- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄376451 > XR-215A (Exar Corporation) Monolithic Phase Locked Loop PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XR-215A |
| 廠商: | Exar Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Monolithic Phase Locked Loop |
| 中文描述: | 單片鎖相環(huán) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 6/32頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 331K |
| 代理商: | XR-215A |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)當(dāng)前第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)
XR-215A
6
Rev. 1.01
6
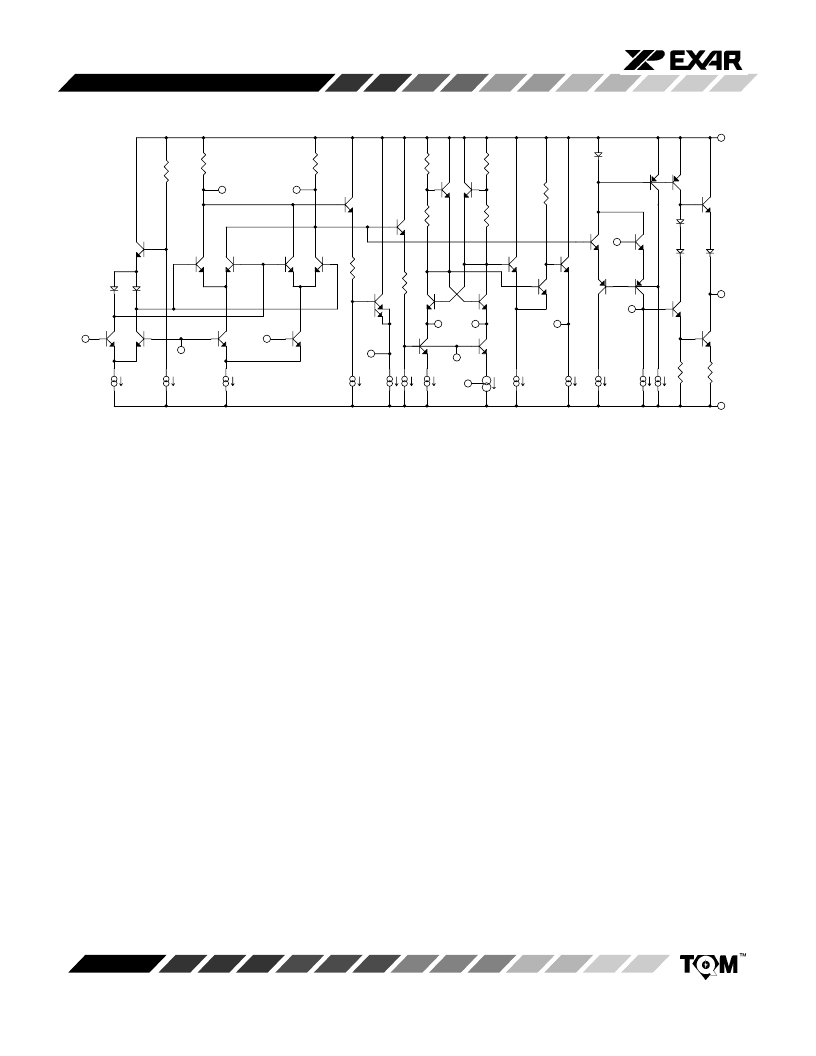
Figure 2. Equivalent Schematic Diagram
1
16
2
3
5
4
11
14 13
15
12
7
8
9
10
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The XR-215A monolithic PLL system consists of a
balanced phase comparator, a highly stable voltage-
controlled oscillator (VCO) and a high speed operational
amplifier. The phase comparator outputs are internally
connected to the VCO inputs and to the noninverting input
of the operational amplifier. A self-contained PLL System
is formed by simply AC coupling the VCO output to either
of the phase comparator inputs and adding a low-pass
filter to the phase comparator output terminals.
The VCO section has frequency sweep, on-off keying,
sync, and digital programming capabilities. Its frequency
is highly stable and is determined by a single external
capacitor. The operational amplifier can be used for audio
preamplification in FM detector applications or as a high
speed sense amplifier (or comparator) in FSK
demodulation.
DESCRIPTION OF CIRCUIT CONTROLS
Phase Comparator Inputs (Pins 4 and 6)
One input to the phase comparator is used as the signal
input. The remaining input should be AC coupled to the
VCO output (pin 15) to complete the PLL (see Figure 3).
For split supply operation, these inputs are biased from
ground as shown in Figure 4. For single supply operation,
a resistive bias string similar to that shown in Figure 3
should be used to set the bias level at approximately
V
CC
/2. The DC bias current at these terminals is
nominally 8 A.
Phase Comparator Bias (Pin 5)
This terminal should be DC biased as shown in Figure 3
and Figure 4 and AC grounded with a bypass capacitor.
Phase Comparator Outputs (Pins 2 and 3)
The low frequency (or DC) voltage across these pins
corresponds to the phase difference between the two
signals at the phase comparator inputs (pins 4 and 6). The
phase comparator outputs are internally connected to the
VCO control terminals (see Figure 2.) One of the outputs
(pin 3) is internally connected to the noninverting input of
the operational amplifier. The low-pass filter is achieved
by connecting an RC network to the phase comparator
outputs as shown in Figure 15.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XR-215 | Monolithic Phase Locked Loop |
| XR-2207 | Voltage-Controlled Oscillator |
| XR-2207CP | Voltage-Controlled Oscillator |
| XR-2207D | Voltage-Controlled Oscillator |
| XR-2207M | Voltage-Controlled Oscillator |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XR-215ACD | 制造商:EXAR 制造商全稱:EXAR 功能描述:Monolithic Phase Locked Loop |
| XR-215ACP | 制造商:EXAR 制造商全稱:EXAR 功能描述:Monolithic Phase Locked Loop |
| XR215CP | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:IC-PHASE LOCKED LOOP |
| XR-215CP | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Analog Phase-Locked Loop |
| XR-215D | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Analog Phase-Locked Loop |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。