- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄378162 > RM5231A-350-H (PMC-SIERRA INC) RM5231A⑩ Microprocessor with 32-Bit System Bus Data Sheet Preliminary PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | RM5231A-350-H |
| 廠商: | PMC-SIERRA INC |
| 元件分類(lèi): | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | RM5231A⑩ Microprocessor with 32-Bit System Bus Data Sheet Preliminary |
| 中文描述: | 64-BIT, 350 MHz, MICROPROCESSOR, PQFP128 |
| 封裝: | MQFP-128 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 12/40頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 595K |
| 代理商: | RM5231A-350-H |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)當(dāng)前第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)
Proprietary and Confidential to PMC-Sierra, Inc and for its Customer’s Internal Use
Document ID: PMC-2002174, Issue 2
12
RM5231A Microprocessor with 32-Bit System Bus Data Sheet
Preliminary
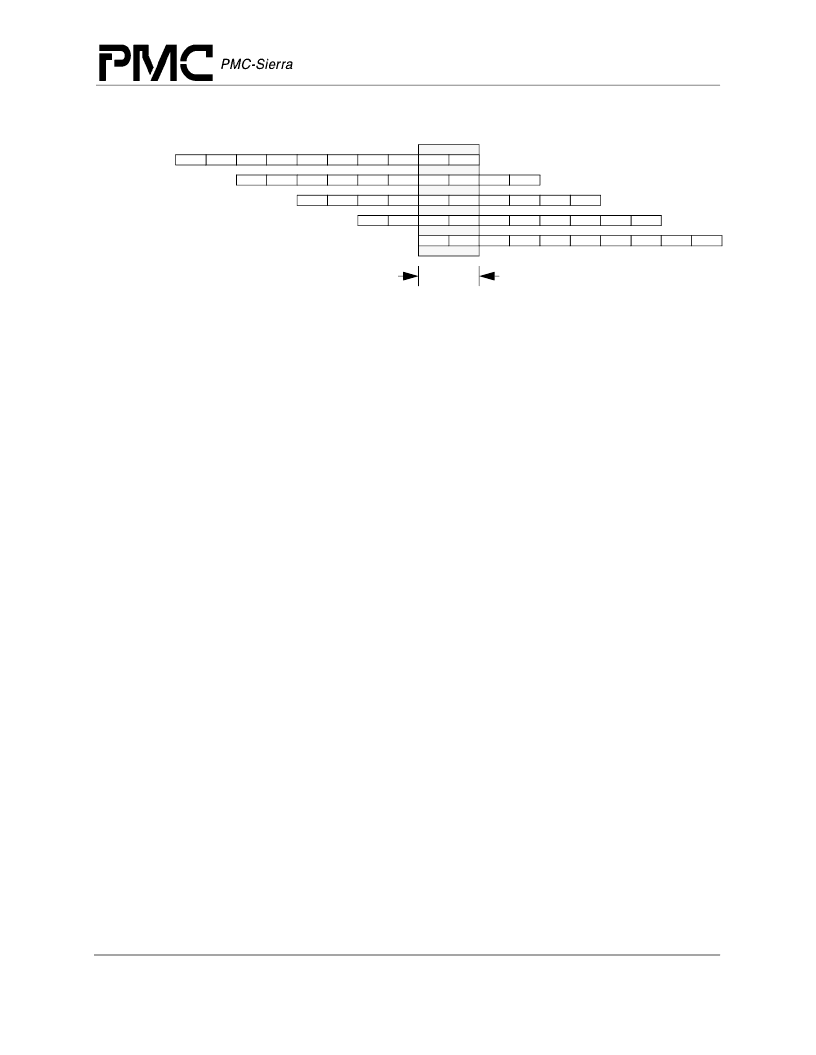
Figure 3 Pipeline
3.4
Integer Unit
The RM5231A integer unit includes thirty-two general purpose 64-bit registers, a load/store
architecture with single cycle ALU operations (add, sub, logical, shift) and an autonomous
multiply/divide unit. Additional register resources include: the HI/LO result registers for the two-
operand integer multiply/divide operations, and the program counter (PC).
The RM5231A implements the MIPS IV Instruction Set Architecture, and is therefore fully
upward compatible with applications that run on processors implementing the earlier generation
MIPS I-III instruction sets.
Register File
3.5
The RM5231A has thirty-two general purpose registers with register location 0 (r0) hard wired to
a zero value. These registers are used for scalar integer operations and address calculation. The
register file has two read ports and one write port and is fully bypassed to minimize operation
latency in the pipeline.
ALU
3.6
The RM5231A ALU consists of an integer adder/subtractor, a logic unit, and a shifter. The adder
performs address calculations in addition to arithmetic operations. The logic unit performs all
logical and zero shift data moves. The shifter performs shifts and store alignment operations. Each
of these units is optimized to perform all operations in a single processor cycle.
Integer Multiply/Divide
3.7
The RM5231A has a dedicated integer multiply/divide unit optimized for high-speed multiply and
multiply-accumulate operations. Table 1 shows the performance of the multiply/divide unit on
each operation
I0
I1
I2
I3
I4
2I
1I
1R
2R
1A
2A
1D
2D
1W
2W
2I
1I
1R
2R
1A
2A
1D
2D
1W
2W
2I
1I
1R
2R
1A
2A
1D
2D
1W
2W
2I
1I
1R
2R
1A
2A
1D
2D
1W
2W
2I
1I
1R
2R
1A
2A
1D
2D
1W
2W
one cycle
1I-1R:
2I:
2R:
1A:
1A:
2A-2A:
1A-2A:
1D:
2W:
Instruction cache access
Instruction virtual to physical address translation
Register file read, Bypass calculation, Instruction decode, Branch address calculation
Issue or slip decision, Branch decision
Data virtual address calculation
Integer add, logical, shift
Store Align
Data cache access and load align
Data virtual to physical address translation
Register file write
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| RM5261A | RM5261A⑩ Microprocessor with 64-Bit System Bus Data Sheet Preliminary |
| RM5261A-250-H | RM5261A⑩ Microprocessor with 64-Bit System Bus Data Sheet Preliminary |
| RM5261A-300-H | CONNECTOR ACCESSORY |
| RM5261A-300-HI | CONNECTOR ACCESSORY |
| RM5261A-350-H | CONNECTOR ACCESSORY |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| RM525A-R2 | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:2U Wallmount Cabinet, Beige |
| RM5260-133Q | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:64-Bit Microprocessor |
| RM5260-150Q | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:64-Bit Microprocessor |
| RM5260-175Q | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:64-Bit Microprocessor |
| RM5260-200Q | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:64-Bit Microprocessor |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。