- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄25635 > MR80C52CXXX-12/883:D (TEMIC SEMICONDUCTORS) 8-BIT, MROM, 12 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MR80C52CXXX-12/883:D |
| 廠商: | TEMIC SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 12 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/125頁 |
| 文件大小: | 6456K |
第1頁第2頁當(dāng)前第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁
11
2486AA–AVR–02/2013
ATmega8(L)
Arithmetic Logic
Unit – ALU
The high-performance Atmel
AVR ALU operates in direct connection with all the 32 general
purpose working registers. Within a single clock cycle, arithmetic operations between general
purpose registers or between a register and an immediate are executed. The ALU operations
are divided into three main categories – arithmetic, logical, and bit-functions. Some implementa-
tions of the architecture also provide a powerful multiplier supporting both signed/unsigned
multiplication and fractional format. For a detailed description, see “Instruction Set Summary” on
Status Register
The Status Register contains information about the result of the most recently executed arithme-
tic instruction. This information can be used for altering program flow in order to perform
conditional operations. Note that the Status Register is updated after all ALU operations, as
specified in the Instruction Set Reference. This will in many cases remove the need for using the
dedicated compare instructions, resulting in faster and more compact code.
The Status Register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt routine and restored
when returning from an interrupt. This must be handled by software.
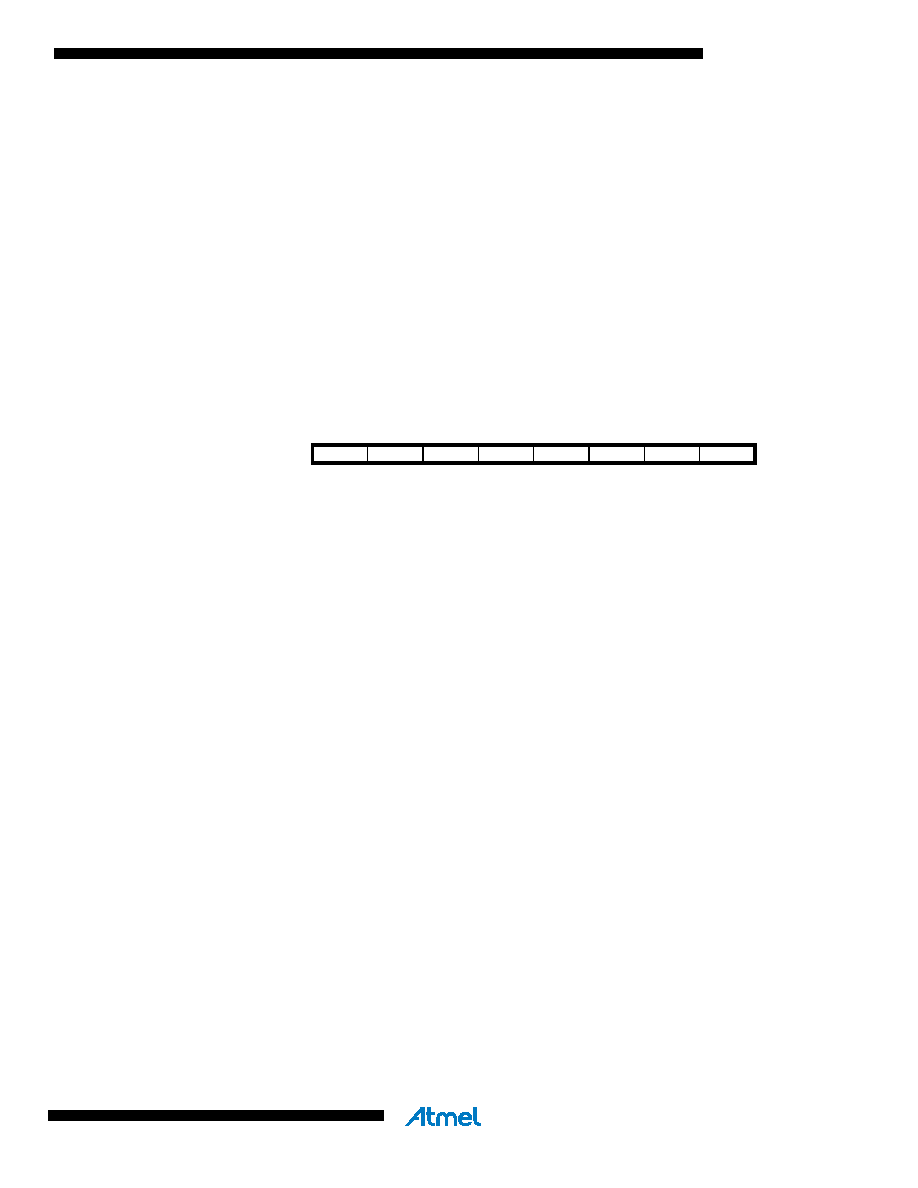
The AVR Status Register – SREG – is defined as:
Bit 7 – I: Global Interrupt Enable
The Global Interrupt Enable bit must be set for the interrupts to be enabled. The individual inter-
rupt enable control is then performed in separate control registers. If the Global Interrupt Enable
Register is cleared, none of the interrupts are enabled independent of the individual interrupt
enable settings. The I-bit is cleared by hardware after an interrupt has occurred, and is set by
the RETI instruction to enable subsequent interrupts. The I-bit can also be set and cleared by
the application with the SEI and CLI instructions, as described in the Instruction Set Reference.
Bit 6 – T: Bit Copy Storage
The Bit Copy instructions BLD (Bit LoaD) and BST (Bit STore) use the T-bit as source or desti-
nation for the operated bit. A bit from a register in the Register File can be copied into T by the
BST instruction, and a bit in T can be copied into a bit in a register in the Register File by the
BLD instruction.
Bit 5 – H: Half Carry Flag
The Half Carry Flag H indicates a Half Carry in some arithmetic operations. Half Carry is useful
in BCD arithmetic. See the “Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
Bit 4 – S: Sign Bit, S = N
V
The S-bit is always an exclusive or between the Negative Flag N and the Two’s Complement
Overflow Flag V. See the “Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
Bit 3 – V: Two’s Complement Overflow Flag
The Two’s Complement Overflow Flag V supports two’s complement arithmetics. See the
“Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
Bit 2 – N: Negative Flag
The Negative Flag N indicates a negative result in an arithmetic or logic operation. See the
“Instruction Set Description” for detailed information.
Bit
765
432
1
0
I
T
H
S
V
N
Z
C
SREG
Read/Write
R/W
Initial Value
0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC80C52EXXX-12SC | 8-BIT, MROM, 12 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 |
| MD80C52TXXX-16SHXXX:D | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 |
| MR80C52CXXX-12SCR | 8-BIT, MROM, 12 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 |
| MQ80C52XXX-25 | 8-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQFP44 |
| MD80C52EXXX-20SB | 8-BIT, MROM, 20 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MR80C86 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:CMOS 16-Bit Microprocessor |
| MR80C86/B | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述:Microprocessor, 16 Bit, 44 Pin, Ceramic, LCC |
| MR80C86-2 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:CMOS 16-Bit Microprocessor |
| MR80C86-2/883 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MR80C86-2/B | 制造商:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:MPU 80C86 16BIT CMOS 8MHZ 44PLCC - Rail/Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。