- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371810 > HGT1S3N60A4S (INTERSIL CORP) 600V, SMPS Series N-Channel IGBT PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | HGT1S3N60A4S |
| 廠商: | INTERSIL CORP |
| 元件分類: | IGBT 晶體管 |
| 英文描述: | 600V, SMPS Series N-Channel IGBT |
| 中文描述: | 17 A, 600 V, N-CHANNEL IGBT, TO-263AB |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/10頁 |
| 文件大小: | 156K |
| 代理商: | HGT1S3N60A4S |
7
Handling Precautions for IGBTs
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors are susceptible to gate-
insulation damage by the electrostatic discharge of energy
through the devices. When handling these devices, care
should be exercised to assure that the static charge built in
the handler’s body capacitance is not discharged through
the device. With proper handling and application procedures,
however, IGBTs are currently being extensively used in
production by numerous equipment manufacturers in
military, industrial and consumer applications, with virtually
no damage problems due to electrostatic discharge. IGBTs
can be handled safely if the following basic precautions are
taken:
1. Prior to assembly into a circuit, all leads should be kept
shorted together either by the use of metal shorting
springs or by the insertion into conductive material such
as “ECCOSORBD LD26” or equivalent.
2. When devices are removed by hand from their carriers,
the hand being used should be grounded by any suitable
means - for example, with a metallic wristband.
3. Tips of soldering irons should be grounded.
4. Devices should never be inserted into or removed from
circuits with power on.
5.
Gate Voltage Rating
- Never exceed the gate-voltage
rating of V
GEM
. Exceeding the rated V
GE
can result in
permanent damage to the oxide layer in the gate region.
6.
Gate Termination
- The gates of these devices are
essentially capacitors. Circuits that leave the gate open-
circuited or floating should be avoided. These conditions
can result in turn-on of the device due to voltage buildup
on the input capacitor due to leakage currents or pickup.
7.
Gate Protection
- These devices do not have an internal
monolithic Zener diode from gate to emitter. If gate
protection is required an external Zener is recommended.
Operating Frequency Information
Operating frequency information for a typical device
(Figure 3) is presented as a guide for estimating device
performance for a specific application. Other typical
frequency vs collector current (I
CE
) plots are possible using
the information shown for a typical unit in Figures 6, 7, 8, 9
and 11. The operating frequency plot (Figure 3) of a typical
device shows f
MAX1
or f
MAX2
; whichever is smaller at each
point. The information is based on measurements of a
typical device and is bounded by the maximum rated
junction temperature.
f
MAX1
is defined by f
MAX1
= 0.05/(t
d(OFF)I
+ t
d(ON)I
).
Deadtime (the denominator) has been arbitrarily held to 10%
of the on-state time for a 50% duty factor. Other definitions
are possible. t
d(OFF)I
and t
d(ON)I
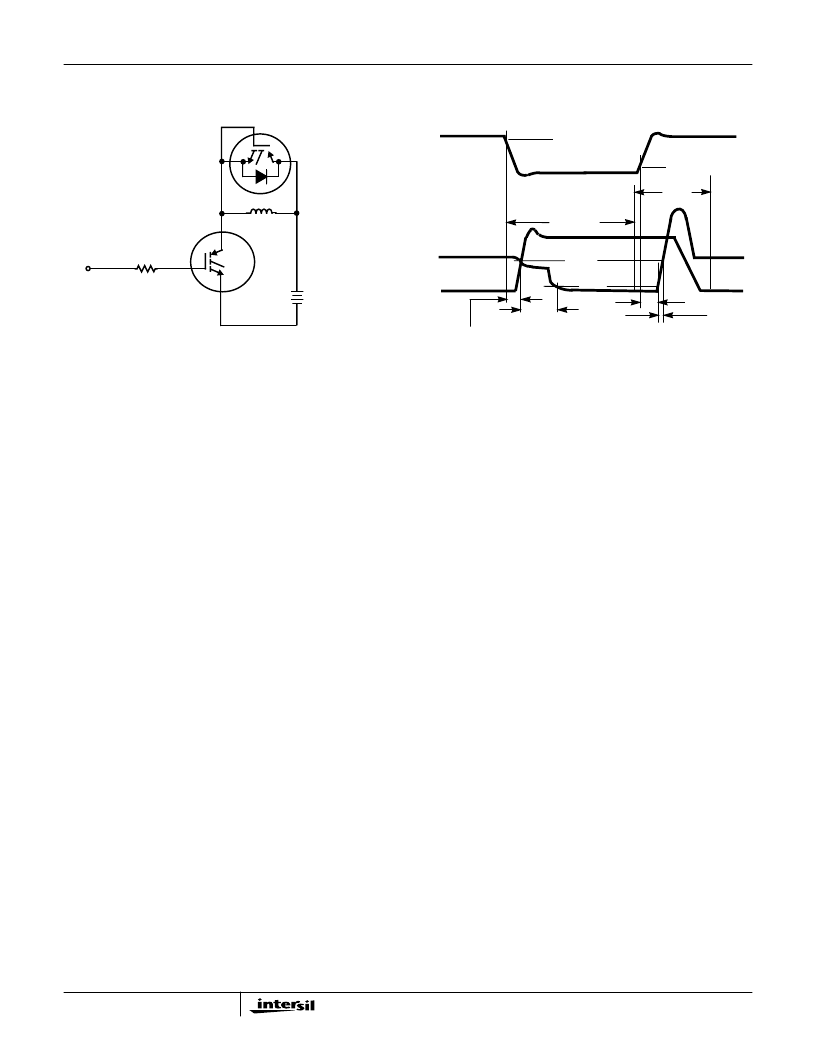
are defined in Figure 21.
Device turn-off delay can establish an additional frequency
limiting condition for an application other than T
JM
.
f
MAX2
is defined by f
MAX2
= (P
D
- P
C
)/(E
OFF
+ E
ON2
). The
allowable dissipation (P
D
) is defined by P
D
= (T
JM
- T
C
)/R
θ
JC
.
The sum of device switching and conduction losses must not
exceed P
D
. A 50% duty factor was used (Figure 3) and the
conduction losses (P
C
) are approximated by P
C
= (V
CE
x
I
CE
)/2.
E
ON2
and E
OFF
are defined in the switching waveforms
shown in Figure 21. E
ON2
is the integral of the
instantaneous power loss (I
CE
x V
CE
) during turn-on and
E
OFF
is the integral of the instantaneous power loss (I
CE
x
V
CE
) during turn-off. All tail losses are included in the
calculation for E
OFF
; i.e., the collector current equals zero
(I
CE
= 0).
Test Circuit and Waveforms
FIGURE 20. INDUCTIVE SWITCHING TEST CIRCUIT
FIGURE 21. SWITCHING TEST WAVEFORMS
R
G
= 50
L = 1mH
V
DD
= 390V
+
-
HGTP3N60A4D
DIODE TA49369
DUT
t
fI
t
d(OFF)I
t
rI
t
d(ON)I
10%
90%
10%
90%
V
CE
I
CE
V
GE
E
OFF
E
ON2
I
CE
HGTD3N60A4S, HGT1S3N60A4S, HGTP3N60A4
ECCOSORBD is a trademark of Emerson and Cumming, Inc.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HGTP3N60B3 | 7A, 600V, UFS Series N-Channel IGBTs |
| HGTP3N60A4 | 600V, SMPS Series N-Channel IGBT |
| HGTP3N60A4D | 600V, SMPS Series N-Channel IGBT with Anti-Parallel Hyperfast Diode |
| HGTP3N60C3 | 72 MACROCELL 3.3 VOLT ISP CPLD |
| HGTP3N60A4D9A | 600V, SMPS Series N-Channel IGBT with Anti-Parallel Hyperfast Diode |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HGT1S3N60A4S9A | 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation 功能描述: |
| HGT1S3N60B3DS | 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| HGT1S3N60B3DS9A | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:TRANSISTOR | IGBT | N-CHAN | 600V V(BR)CES | 3.5A I(C) | TO-263AB |
| HGT1S3N60B3S | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| HGT1S3N60B3S9A | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:TRANSISTOR | IGBT | N-CHAN | 600V V(BR)CES | 3.5A I(C) | TO-263AB |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。