- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄372886 > XCS05XL-3CS240C (Xilinx, Inc.) Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XCS05XL-3CS240C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| 中文描述: | 斯巴達和Spartan - xL的家庭現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/66頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 809K |
| 代理商: | XCS05XL-3CS240C |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁
R
Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays
4-10
DS060 (v1.5) March 2, 2000
CLB Routing Channels
The routing channels around the CLB are derived from
three types of interconnects; single-length, double-length,
and longlines. At the intersection of each vertical and hori-
zontal routing channel is a signal steering matrix called a
Programmable Switch Matrix (PSM).
Figure 8
shows the
basic routing channel configuration showing single-length
lines, double-length lines and longlines as well as the CLBs
and PSMs. The CLB to routing channel interface is shown
as well as how the PSMs interface at the channel intersec-
tions.
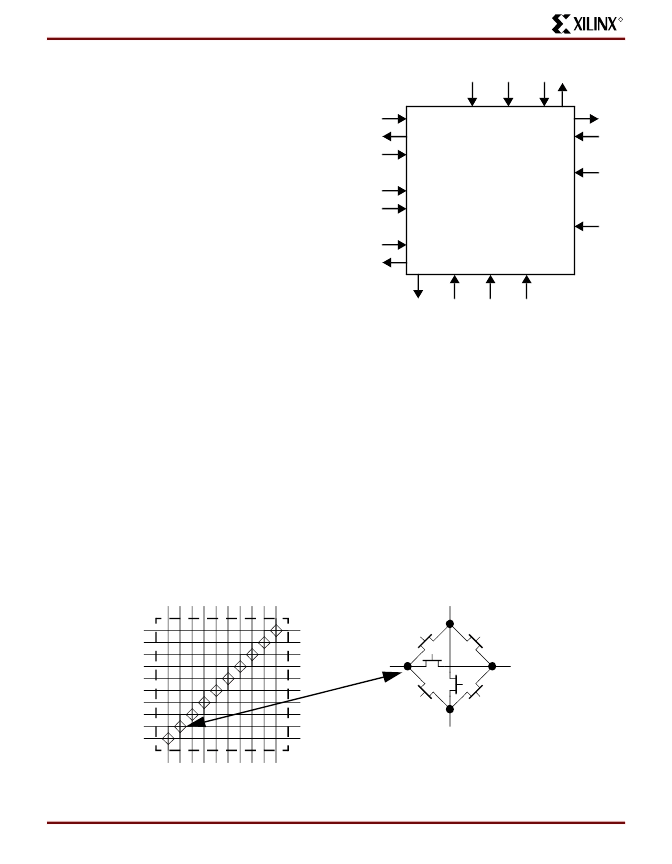
CLB Interface
A block diagram of the CLB interface signals is shown in
Figure 9
. The input signals to the CLB are distributed
evenly on all four sides providing maximum routing flexibil-
ity. In general, the entire architecture is symmetrical and
regular. It is well suited to established placement and rout-
ing algorithms. Inputs, outputs, and function generators can
freely swap positions within a CLB to avoid routing conges-
tion during the placement and routing operation. The
exceptions are the clock (K) input and CIN/COUT signals.
The K input is routed to dedicated global vertical lines as
well as four single-length lines and is on the left side of the
CLB. The CIN/COUT signals are routed through dedicated
interconnects which do not interfere with the general rout-
ing structure. The output signals from the CLB are available
to drive both vertical and horizontal channels.
Programmable Switch Matrices
The horizontal and vertical single- and double-length lines
intersect at a box called a programmable switch matrix
(PSM). Each PSM consists of programmable pass transis-
tors used to establish connections between the lines (see
Figure 10
).
For example, a single-length signal entering on the right
side of the switch matrix can be routed to a single-length
line on the top, left, or bottom sides, or any combination
thereof, if multiple branches are required. Similarly, a dou-
ble-length signal can be routed to a double-length line on
any or all of the other three edges of the programmable
switch matrix.
Single-Length Lines
Single-length lines provide the greatest interconnect flexi-
bility and offer fast routing between adjacent blocks. There
are eight vertical and eight horizontal single-length lines
associated with each CLB. These lines connect the switch-
ing matrices that are located in every row and column of
CLBs.
Figure 9: CLB Interconnect Signals
Rev 1.1
CLB
F
F3
G3
C3
Y
Y
C
C1
G1
F1
X
CIN
G
F
X
C
K
G
COUT
Figure 10: Programmable Switch Matrix
Six Pass Transistors Per
Switch Matrix Interconnect Point
Powered by ICminer.com Electronic-Library Service CopyRight 2003
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XCS05XL-3CS240I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS256C | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS256I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS280C | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS280I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCS05XL-3CS240I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS256C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS256I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS280C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05XL-3CS280I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。