- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4224 > XCV400E-8PQ240C (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 1.8V C-TEMP 240-PQFP PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XCV400E-8PQ240C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 46/233頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 1.8V C-TEMP 240-PQFP |
| 產(chǎn)品變化通告: | FPGA Family Discontinuation 18/Apr/2011 |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | Virtex®-E |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 2400 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 10800 |
| RAM 位總計(jì): | 163840 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 158 |
| 門數(shù): | 569952 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.71 V ~ 1.89 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 240-BFQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 240-PQFP(32x32) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁當(dāng)前第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁第221頁第222頁第223頁第224頁第225頁第226頁第227頁第228頁第229頁第230頁第231頁第232頁第233頁
Virtex-E 1.8 V Field Programmable Gate Arrays
R
Module 2 of 4
DS022-2 (v3.0) March 21, 2014
8
Production Product Specification
— OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE —
The DLL also operates as a clock mirror. By driving the out-
put from a DLL off-chip and then back on again, the DLL can
be used to deskew a board level clock among multiple
devices.
To guarantee that the system clock is operating correctly
prior to the FPGA starting up after configuration, the DLL
can delay the completion of the configuration process until
after it has achieved lock. For more information about DLL
functionality, see the Design Consideration section of the
data sheet.
Boundary Scan
Virtex-E devices support all the mandatory Boundary Scan
instructions specified in the IEEE standard 1149.1. A Test
Access Port (TAP) and registers are provided that imple-
ment the EXTEST, INTEST, SAMPLE/PRELOAD, BYPASS,
IDCODE, USERCODE, and HIGHZ instructions. The TAP
also supports two internal scan chains and configura-
tion/readback of the device.
The JTAG input pins (TDI, TMS, TCK) do not have a VCCO
requirement and operate with either 2.5 V or 3.3 V input sig-
nalling levels. The output pin (TDO) is sourced from the
VCCO in bank 2, and for proper operation of LVTTL 3.3 V lev-
els, the bank should be supplied with 3.3 V.
Boundary Scan operation is independent of individual IOB
configurations, and unaffected by package type. All IOBs,
including un-bonded ones, are treated as independent
3-state bidirectional pins in a single scan chain. Retention of
the bidirectional test capability after configuration facilitates
the testing of external interconnections, provided the user
design or application is turned off.
Table 6 lists the Boundary Scan instructions supported in
Virtex-E FPGAs. Internal signals can be captured during
EXTEST by connecting them to un-bonded or unused IOBs.
They can also be connected to the unused outputs of IOBs
defined as unidirectional input pins.
Before the device is configured, all instructions except
USER1 and USER2 are available. After configuration, all
instructions are available. During configuration, it is recom-
mended that those operations using the Boundary Scan
register (SAMPLE/PRELOAD, INTEST, EXTEST) not be
performed.
In addition to the test instructions outlined above, the
Boundary Scan circuitry can be used to configure the
FPGA, and also to read back the configuration data.
Figure 11 is a diagram of the Virtex-E Series Boundary
Scan logic. It includes three bits of Data Register per IOB,
the IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port controller, and the
Instruction Register with decodes.
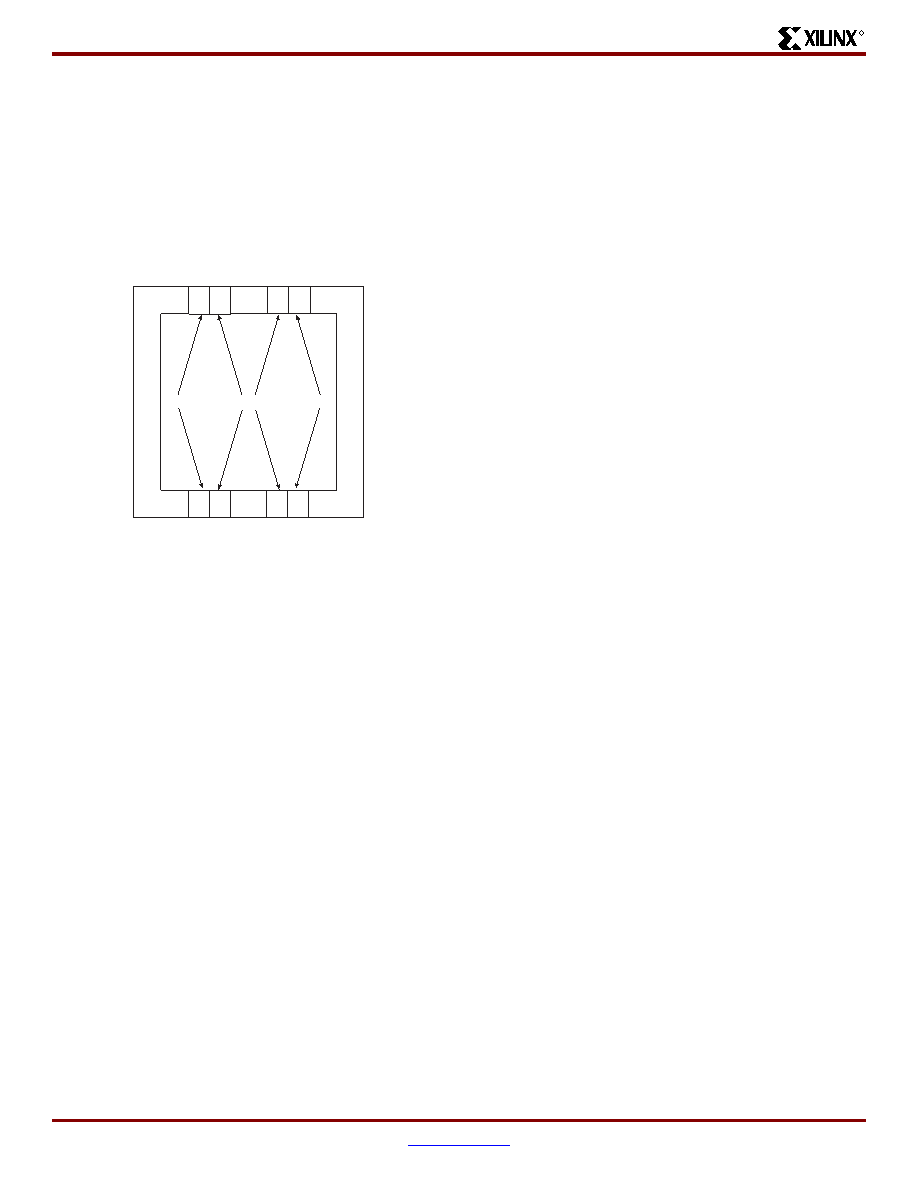
Figure 10: DLL Locations
XCVE_0010
DLLDLL
Primary DLLs
Secondar
y
DLLs
Secondar
y
DLLs
DLLDLL
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XCV400E-7PQ240I | IC FPGA 1.8V I-TEMP 240-PQFP |
| BR24L01AF-WE2 | IC EEPROM 1KBIT 400KHZ 8SOP |
| BR93L56RFVM-WTR | IC EEPROM 2KBIT 2MHZ 8MSOP |
| BR24L01AFVM-WTR | IC EEPROM 1KBIT 400KHZ 8MSOP |
| XC2V2000-4FFG896C | IC VIRTEX-II FPGA 2M 896-FCBGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCV400E-8PQ240I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV400E-8PQG240C | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:FPGA VIRTEX-E 129.6K GATES 10800 CELLS 416MHZ 0.18UM 1.8V 24 - Trays |
| XCV405E | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-6BG404C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-6BG404I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。