- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369945 > PA28F008SA-85 (INTEL CORP) 8-MBIT (1-MBIT x 8) FlashFileTM MEMORY PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PA28F008SA-85 |
| 廠商: | INTEL CORP |
| 元件分類: | PROM |
| 英文描述: | 8-MBIT (1-MBIT x 8) FlashFileTM MEMORY |
| 中文描述: | 1M X 8 FLASH 12V PROM, 85 ns, PDSO44 |
| 封裝: | 0.525 X 1.110 INCH, PLASTIC, SOP-44 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/33頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 466K |
| 代理商: | PA28F008SA-85 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁
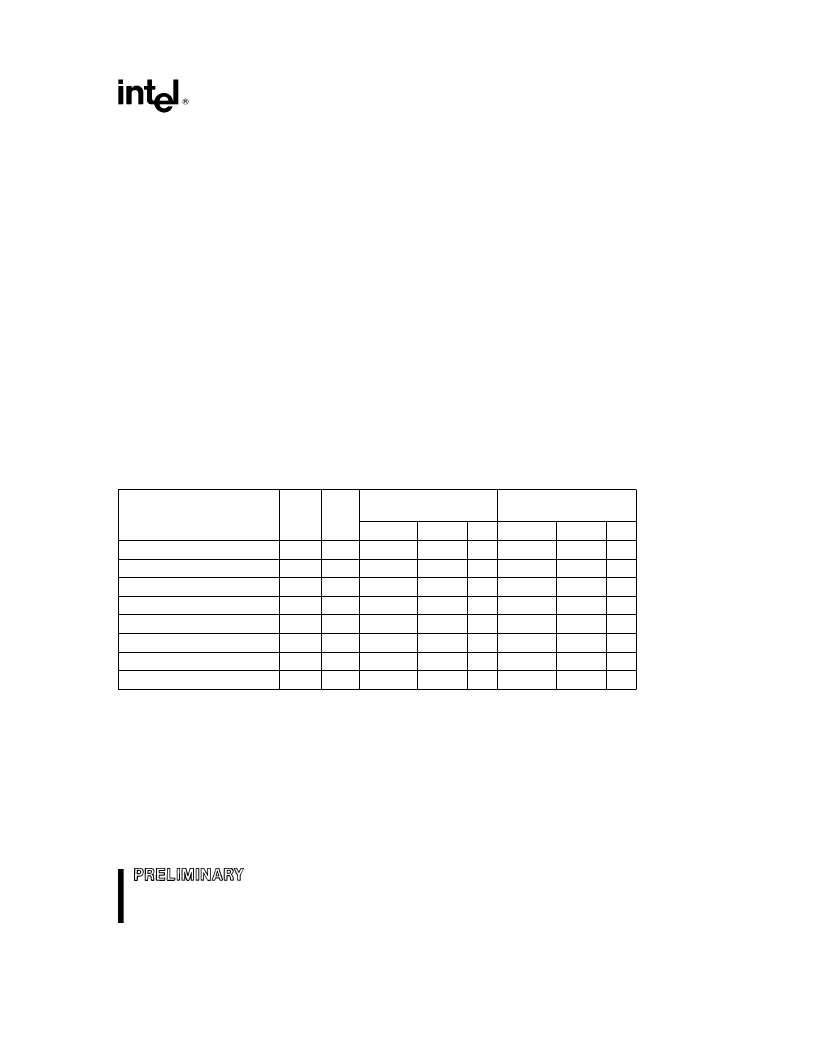
28F008SA
Deep Power-Down
The 28F008SA offers a deep power-down feature,
entered when RP
Y
is at V
IL
. Current draw thru V
CC
is 0.20
m
A typical in deep power-down mode, with
current draw through V
PP
typically 0.1
m
A. During
read modes, RP
Y
-low deselects the memory,
places output drivers in a high-impedence state and
turns off all internal circuits. The 28F008SA requires
time t
PHQV
(see AC Characteristics-Read-Only Op-
erations) after return from powerdown until initial
memory access outputs are valid. After this wakeup
interval, normal operation is restored. The Com-
mand User Interface is reset to Read Array, and the
upper 5 bits of the Status Register are cleared to
value 10000, upon return to normal operation.
During block erase or byte write modes, RP
Y
low
will abort either operation. Memory contents of the
block being altered are no longer valid as the data
will be partially written or erased. Time t
PHWL
after
RP
Y
goes to logic-high (V
IH
) is required before an-
other command can be written.
This use of RP
Y
during system reset is important
with automated write/erase devices. When the sys-
tem comes out of reset it expects to read from the
flash memory. Automated flash memories provide
status information when accessed during write/
erase modes. If a CPU reset occurs with no flash
memory reset, proper CPU initialization would not
occur because the flash memory would be providing
the status information instead of array data. Intel’s
Flash Memories allow proper CPU initialization fol-
lowing a system reset through the use of the RP
Y
input. In this application RP
Y
is controlled by the
same RESET
Y
signal that resets the system CPU.
Intelligent Identifier Operation
The intelligent identifier operation outputs the manu-
facturer code, 89H; and the device code, A2H for
the 28F008SA. The system CPU can then automati-
cally match the device with its proper block erase
and byte write algorithms.
The manufacturer- and device-codes are read via
the Command User Interface. Following a write of
90H to the Command User Interface, a read from
address location 00000H outputs the manufacturer
code (89H). A read from address 00001H outputs
the device code (A2H). It is not necessary to have
high voltage applied to V
PP
to read the intelligent
identifiers from the Command User Interface.
Table 3. Command Definitions
Command
Cycles
Req’d
Bus
Notes
First Bus Cycle
Second Bus Cycle
Operation Address Data Operation Address Data
Read Array/Reset
1
1
Write
X
FFH
Intelligent Identifier
3
2, 3, 4
Write
X
90H
Read
IA
IID
Read Status Register
2
3
Write
X
70H
Read
X
SRD
Clear Status Register
1
Write
X
50H
Erase Setup/Erase Confirm
2
2
Write
BA
20H
Write
BA
D0H
Erase Suspend/Erase Resume
2
Write
X
B0H
Write
X
D0H
Byte Write Setup/Write
2
2, 3, 5
Write
WA
40H
Write
WA
WD
Alternate Byte Write Setup/Write
2
2, 3, 5
Write
WA
10H
Write
WA
WD
NOTES:
1. Bus operations are defined in Table 2.
2. IA
e
Identifier Address: 00H for manufacturer code, 01H for device code.
BA
e
Address within the block being erased.
WA
e
Address of memory location to be written.
3. SRD
e
Data read from Status Register. See Table 4 for a description of the Status Register bits.
WD
e
Data to be written at location WA. Data is latched on the rising edge of WE
Y
.
IID
e
Data read from Intelligent Identifiers.
4. Following the Intelligent Identifier command, two read operations access manufacture and device codes.
5. Either 40H or 10H are recognized by the WSM as the Byte Write Setup command.
6. Commands other than those shown above are reserved by Intel for future device implementations and should not be
used.
11
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PA28F008SC-85 | BYTE-WIDE SmartVoltage FlashFile MEMORY FAMILY 4, 8, AND 16 MBIT |
| PA28F008SA-120 | 8-MBIT (1-MBIT x 8) FlashFileTM MEMORY |
| PA28F008SC-120 | BYTE-WIDE SmartVoltage FlashFile MEMORY FAMILY 4, 8, AND 16 MBIT |
| PA34 | POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS |
| PA44 | HIGH VOLTAGE POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PA28F008SA-L200 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:x8 Flash EEPROM |
| PA28F008SA-L250 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:x8 Flash EEPROM |
| PA28F008SC-120 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:BYTE-WIDE SmartVoltage FlashFile⑩ MEMORY FAMILY 4, 8, AND 16 MBIT |
| PA28F008SC-85 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:BYTE-WIDE SmartVoltage FlashFile⑩ MEMORY FAMILY 4, 8, AND 16 MBIT |
| PA28F016S5-120 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:BYTE-WIDE SMART 5 FlashFile MEMORY FAMILY 4, 8, AND 16 MBIT |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。