- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371014 > MC145193 (Motorola, Inc.) 1.1GHz PLL Frequency Synthesizer(1.1GHz PLL頻率合成器) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC145193 |
| 廠商: | Motorola, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | 1.1GHz PLL Frequency Synthesizer(1.1GHz PLL頻率合成器) |
| 中文描述: | 1.1GHz的鎖相環(huán)頻率合成器(1.1GHz的鎖相環(huán)頻率合成器) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 15/23頁 |
| 文件大小: | 269K |
| 代理商: | MC145193 |
MC145193
15
MOTOROLA WIRELESS SEMICONDUCTOR
SOLUTIONS – RF AND IF DEVICE DATA
ENB
CLK
Din
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MSB
LSB
R10
R9
R8
R7
R6
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
·
·
·
F
F
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
·
·
·
F
F
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
·
·
·
E
F
Not Allowed
R COUNTER =
÷
1 (Note 6)
Not Allowed
Not Allowed
Not Allowed
R COUNTER =
÷
5
R COUNTER =
÷
6
R COUNTER =
÷
7
R COUNTER =
÷
8
R COUNTER =
÷
8190
R COUNTER =
÷
8191
Hexadecimal Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
·
·
·
1
1
Binary Value
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Crystal Mode, Shut Down
Crystal Mode, Active
Reference Mode, REFin Enabled and REFout
Static Low
Reference Mode, REFout = REFin (Buffered)
Reference Mode, REFout = REFin/2
Reference Mode, REFout = REFin/4
Reference Mode, REFout = REFin/8 (Note 3)
Reference Mode, REFout = REFin/16
Octal Value
NOTES:
1
2
3
4
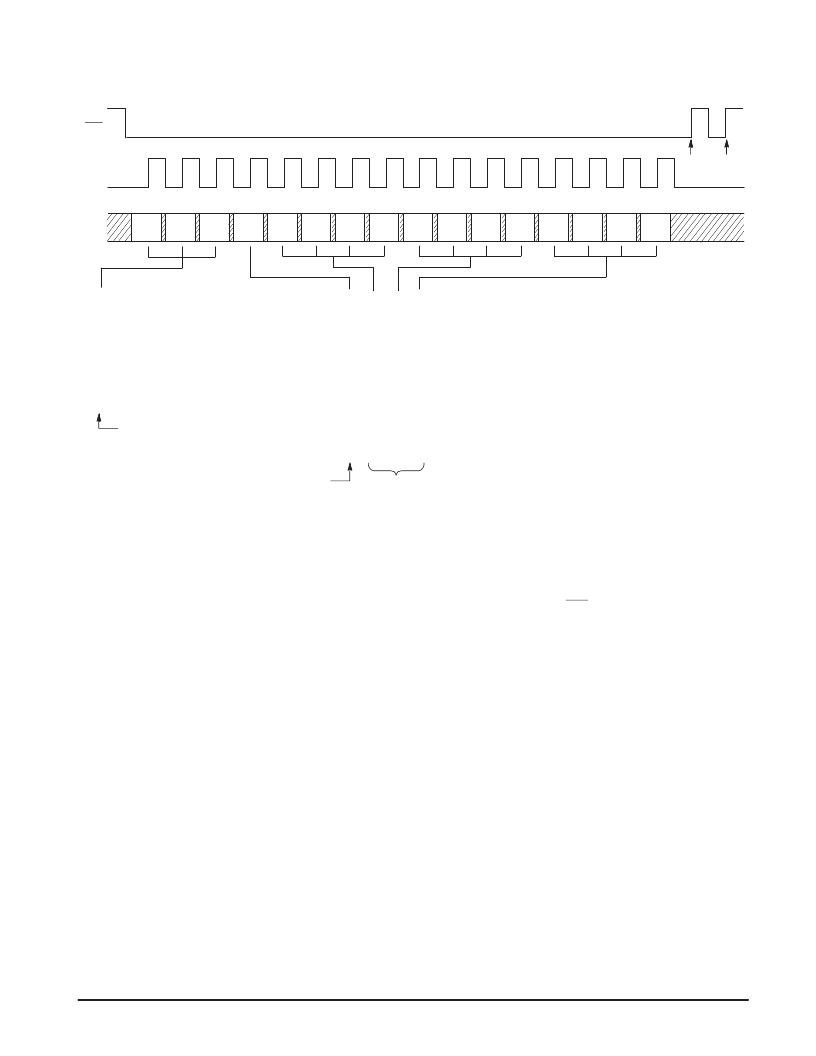
Bits R15 through R13 control the configurable “OSC or 4–stage divider” block (see Block Diagram).
Bits R12 through R0 control the “13–stage R counter” block (see Block Diagram).
A power–on initialize circuit forces a default REFin to REFout ratio of eight.
At this point, bits R13, R14, and R15 are stored and sent to the “OSC or 4–Stage Divider” block in the Block Diagram. Bits R0 – R12
are loaded into the first buffer in the double–buffered section of the R register. Therefore, the R counter divide ratio is not altered yet
and retains the previous ratio loaded. The C and A registers are not affected.
Optional load pulse. At this point, bits R0 – R12 are transferred to the second buffer of the R register. The R counter begins dividing
by the new ratio after completing the rest of the present count cycle. CLK must be low during the ENB pulse, as shown. The C and A
registers are not affected. The first buffer of the R register is not affected. Also, see Note 3 of Figure 15 for an alternate method of loading
the second buffer in the R register.
Allows direct access to reference input of phase/frequency detectors.
5
6
Note
4
Note
5
Figure 16. R Register Access and Format
(16 Clock Cycles are Used)
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC145202-1 | PLL Frequency Synthesizer(2.0GHz PLL頻率合成器) |
| MC145225 | Dual PLL Frequency Synthesizers With DACs and Voltage Multipliers(帶DACs和電壓乘法器的雙PLL頻率合成器) |
| MC145230 | Dual PLL Frequency Synthesizers With DACs and Voltage Multipliers(帶DACs和電壓乘法器的雙PLL頻率合成器) |
| MC14528BCL | Dual Monostable Multivibrator |
| MC14528 | DEFLECTION PROCESSOR FOR MULTISYNC MONITORS |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC14519BCL | 制造商:Motorola Inc 功能描述: 制造商:Motorola Inc 功能描述:LOGIC MUX, QUAD, 2-INPUT, CMOS, 16 Pin, Ceramic, DIP |
| MC14519BD | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC14519BF | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:IC |
| MC1451CCP | 制造商:PMD 功能描述: |
| MC14520B | 制造商:Motorola Inc 功能描述: 制造商:ON Semiconductor 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。