- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371200 > X24256ZI-1.8 30V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-Pak package; A IRL7833S with Standard Packaging PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | X24256ZI-1.8 |
| 英文描述: | 30V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-Pak package; A IRL7833S with Standard Packaging |
| 中文描述: | EEPROM的 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/18頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 144K |
| 代理商: | X24256ZI-1.8 |
X24256
Characteristics subject to change without notice.
7 of 18
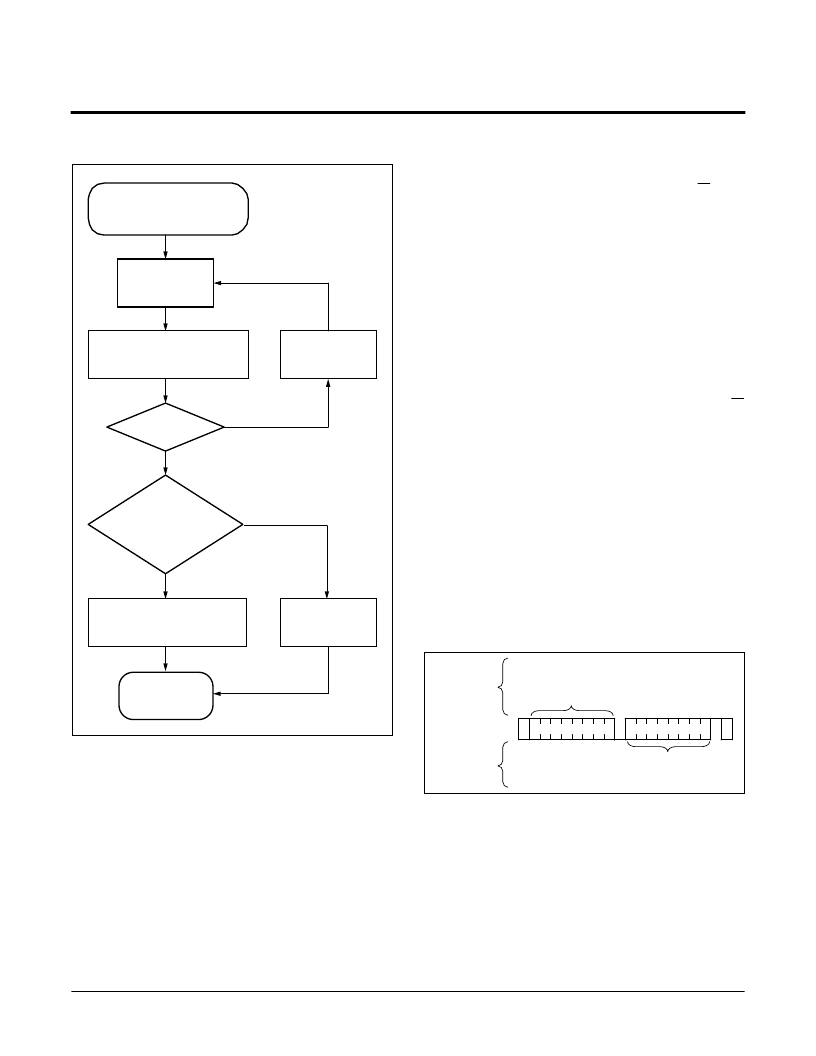
Figure 7. Acknowledge Polling Sequence
READ OPERATIONS
Read operations are initiated in the same manner as
write operations with the exception that the R/W bit of
the Slave Address Byte is set to one. There are three
basic read operations: Current Address Reads, Ran-
dom Reads, and Sequential Reads.
Current Address Read
Internally, the device contains an address counter that
maintains the address of the last word read or written
incremented by one. After a read operation from the
last address in the array, the counter will “roll over” to
the first address in the array. After a write operation to
the last address in a given page, the counter will “roll
over” to the first address on the same page.
Upon receipt of the Slave Address Byte with the R/W
bit set to one, the device issues an acknowledge and
then transmits the eight bits of the Data Byte. The
master terminates the read operation when it does not
respond with an acknowledge during the ninth clock
and then issues a stop condition. Refer to Figure 8 for
the address, acknowledge, and data transfer
sequence.
It should be noted that the ninth clock cycle of the read
operation is not a “don’t care.” To terminate a read
operation, the master must either issue a stop condi-
tion during the ninth cycle or hold SDA HIGH during
the ninth clock cycle and then issue a stop condition.
Figure 8. Current Address Read Sequence
BYTE LOAD COMPLETED
BY ISSUING STOP.
ENTER ACK POLLING
ISSUE
START
ISSUE SLAVE
ADDRESS BYTE
(READ OR WRITE)
ACK
RETURNED
HIGH
VOLTAGE
CYCLE COMPLETE.
CONTINUE
SEQUENCE
CONTINUE NORMAL
READ ORWRITE
COMMAND SEQUENCE
PROCEED
ISSUE STOP
NO
YES
YES
ISSUE STOP
NO
FROM THE
SLAVE
S
T
A
R
T
S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
DATA
SIGNALS
FROM THE
MASTER
SDA BUS
SIGNALS
1
0 1 0
1
0
Powered by ICminer.com Electronic-Library Service CopyRight 2003
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| X24256ZI-2.5 | EEPROM |
| X24320S8-1.8 | 16 Characters x 2 Lines, 5x7 Dot Matrix Character and Cursor |
| X24320S8-2.5 | 16 Characters x 2 Lines, 5x7 Dot Matrix Character and Cursor |
| X24320V14-2.5 | 400KHz 2-Wire Serial E2PROM with Block Lock |
| X24320 | 400KHz 2-Wire Serial E2PROM with Block Lock |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| X24256ZI-2.5 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM |
| X24257Z-2.5 | 制造商:XICOR 制造商全稱:Xicor Inc. 功能描述:400kHz 2-Wire Serial EEPROM with Block Lock |
| X242-883B | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:X200 SERIES (CMOS) STANDARD SPECFITIONS |
| X242-SERIES | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Peripheral IC |
| X243 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:X200 SERIES (CMOS) STANDARD SPECFITIONS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。