- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370955 > M38867M8A-A04HP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M38867M8A-A04HP |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片8位CMOS微機(jī) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 33/110頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1601K |
| 代理商: | M38867M8A-A04HP |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)當(dāng)前第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)
33
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
Data Setup (PWM0)
The PWM0 output pin also functions as port P3
0
or P5
6
. The
PWM0 output pin is selected from either P3
0
/PWM
00
or
P5
6
/PWM
01
by bit 4 of the AD/DA control register (address
0034
16
).
The PWM0 output becomes enabled state by setting bit 6 of the
port control register 1 (address 002E
16
). The high-order eight bits
of output data are set in the PWM0H register (address 0030
16
)
and the low-order six bits are set in the PWM0L register (address
0031
16
).
PWM1 is set as the same way.
PWM Operation
The 14-bit PWM data is divided into the low-order six bits and the
high-order eight bits in the PWM latch.
The high-order eight bits of data determine how long an “H”-level
signal is output during each sub-period. There are 64 sub-periods
in each period, and each sub-period is 256
τ
(64
μ
s) long. The
signal is “H” for a length equal to N times
τ
, where
τ
is the mini-
mum resolution (250 ns).
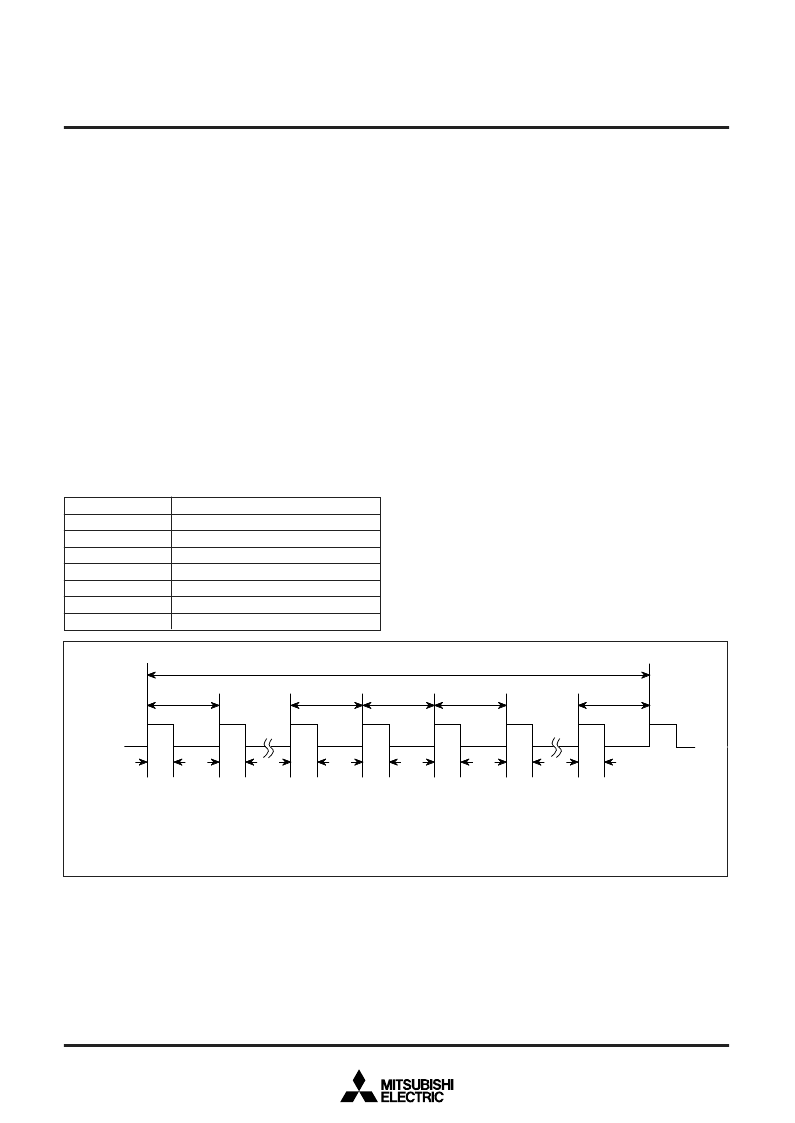
“H” or “L” of the bit in the ADD part shown in Figure 30 is added to
this “H” duration by the contents of the low-order 6-bit data accord-
ing to the rule in Table 7.
That is, only in the sub-period tm shown by Table 7 in the PWM
cycle period T = 64t, its “H” duration is lengthened to the minimum
resolution
τ
added to the length of other periods.
For example, if the high-order eight bits of the 14-bit data are 03
16
and the low-order six bits are 05
16
, the length of the “H”-level out-
put in sub-periods t
8
, t
24
, t
32
, t
40
, and t
56
is 4
τ
, and its length is 3
τ
in all other sub-periods.
Time at the “H” level of each sub-period almost becomes equal,
because the time becomes length set in the high-order 8 bits or
becomes the value plus
τ
, and this sub-period t (= 64
μ
s, approxi-
mate 15.6 kHz) becomes cycle period approximately.
Transfer From Register to Latch
Data written to the PWML register is transferred to the PWM latch
at each PWM period (every 4096
μ
s), and data written to the
PWMH register is transferred to the PWM latch at each sub-period
(every 64
μ
s). The signal which is output to the PWM output pin is
corresponding to the contents of this latch. When the PWML regis-
ter is read, the latch contents are read. However, bit 7 of the
PWML register indicates whether the transfer to the PWM latch is
completed; the transfer is completed when bit 7 is “0” and it is not
done when bit 7 is “1.”
Table 7 Relationship between low-order 6 bits of data and
period set by the ADD bit
Low-order 6 bits of data (PWML)
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
Sub-periods tm Lengthened (m=0 to 63)
None
m=32
m=16, 48
m=8, 24, 40, 56
m=4, 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, 52, 60
m=2, 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 54, 58, 62
m=1, 3, 5, 7, ................................................ ,57, 59, 61, 63
Fig. 30 PWM timing
4
0
9
6
μ
s
6
4
μ
s
6
4
μ
s
m
=
6
4
m
μ
s
=
6
4
m
μ
s
=
6
4
m
μ
s
=
m
=
0
7
9
6
3
8
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
1
6
.
0
μ
s
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
1
5
.
7
5
μ
s
P
P
S
S
u
l
l
b
b
s
s
e
e
-
p
-
p
w
w
e
e
i
i
i
i
d
d
o
o
t
t
d
d
h
h
m
m
w
w
o
o
h
h
d
d
e
e
u
u
r
r
l
l
e
e
a
a
t
t
“
“
i
i
H
H
o
o
n
n
”
”
p
p
r
r
e
e
u
u
g
g
l
s
l
s
i
i
s
s
e
e
t
t
e
e
w
w
r
r
i
i
d
d
H
L
t
t
u
u
u
r
r
s
s
h
h
i
i
s
s
1
1
6
5
.
.
0
7
μ
s
5
μ
s
:
:
:
:
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
m
m
=
=
8
a
,
l
l
2
o
4
t
,
h
3
e
2
r
,
v
4
a
0
l
u
,
e
5
s
6
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M38867M8A-A06HP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38867M8A-A07HP | connectors |
| M38867M8A-A11HP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38869FFAHP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38869M8A-XXXGP | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M38867M8A-A06HP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38867M8A-A07HP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38867M8A-A11HP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38867M8A-XXXHP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38867M8-XXXHP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。