- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄375931 > FSD1000 (FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) Combo Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | FSD1000 |
| 廠商: | FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | Combo Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) |
| 中文描述: | 1.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 73 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDIP12 |
| 封裝: | HEAT SINK/SLUG, DIP-12 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 9/20頁 |
| 文件大小: | 375K |
| 代理商: | FSD1000 |
FSD1000
9
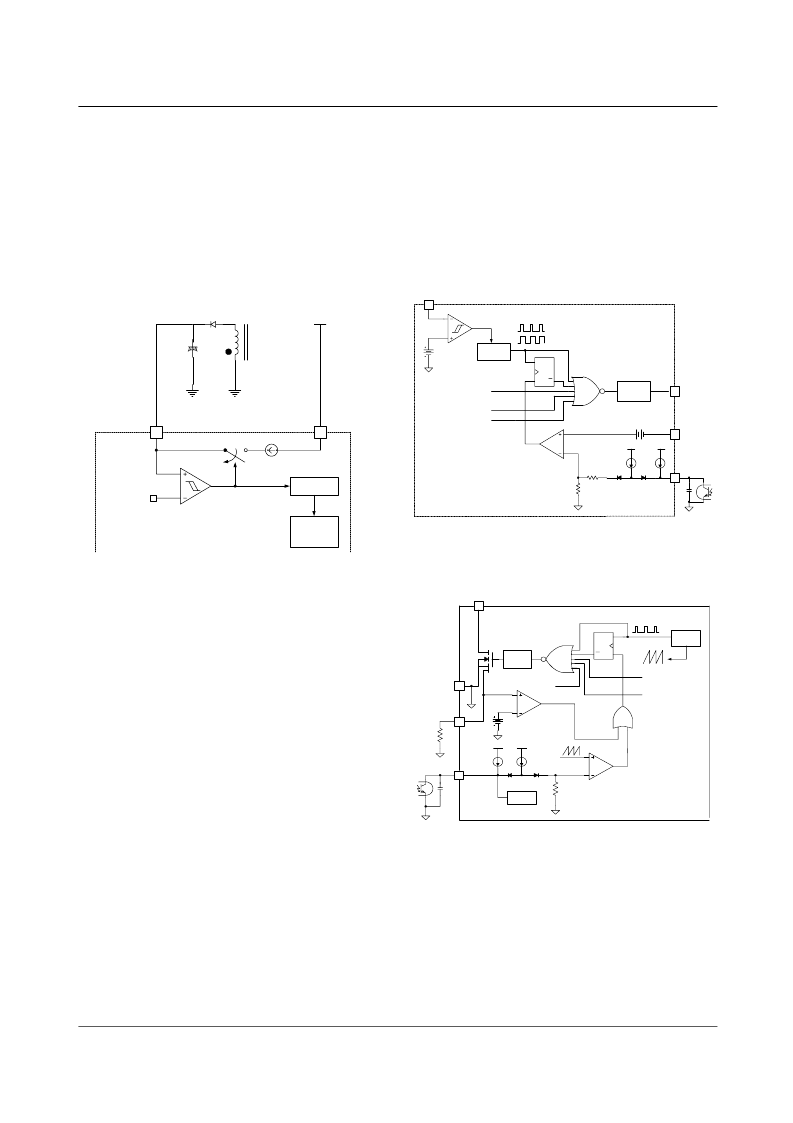
Functional Description
Startup
: At startup, an internal high voltage current
source supplies the internal bias and charges the external
capacitor that is connected to the Vcc pin as illustrated in
figure 4. When Vcc reaches 13.5 V, the FPS begins switching
operation and the internal high voltage current source is
disabled. Then, the FPS continues its normal switching
operation unless Vcc goes below the stop voltage of 9.5 V
and the power is supplied from the auxiliary transformer
winding. Once the auxiliary power starts up, the main power
starts up with a time delay of 30ms.
1.
Figure 4. Internal startup circuit
2. Feedback Control
: FSD1000 has two PWM controllers
in a single package; one is for the main power and the other
is for the auxiliary power. The PWM block for the main
controls the external MOSFET, while the PWM block for the
auxiliary power controls the internal SenseFET.
2.1 Feedback Control for the main power
: Figure 5
illustrates the simplified PWM block for the main power.
The current mode control is employed for the main power.
The voltage of the feedback pin is compared with the current
sense voltage for pulse width modulation (PWM). As shown
in figure 5, the feedback voltage determines the peak value
of the drain current of the external power MOSFET for main
power. Usually opto-coupler is used to implement feedback
network. The collector of the opto-coupler transistor is
connected to feedback pin and the emitter is connected to the
ground pin. For stable operation, a capacitor should be
placed between this pin and GND.
2.2 Feedback Control for the auxiliary power
: Figure 6
shows the internal high voltage SenseFET together with
PWM block for auxiliary power. Auxiliary power employs
voltage mode control and the feedback pin voltage is
compared with internal ramp signal for pulse width
modulation (PWM). The pulse-by-pulse current limit level of
the SenseFET is programmed by an external resistor on the
I
LIM
pin. Since the sense ratio is 1/110 and the reference
voltage of the comparator is 0.3V, the pulse-by-pulse current
limit level (I
CL
) is given by
Figure 5. PWM control block for the main power
Figure 6. PWM control block for the auxiliary power
3. Protection Circuit
: Besides pulse-by-pulse current limit,
FSD1000 has various self protection functions; over load
protections (OLP) for main and auxiliary powers, over
voltage protection (OVP), line over/under voltage lockout
and over temperature protection (OTP). Because these
protection circuits are fully integrated into the IC without
external components, the reliability can be improved. In the
event of fault conditions such as OLP of auxiliary power and
9.5V/13.5V
3
Vref
Internal
Bias
Vcc
6
Vstr
I
start
Vcc good
DC link
voltage
I
CL
------------------------
R
LIM
=
A
( )
6
S
Q
Q
R
Isense
Gate
drive
4 Output
I
delay
I
FB
2
V
FB.MAIN
Vcc
Vcc
PWM
Comparator
R
3R
OSC
5
Max duty
control
2.0 V
2.4 V
LS2
C
FB
D1
D2
4
11
OSC
I
delay
I
FB
R
V
FB,AUX
Soft start
9
S
Q
Q
R
Gate
drive
Burst
OSC
Drain
GND
I
LIM
Vref
Vref
1/110
0.3V
C
FB
D1
D2
R
LIM
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| FSD200B | Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) |
| FSD200BM | Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) |
| FSD210B | Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) |
| FSD210BM | Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) |
| FSD270 | SILICON DUAL VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| FSD-10A | 制造商:OPTIFUSE 功能描述: |
| FSD146MRBN | 功能描述:軟開關(guān) PWM 控制器 SER BOOST LED DRVR RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 輸出端數(shù)量: 輸出電流: 開關(guān)頻率: 工作電源電壓:30 V 電源電流: 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 封裝:Reel |
| FSD156MRBN | 功能描述:軟開關(guān) PWM 控制器 SER BOOST LED DRVR RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 輸出端數(shù)量: 輸出電流: 開關(guān)頻率: 工作電源電壓:30 V 電源電流: 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 封裝:Reel |
| FSD-15A | 制造商:OPTIFUSE 功能描述: |
| FSD176MRT | 制造商:FAIRCHILD 制造商全稱:Fairchild Semiconductor 功能描述:Green-Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPSa?¢) |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。