- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369919 > MJH6287 (MOTOROLA INC) DARLINGTON 20 AMPERE COMPLEMENTARY SILICON POWER TRANSISTORS 60, 80, 100 VOLTS 160 WATTS PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MJH6287 |
| 廠商: | MOTOROLA INC |
| 元件分類(lèi): | 功率晶體管 |
| 英文描述: | DARLINGTON 20 AMPERE COMPLEMENTARY SILICON POWER TRANSISTORS 60, 80, 100 VOLTS 160 WATTS |
| 中文描述: | 20 A, 100 V, PNP, Si, POWER TRANSISTOR, TO-218 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 3/6頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 209K |
| 代理商: | MJH6287 |
3
Motorola Bipolar Power Transistor Device Data
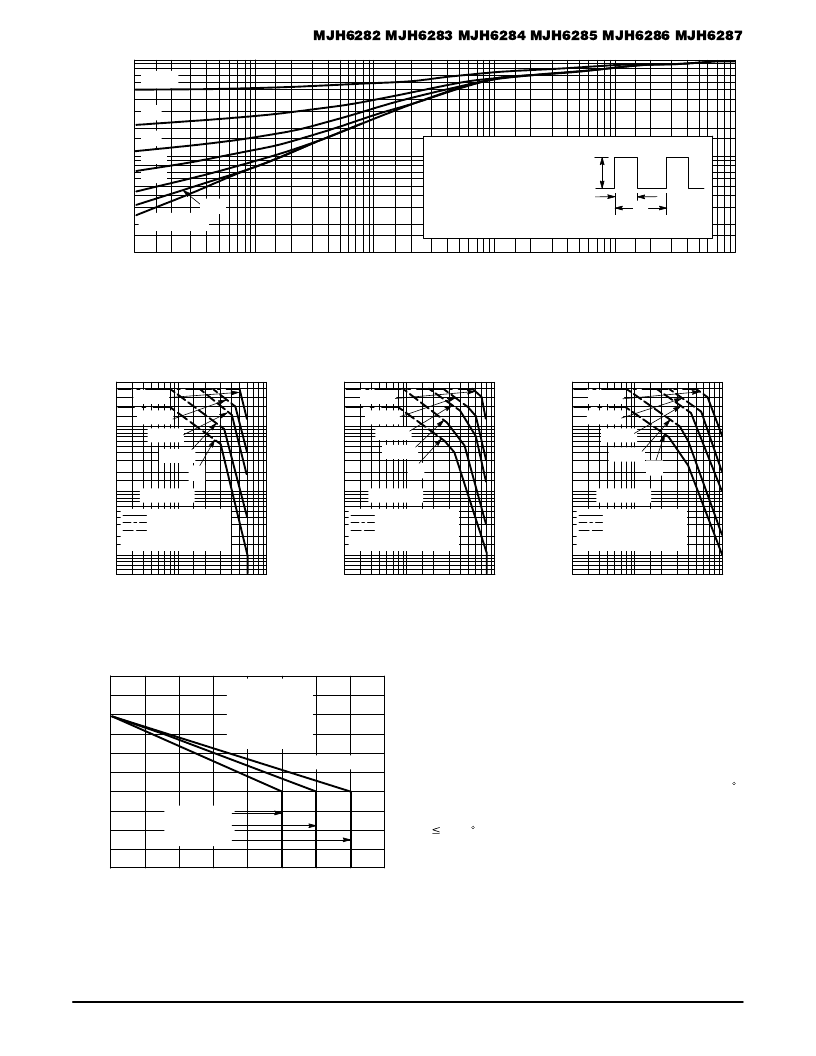
Figure 4. Thermal Response
t, TIME (ms)
1.0
0.7
0.5
0.01
0.03
0.2
0.1
0.07
0.05
0.02
r
0.05
1.0
3.0
5.0
10
30
50
100
300
500
R
θ
JC(t) = r(t) R
θ
JC
R
θ
JC = 0.78
°
C/W MAX
D CURVES APPLY FOR POWER
PULSE TRAIN SHOWN
READ TIME AT t1
TJ(pk) – TC = P(pk) R
θ
JC(t)
P(pk)
t1
t2
DUTY CYCLE, D = t1/t2
D = 0.5
SINGLE PULSE
0.1
0.5
0.2
R
1000
0.3
0.03
0.01
0.02
2.0
20
200
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
SECOND BREAKDOWN LIMIT
BONDING WIRE LIMITED
THERMAL LIMITATION
@ T
= 25
°
C
SINGLE PULSE
TJ = 150
°
C
0.5 ms
Figure 5. MJH6282, MJH6285
Figure 6. MJH6283, MJH6286
Figure 7. MJH6284, MJH6287
dc
VCE, COLLECTOR–EMITTER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
2.0
50
2.0
I
0.1
5.0
10
10
0.5
50
0.2
5.0
20
1.0
20
100
0.05
TJ = 150
°
C
dc
VCE, COLLECTOR–EMITTER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
2.0
50
2.0
I
0.1
5.0
10
10
0.5
50
0.2
5.0
20
1.0
20
100
0.05
TJ = 150
°
C
dc
VCE, COLLECTOR–EMITTER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
2.0
50
2.0
I
0.1
5.0
10
10
0.5
50
0.2
5.0
20
1.0
20
100
0.05
1.0 ms
5.0 ms
0.1 ms
0.5 ms
1.0 ms
5.0 ms
0.1 ms
0.5 ms
1.0 ms
5.0 ms
0.1 ms
SECOND BREAKDOWN LIMIT
BONDING WIRE LIMITED
THERMAL LIMITATION
@ T
= 25
°
C
SINGLE PULSE
SECOND BREAKDOWN LIMIT
BONDING WIRE LIMITED
THERMAL LIMITATION
@ T
= 25
°
C
SINGLE PULSE
FBSOA, FORWARD BIAS SAFE OPERATING AREA
VCE, COLLECTOR–EMITTER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
0
50
60
I
10
20
80
40
40
10
DUTY CYCLE = 10%
30
20
30
110
100
0
Figure 8. Maximum RBSOA, Reverse Bias
Safe Operating Area
L = 200
μ
H
IC/IB
≥
100
TC = 25
°
C
VBE(off) = 0–5.0 V
RBE = 47
MJH6282, 6285
MJH6283, 6286
MJH6284, 6287
FORWARD BIAS
There are two limitations on the power handling ability of a
transistor: average junction temperature and second break-
down. Safe operating area curves indicate IC – VCE limits of
the transistor that must be observed for reliable operation;
i.e., the transistor must not be subjected to greater dissipa-
tion than the curves indicate.
The data of Figure 5, 6 and 7 is based on TJ(pk) = 150 C;
TC is variable depending on conditions. Second breakdown
pulse limits are valid for duty cycles to 10% provided TJ(pk)
150 C. TJ(pk) may be calculated from the data in
Figure 4. At high case temperatures, thermal limitations will
reduce the power that can be handled to values less than the
limitations imposed by second breakdown.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MLED930 | Infrared LED |
| MLVS-0603 | This specification is applicable to Chip Metal Oxide Varistor in multilayer technology |
| MLVS0603K11 | This specification is applicable to Chip Metal Oxide Varistor in multilayer technology |
| MLVS0603K14 | This specification is applicable to Chip Metal Oxide Varistor in multilayer technology |
| MLVS0603L08 | This specification is applicable to Chip Metal Oxide Varistor in multilayer technology |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MJH62873601 | 制造商:LG Corporation 功能描述:SUPPORTER |
| MJH62873602 | 制造商:LG Corporation 功能描述:SUPPORTER |
| MJH62874201 | 制造商:LG Corporation 功能描述:SUPPORTER |
| MJH62874202 | 制造商:LG Corporation 功能描述:SUPPORTER |
| MJH62874301 | 制造商:LG Corporation 功能描述:SUPPORTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。