- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄300163 > ZL30316GKG2 (ZARLINK SEMICONDUCTOR INC) SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, PBGA256 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | ZL30316GKG2 |
| 廠商: | ZARLINK SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分類: | 通信及網(wǎng)絡(luò) |
| 英文描述: | SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, PBGA256 |
| 封裝: | 17 X 17 MM, 1 MM PITCH, MO-034B, TEBGA-256 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/5頁 |
| 文件大小: | 112K |
| 代理商: | ZL30316GKG2 |
ZL30316
Data Sheet
3
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
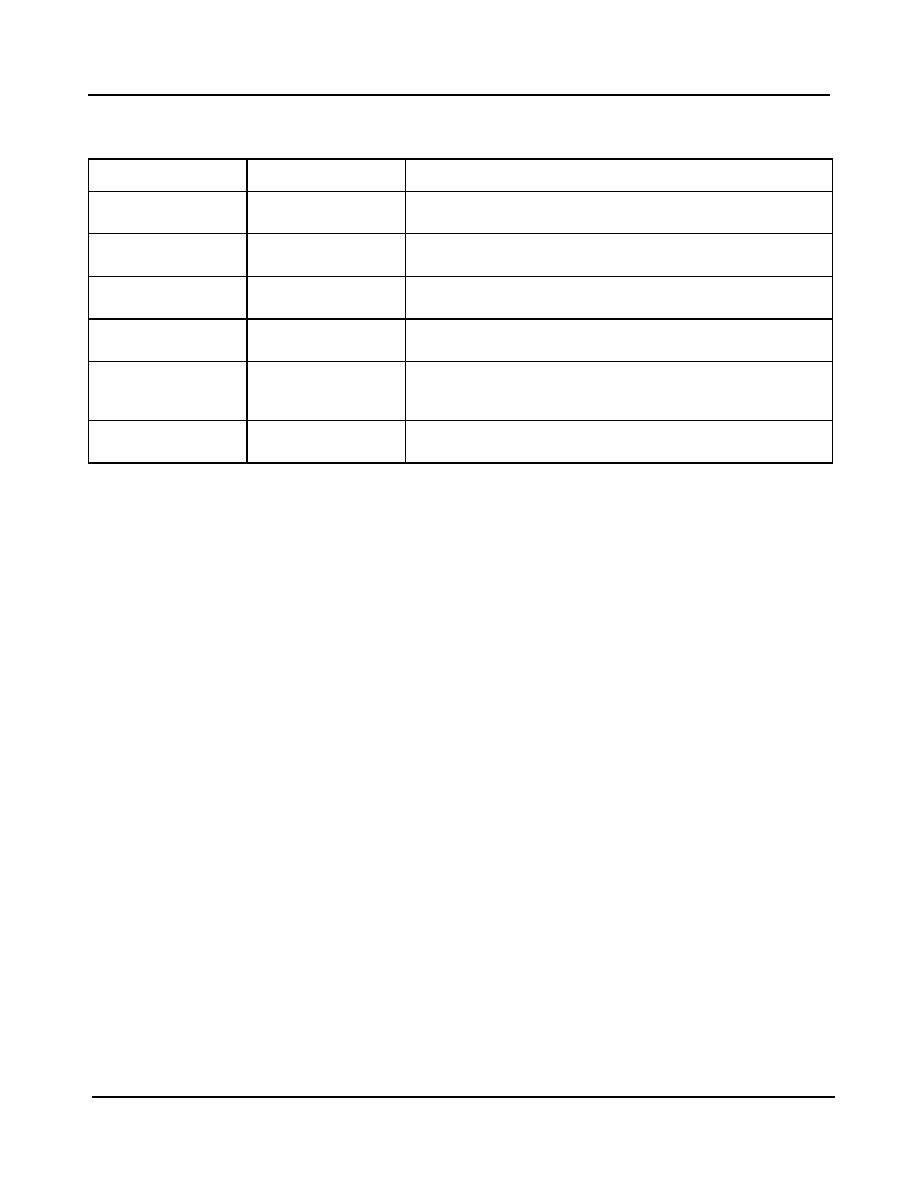
The Zarlink device offers the following clock routing options:
When operating as a server, the Zarlink device locks onto the incoming clock reference as a conventional PLL,
filtering any jitter that may be present. It also synchronizes to any low-frequency alignment signal, e.g., an 8 kHz
TDM frame pulse, or a 1 Hz alignment input. The device delivers streams of packets, each containing a timestamp
indicating the precise time that the packet was launched into the network, relative to the acquired reference. It also
receives packets from clients, and returns a message indicating the exact time that the client message was
received at the server. Using this information, clients are able to align their own timebase with that of the server.
As a client, the Zarlink device can track two independent servers, and determine which one is providing the best
time reference. If either the primary reference or the network between the server and client fails, the device can
switch to the alternative reference without introducing a phase discontinuity. Alternatively, the client can switch to a
conventional clock reference.
The solution timing recovery algorithm continuously tracks the frequency offset and phase drift between the clocks
located at the server and the client nodes connected via the packet switched network. The algorithm is tolerant of
lost packets, and of packet delay variation caused by packet queuing, route changes and other effects. In the event
of a failure in the packet network, or the advent of severe congestion preventing or seriously delaying the delivery of
timing packets, the device will put the recovered clocks into holdover until the flow of timing packets is restored.
When the device is in holdover mode the drift of the local oscillator directly affects the accuracy of the output clocks.
When using ToP technology, the device is designed to meet ANSI standard T1.101 and ITU-T standards G.823 and
G.824 for synchronization distribution. It maintains a mean frequency accuracy of better than ±10 ppb and time
alignment of better than ±1
μs when operated over a suitable network.
Input
Output
Description
clock reference
clock
conventional PLL behaviour,
e.g., Synchronous Ethernet node
clock reference
packet stream
server behaviour,
e.g., IEEE1588 server
clock reference
clock and/or packet
stream
conventional PLL behaviour coupled with packet time server,
e.g., combined Synchronous Ethernet and IEEE1588 server
packet reference
clock
client behaviour,
e.g., IEEE1588 client
clock and/or packet
reference
clock
conventional PLL behaviour, coupled with packet time client,
either as fail-over from one to the other, or in combination
e.g., combined Synchronous Ethernet and IEEE1588 client
packet reference
clock and/or packet
stream
combination of client and repeater behaviour,
e.g., IEEE1588 repeater
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ZL30316GKG | SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, PBGA256 |
| ZL30402/QCC1 | ATM/SONET/SDH SUPPORT CIRCUIT, PQFP80 |
| ZL30402/QCG1 | ATM/SONET/SDH SUPPORT CIRCUIT, PQFP80 |
| ZL50112GAG2 | SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, PBGA552 |
| ZL50112GAG | SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, PBGA552 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| ZL30320GKG | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:TIMING OVER PACKET AND SYNCHRONOUS ETHERNET DEVICE - Trays 制造商:MICROSEMI CONSUMER MEDICAL PRODUCT GROUP 功能描述:IC TIMING-OVER-PACKET 256TEBGA-2 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:IC TIMING-OVER-PACKET 256TEBGA-2 |
| ZL30320GKG2 | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:TIMING OVER PACKET AND SYNCHRONOUS ETHERNET DEVICE - Trays 制造商:MICROSEMI CONSUMER MEDICAL PRODUCT GROUP 功能描述:IC TIMING-OVER-PACKET 256TEBGA-2 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:IC TIMING-OVER-PACKET 256TEBGA-2 |
| ZL30321GGG | 制造商:MICROSEMI CONSUMER MEDICAL PRODUCT GROUP 功能描述:IC NETWORK SYNCHRONIZE 100LFBGA 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:IC NETWORK SYNCHRONIZE 100LFBGA |
| ZL30321GGG2 | 制造商:MICROSEMI CONSUMER MEDICAL PRODUCT GROUP 功能描述:IC NETWORK SYNCHRONIZE 100LFBGA 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:IC NETWORK SYNCHRONIZE 100LFBGA |
| ZL30342GGG | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:STRATUM 3 NETWORK - Bulk |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。