- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4280 > XC2S200-6PQ208C (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 2.5V C-TEMP 208-PQFP PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XC2S200-6PQ208C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 33/99頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 2.5V C-TEMP 208-PQFP |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 24 |
| 系列: | Spartan®-II |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 1176 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 5292 |
| RAM 位總計: | 57344 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 140 |
| 門數(shù): | 200000 |
| 電源電壓: | 2.375 V ~ 2.625 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 208-BFQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 208-PQFP(28x28) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁當(dāng)前第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁
Spartan-II FPGA Family: Functional Description
DS001-2 (v2.8) June 13, 2008
Module 2 of 4
Product Specification
39
R
the LOC property is described below. Table 16 summarizes
the input standards compatibility requirements.
An optional delay element is associated with each IBUF.
When the IBUF drives a flip-flop within the IOB, the delay
element by default activates to ensure a zero hold-time
requirement. The NODELAY=TRUE property overrides this
default.
When the IBUF does not drive a flip-flop within the IOB, the
delay element de-activates by default to provide higher
performance. To delay the input signal, activate the delay
element with the DELAY=TRUE property.
IBUFG
Signals used as high fanout clock inputs to the
Spartan-II device should drive a global clock input buffer
(IBUFG) via an external input port in order to take
advantage of one of the four dedicated global clock
distribution networks. The output of the IBUFG primitive can
only drive a CLKDLL, CLKDLLHF, or a BUFG primitive. The
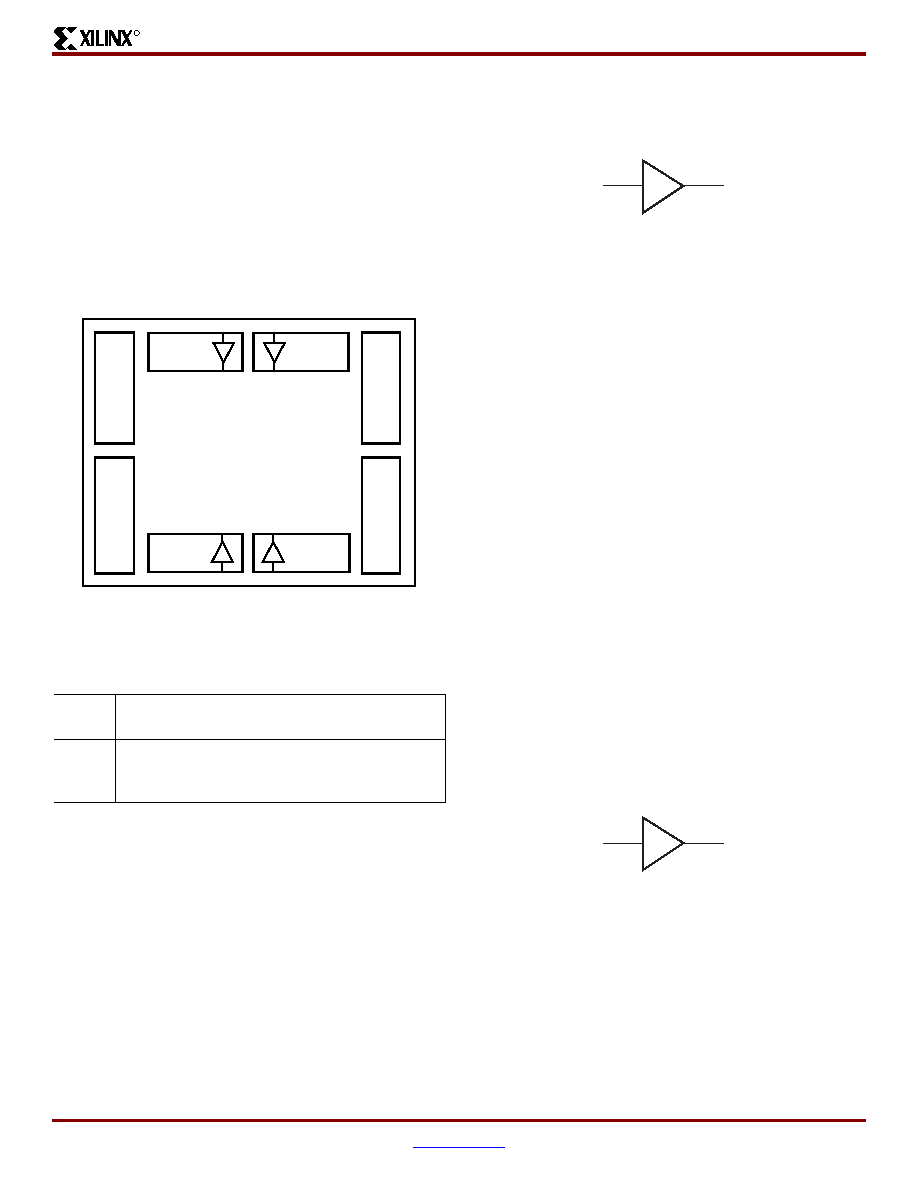
generic IBUFG primitive appears in Figure 37.
With no extension or property specified for the generic
IBUFG primitive, the assumed standard is LVTTL.
The voltage reference signal is "banked" within the
Spartan-II device on a half-edge basis such that for all
packages there are eight independent VREF banks
internally. See Figure 36 for a representation of the I/O
banks. Within each bank approximately one of every six I/O
pins is automatically configured as a VREF input.
IBUFG placement restrictions require any differential
amplifier input signals within a bank be of the same
standard. The LOC property can specify a location for the
IBUFG.
As an added convenience, the BUFGP can be used to
instantiate a high fanout clock input. The BUFGP primitive
represents a combination of the LVTTL IBUFG and BUFG
primitives, such that the output of the BUFGP can connect
directly to the clock pins throughout the design.
The Spartan-II FPGA BUFGP primitive can only be placed
in a global clock pad location. The LOC property can specify
a location for the BUFGP.
OBUF
An OBUF must drive outputs through an external output
port. The generic output buffer (OBUF) primitive appears in
With no extension or property specified for the generic
OBUF primitive, the assumed standard is slew rate limited
LVTTL with 12 mA drive strength.
The LVTTL OBUF additionally can support one of two slew
rate modes to minimize bus transients. By default, the slew
rate for each output buffer is reduced to minimize power bus
transients when switching non-critical signals.
Figure 36: I/O Banks
Table 16: Xilinx Input Standards Compatibility
Requirements
Rule 1
All differential amplifier input signals within a
bank are required to be of the same standard.
Rule 2
There are no placement restrictions for inputs
with standards that require a single-ended input
buffer.
DS001_03_060100
Bank 0
GCLK3
GCLK2
GCLK1
GCLK0
Bank 1
Bank 5
Bank 4
Spartan-II
Device
Bank
7
Bank
6
Bank
2
Bank
3
Figure 37: Global Clock Input Buffer (IBUFG) Primitive
Figure 38: Output Buffer (OBUF) Primitive
O
I
IBUFG
DS001_37_061200
O
I
OBUF
DS001_38_061200
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XC2S200-5PQ208I | IC FPGA 2.5V I-TEMP 208-PQFP |
| XCS30XL-4VQG100C | IC SPARTAN-XL FPGA 30K 100-VQFP |
| 5205817-3 | CONN FEMALE D-SUB SCREWLOCK KIT |
| XA6SLX16-2CSG324I | IC FPGA SPARTAN 6 14K 324CSGBGA |
| XA3S200-4FTG256Q | IC FPGA SPARTAN-3 200K 256-FTBGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XC2S200-6PQ208I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
| XC2S200-6PQG208C | 功能描述:IC SPARTAN-II FPGA 200K 208-PQFP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:Spartan®-II 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:60 系列:XP LAB/CLB數(shù):- 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):10000 RAM 位總計:221184 輸入/輸出數(shù):244 門數(shù):- 電源電壓:1.71 V ~ 3.465 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:0°C ~ 85°C 封裝/外殼:388-BBGA 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:388-FPBGA(23x23) 其它名稱:220-1241 |
| XC2S200-6PQG208I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
| XC2S200-6TQ144C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
| XC2S200-6TQ144I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。