- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371188 > TSA5059ATS (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) 2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TSA5059ATS |
| 廠商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | XO, clock |
| 英文描述: | 2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| 中文描述: | PLL FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER, 2700 MHz, PDSO16 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, SSOP-16 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 5/24頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 118K |
| 代理商: | TSA5059ATS |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)當(dāng)前第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)
2000 Oct 24
5
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
2.7 GHz I
2
C-bus controlled low phase
noise frequency synthesizer
TSA5059A
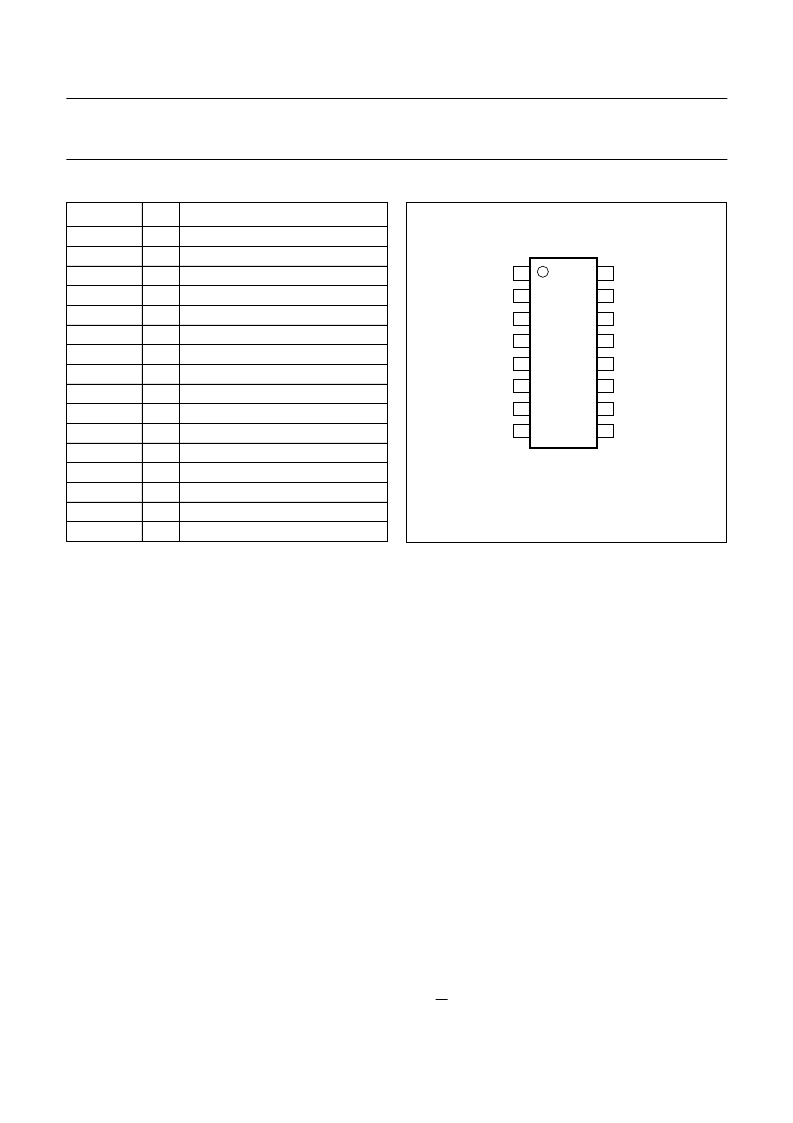
PINNING
SYMBOL
PIN
DESCRIPTION
CP
XTAL
XT/COMP
AS
SDA
SCL
P3
P2
P1
P0
ADC
V
CC
RFA
RFB
GND
DRIVE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
charge pump output
crystal oscillator input
f
xtal
or f
comp
signal output
I
2
C-bus address selection input
I
2
C-bus serial data input/output
I
2
C-bus serial clock input
general purpose output Port 3
general purpose input/output Port 2
general purpose input/output Port 1
general purpose input/output Port 0
analog-to-digital converter input
supply voltage
RF signal input A
RF signal input B
ground supply
external NPN drive output
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
16
15
14
CP
XTAL
XT/COMP
AS
SDA
GND
RFB
RFA
VCC
ADC
P0
P1
SCL
P3
P2
DRIVE
TSA5059A
FCE713
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TSA5059A contains all the necessary elements but a
reference source, a loop filter and an external NPN
transistor to control a varicap tuned local oscillator forming
aphaselockedloopfrequencysynthesizedsource.The IC
is designed in a high speed process with a fast phase
detector to allow a high comparison frequency to reach a
low phase noise level on the oscillator.
The block diagram is shown in Fig.1. The RF signal is
applied at pins RFA and RFB. Thanks to the input
preamplifier a good sensitivity is provided. The output of
the preamplifier is fed to the 17-bit programmable divider
either through a divide-by-two prescaler or directly.
Becauseoftheinternalhighspeedprocess,theRF divider
is working for a frequency up to 2.3 GHz, without the need
for the divide-by-two prescaler to be used. This prescaler
is needed for frequencies above 2.3 GHz.
The output of the 17-bit programmable divider f
DIV
is fed
into the phase comparator, where it is compared in both
phase and frequency with the comparison frequency f
comp
.
This frequency is derived from the signal present at
pin XTAL, f
xtal
, divided down in the reference divider. It is
possible either to connect a quartz crystal to pin XTAL and
then using the on-chip crystal oscillator, or to feed this pin
with a reference signal from an external source.
The reference divider can have a dividing ratio selected
from 16 different values between 2 and 320 (see Table 8).
The output of the phase comparator drives the
charge pump and the loop amplifier section. This amplifier
requires the use of an external NPN transistor. Pin CP is
the output of the charge pump, and pin DRIVE is the pin to
connect the base of the external transistor. This transistor
has its emitter grounded and the collector drives the tuning
voltage to the varicap diode of the Voltage Controlled
Oscillator (VCO). The loop filter has to be connected
between pin CP and the collector of the external NPN
transistor.
In addition, it is possible to drive another PLL synthesizer,
or the clock input of a digital demodulation IC, from
pin XT/COMP. It is possible to select by software either
f
xtal
, the crystal oscillator frequency or f
comp
, the frequency
present after the reference divider at this pin. It is also
possible to switch off this output, in case it is not used.
For test and alignment purposes, it is possible to release
the drive output to be able to apply an external voltage on
it, to select one of the three charge pump test modes, and
to monitor half the f
DIV
at Port P0. See Table 10 for all
possible modes.
Four open-collector output ports are provided on the IC for
general purpose; three of these can also be used as input
ports. A 3-bit ADC is also available.
The TSA5059A is controlled via the two-wire I
2
C-bus.
For programming, there is one 7-bit module address and
bit R/W for selecting READ or WRITE mode.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TSA5059TS | 2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| TSA5059 | 2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| TSA5059T | 2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| TSC2200 | PDA ANALOG INTERFACE CIRCUIT |
| TSC2200IPW | PDA ANALOG INTERFACE CIRCUIT |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TSA5059ATS/C1,118 | 功能描述:鎖相環(huán) - PLL 2,7GHZI2C BUS RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 類型:PLL Clock Multiplier 電路數(shù)量:1 最大輸入頻率:710 MHz 最小輸入頻率:0.002 MHz 輸出頻率范圍:0.002 MHz to 808 MHz 電源電壓-最大:3.63 V 電源電壓-最小:1.71 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-36 封裝:Tray |
| TSA5059ATS/C2,118 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述: |
| TSA5059T | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| TSA5059TS | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:2.7 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
| TSA5060A | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1.3 GHz I2C-bus controlled low phase noise frequency synthesizer |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。