black level). Next, the signal goes to a
comparator with a variable trigger level (set by Register 0x1D,
Bits[7:3]), but nominally 0.128 V above the clamped level. The
sync slicer output is a digital composite sync signal containing
both Hsync and Vsync information (see Figure 9).
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD9985KSTZ-140 | IC INTERFACE 8BIT 140MSPS 80LQFP |
| AD9990BBCZ | IC CCD SGNL PROCESSOR 112CSPBGA |
| AD9991KCPZRL | IC CCD SIGNAL PROCESSOR 56-LFCSP |
| AD9992BBCZRL | IC CCD SGNL PROC 12BIT 105CSPBGA |
| AD9995KCPZ | IC CCD SIGNAL PROCESSOR 56-LFCSP |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AD9983AKSTZ-1701 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱(chēng):Analog Devices 功能描述:High Performance 8-Bit Display Interface |
| AD9983KSTZ-110 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述: 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: |
| AD9983KSTZ-140 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述: 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: |
| AD9983KSTZ-170 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: |
| AD9984A | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱(chēng):Analog Devices 功能描述:High Performance 10-Bit Display Interface |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。