- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄24826 > 935263156557 (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) 8-BIT, FLASH, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 935263156557 |
| 廠商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, FLASH, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, QFP-80 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/76頁 |
| 文件大小: | 567K |
| 代理商: | 935263156557 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
P83C557E4/P80C557E4/P89C557E4
Single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1999 Mar 02
18
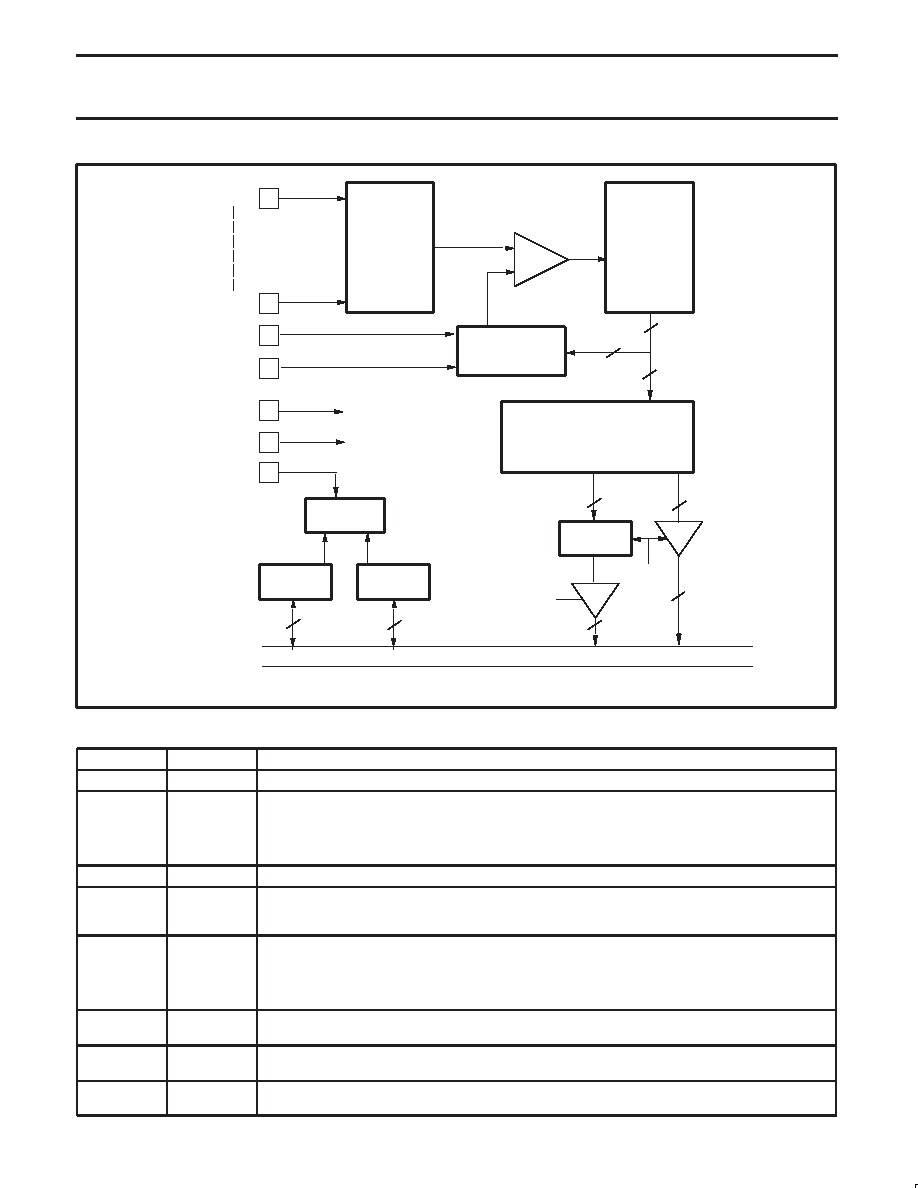
Figure 15. Functional diagram of AD converter.
+
–
88
8
2
10
COMPARATOR
SAR
DAC
8x
10–bit result
registers
SCAN LOGIC
ADPSS
ADCON
2 LATCHES
Read
ADRSH
Read
ADRSLn
ANALOG
Mux.
ADC0
ADC7
AVref+
AVref–
AVDD1
AVSS1
ADEXS
INTERNAL BUS
Table 10.
Description of ADCON bits
SYMBOL
BIT
FUNCTION
ADCON.7
ADPR1
Control bit for the prescaler.
ADCON.6
ADPR0
Control bit for the prescaler.
ADPR1=0 ADPR0=0 Prescaler divides by 2 (default by reset)
ADPR1=0 ADPR0=1 Prescaler divides by 4
ADPR1=1 ADPR0=0 Prescaler divides by 6
ADPR1=1 ADPR0=1 Prescaler divides by 8
ADCON.5
ADPOS
ADPOS is reserved for future use. Must be ’0’ if ADCON is written.
ADCON.4
ADINT
ADC interrupt flag. This flag is set when all selected analog inputs are converted, as well in continuous
scan as in one-time scan mode. An interrupt is invoked if this interrupt is enabled. ADINT must be cleared
by software. It cannot be set by software.
ADCON.3
ADSST
ADC start and status. Setting this bit by software or by hardware (via ADEXS input) starts the A/D
conversion of the selected analog inputs. ADSST stays a ‘one’ in continuous scan mode. In one-time scan
mode, ADSST is cleared by hardware when the last selected analog input channel has been converted. As
long as ADSST is ’1’, new start commands to the ADC-block are ignored.
An A/D conversion in progress is aborted if ADSST is cleared by software.
ADCON.2
ADCSA
1
=
Continuous scan of the selected analog inputs after a start of an A/D conversion.
0
=
One-time scan of the selected analog inputs after a start of an A/D conversion.
ADCON.1
ADSRE
1
=
A rising edge at input ADEXS will start the A/D conversion and generate a capture signal.
0
=
A rising edge at input ADEXS has no effect.
ADCON.0
ADSFE
1
=
A falling edge at input ADEXS will start the A/D conversion and generate a capture signal.
0
=
A falling edge at input ADEXS has no effect.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 935263261557 | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 935263206557 | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 935268065557 | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 935263263557 | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 935263262557 | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 935264217557 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:SUB ONLY IC |
| 935267356112 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:IC TEA1507PN |
| 935268081112 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:SUB ONLY IC |
| 935268721125 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Buffer/Line Driver 1-CH Non-Inverting 3-ST CMOS 5-Pin TSSOP T/R |
| 935269304128 | 制造商:ST-Ericsson 功能描述:IC AUDIO CODEC W/TCH SCRN 48LQFP |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。