- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371885 > HS9-RTX2010RH-Q (INTERSIL CORP) Radiation Hardened Real Time Express⑩ Microcontroller PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HS9-RTX2010RH-Q |
| 廠商: | INTERSIL CORP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | Radiation Hardened Real Time Express⑩ Microcontroller |
| 中文描述: | 16-BIT, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQFP84 |
| 封裝: | CERAMIC, QFP-84 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/36頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 406K |
| 代理商: | HS9-RTX2010RH-Q |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當(dāng)前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁
11
RTX Data Buses and Address Buses
The RTX core bus architecture provides for unidirectional
data paths and simultaneous operation of some data buses.
This parallelism allows for maximum efficiency of data flow
internal to the core.
Addresses for accessing external (off-chip) memory or
ASIC devices are output via either the Memory Data Bus
(MA19-MA01) or the ASIC Address Bus (GA02-GA00). See
Table 3. External data is transferred by the ASIC Data Bus
(GD15-GD00) and the Memory Data Bus (MD15-MD00),
both of which are bidirectional.
RTX Internal Registers
The core of the HS-RTX2010RH is a macrocell available
through the Intersil Standard Cell Library. This core contains
eight 16-bit internal registers, which may be accessed
implicitly or explicitly, depending upon the register accessed
and the function being performed.
: The Top Register contains the top element of the
Parameter Stack++.
is the implicit data source or
destination for certain instructions, and has no ASIC address
assignment. The contents of this register may be directed to
any I/O device or to any processor register except the
Instruction Register.
is also the T input to the ALU.
Input to
must come through the ALU. This register
TOP
also holds the most significant 16 bits of 32-bit products and
32-bit dividends.
: The Next Register holds the second element of the
Parameter Stack.
is the implicit data source or
destination for certain instructions, and has no ASIC address
assignment. During a stack “push”, the contents of
are transferred to stack memory, and the contents of
are put into
. This register is used to hold the least
significant 16 bits of 32-bit products. Memory data is
accessed through
, as described in the Memory
Access section of this document.
: The Instruction Register is actually a latch which
contains the instruction currently being executed, and has no
ASIC address assignment. In certain instructions, an
operand can be embedded in the instruction code, making
the implicit source for that operand (as in the case of
short literals). Input to this register comes from Main
Memory (see Tables 6 thru 22 for code information).
: The Configuration Register is used to indicate and
control the current status/setup of the RTX microcontroller,
through the bit assignments shown in Figure 11. This
register is accessed explicitly through read and write
operations, which cause interrupts to be suppressed for one
cycle, guaranteeing that the next instruction will be
performed before an Interrupt Acknowledge cycle is allowed
to be performed.
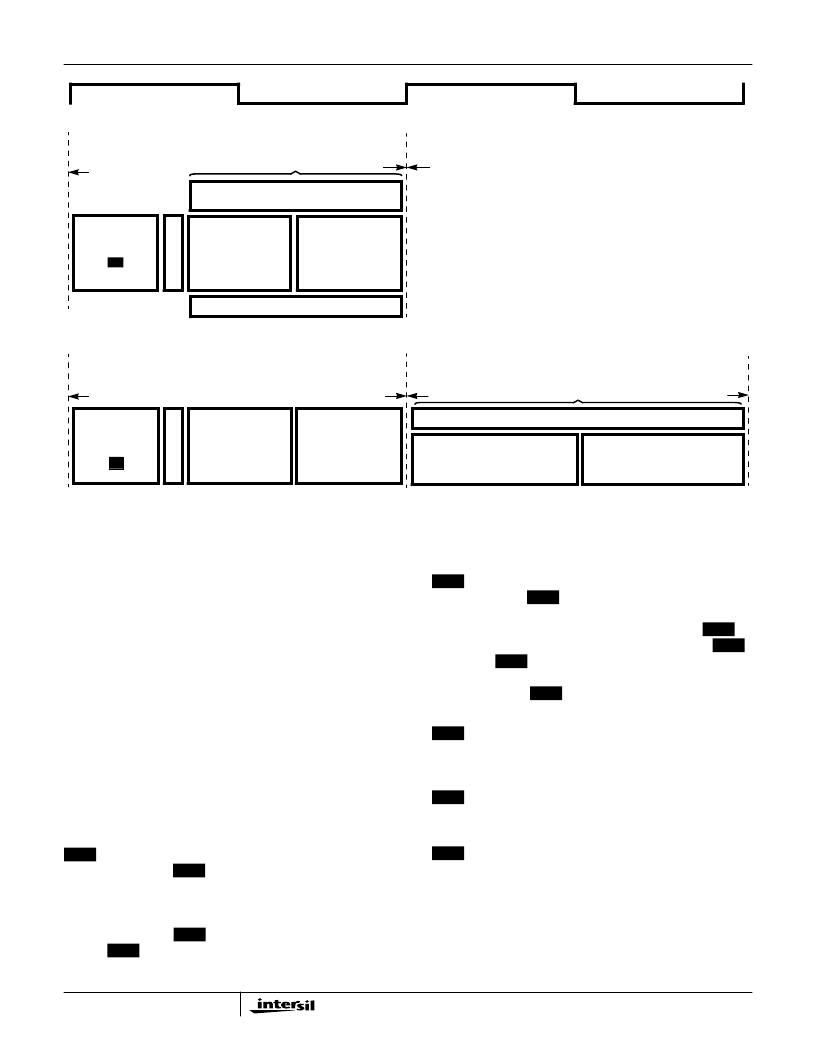
CYCLE
CLOCK
BEGIN
CONCURRENT
OPERATIONS
EXECUTION SEQUENCE WITH NO MEMORY DATA ACCESS:
EXECUTION SEQUENCE WITH MEMORY DATA ACCESS:
CYCLE
FIRST
END OF
FETCH
D
D
OPERATIONS
CONCURRENT
PCLK
MEMORY DATA
READ OR WRITE
PERFORM INTERNAL OPERATIONS AND
ALU OPERATIONS, AS REQUIRED
CYCLE
FIRST
END OF
CYCLE
CLOCK
BEGIN
CYCLE
CLOCK
BEGIN
ASIC BUS OPERATIONS
END OF
CLOCK
CYCLE
CYCLE
CLOCK
BEGIN
ADDRESS OF
MEMORY
LOCATION
IS PLACED ONTO
MA19-MA01
BUS
PLACE ADDRESS OF
NEXT INSTRUCTION
ONTO MA19-MA01
FETCH NEXT
INSTRUCTION
PERFORM ALU OPERATIONS
INSTRUCTION
LATCHES INTO
IR
ADDRESS OF
NEXT
INSTRUCTION
IS PLACED ONTO
MA19-MA01
BUS
INSTRUCTION
LATCHES
INTO
IR
FIGURE 10. INSTRUCTION EXECUTION SEQUENCE
TOP
TOP
TOP
NEXT
EXT
NEXT
TOP
NEXT
NEXT
IR
IR
CR
HS-RTX2010RH
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HS1-1412RH-Q | Radiation Hardened, Quad, High Speed, Low Power, Video Closed Loop Buffer |
| HS1B-1412RH-Q | Radiation Hardened, Quad, High Speed, Low Power, Video Closed Loop Buffer |
| HS-1412RH | Radiation Hardened, Quad, High Speed, Low Power, Video Closed Loop Buffer |
| HS1-1825ARH-8 | ER 2C 2#8 SKT RECP WALL |
| HS9-1825ARH-8 | Radiation Hardened High-Speed, Dual Output PWM |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HS9S-117RH/PROTO | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述: |
| HS9S-117RH-8 | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:REG STD LIN ADJ POS 1.2V TO 37V 1.25A 3PIN SOT-23 - Trays |
| HS9S-117RH-8S2740 | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:RADIATION HARDENED LINEAR VOLTAGE REGULATOR, CLASS Q, 36MDC, - Trays |
| HS9S-117RHPROTO | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Radiation Hardened Adjustable Positive Voltage Regulator |
| HS9S-117RH-Q | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:REG STD LIN ADJ POS 1.2V TO 37V 1.25A 3PIN SOT-23 - Trays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。