- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄372886 > XCS05-3CS256C (Xilinx, Inc.) Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XCS05-3CS256C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| 中文描述: | 斯巴達(dá)和Spartan - xL的家庭現(xiàn)場(chǎng)可編程門陣列 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 4/66頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 809K |
| 代理商: | XCS05-3CS256C |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)當(dāng)前第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)
R
Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays
4-4
DS060 (v1.5) March 2, 2000
A CLB can implement any of the following functions:
Any function of up to four variables, plus any second
function of up to four unrelated variables, plus any third
function of up to three unrelated variables
1
Any single function of five variables
Any function of four variables together with some
functions of six variables
Some functions of up to nine variables.
Implementing wide functions in a single block reduces both
the number of blocks required and the delay in the signal
path, achieving both increased capacity and speed.
The versatility of the CLB function generators significantly
improves system speed. In addition, the design-software
tools can deal with each function generator independently.
This flexibility improves cell usage.
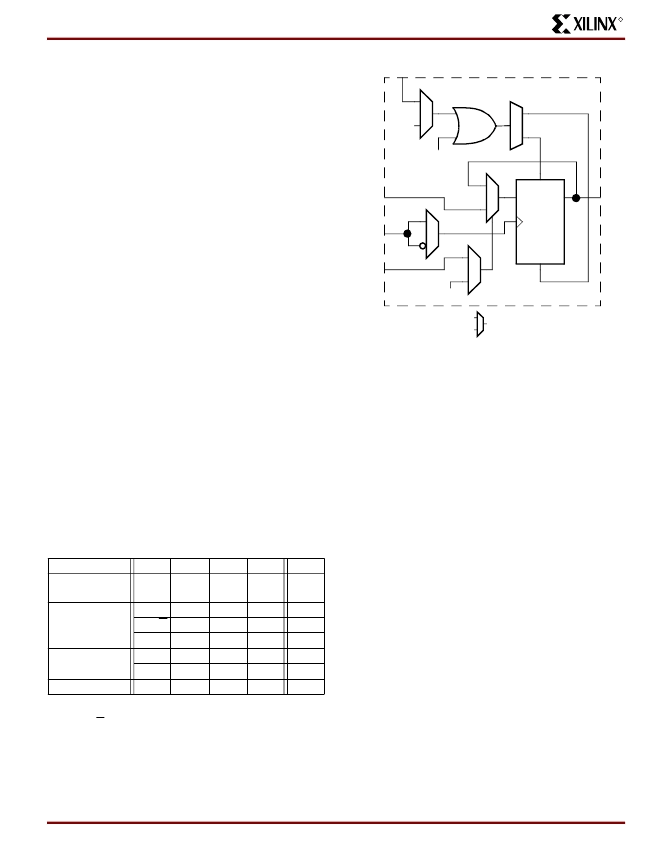
Flip-Flops
Each CLB contains two flip-flops that can be used to regis-
ter (store) the function generator outputs. The flip-flops and
function generators can also be used independently (see
Figure 2 on page 3
). The CLB input DIN can be used as a
direct input to either of the two flip-flops. H1 can also drive
either flip-flop via the H-LUT with a slight additional delay.
The two flip-flops have common clock (CK), clock enable
(EC) and set/reset (SR) inputs. Internally both flip-flops are
also controlled by a global initialization signal (GSR) which
is described in detail in
“
Global Signals: GSR and GTS
”
on
page 18
.
Latches (Spartan-XL only)
The Spartan-XL CLB storage elements can also be config-
ured as latches. The two latches have common clock (K)
and clock enable (EC) inputs. Functionality of the storage
element is described in
Table 2
.
Clock Input
Each flip-flop can be triggered on either the rising or falling
clock edge. The CLB clock line is shared by both flip-flops.
However, the clock is individually invertible for each flip-flop
(see CK path in
Figure 3
). Any inverter placed on the clock
line in the design is automatically absorbed into the CLB.
Clock Enable
The clock enable line (EC) is active High. The EC line is
shared by both flip-flops in a CLB. If either one is left dis-
connected, the clock enable for that flip-flop defaults to the
active state. EC is not invertible within the CLB. The clock
enable is synchronous to the clock and must satisfy the
setup and hold timing specified for the device.
Set/Reset
The set/reset line (SR) is an asynchronous active High con-
trol of the flip-flop. SR can be configured as either set or
reset at each flip-flop. This configuration option determines
the state in which each flip-flop becomes operational after
configuration. It also determines the effect of a GSR pulse
during normal operation, and the effect of a pulse on the
SR line of the CLB. The SR line is shared by both flip-flops.
If SR is not specified for a flip-flop the set/reset for that
flip-flop defaults to the inactive state. SR is not invertible
within the CLB.
1. When three separate functions are generated, one of the function outputs must be captured in a flip-flop internal to the CLB. Only two
unregistered function generator outputs are available from the CLB.
Table 2: CLB Storage Element Functionality
Mode
Power-Up or
GSR
CK
EC
SR
D
Q
X
X
X
X
SR
Flip-Flop
Operation
X
X
1*
X
1*
1*
0
1
0*
0*
0*
0*
0*
X
D
X
X
D
X
SR
D
Q
Q
D
Q
__/
0
1
0
X
Latch Operation
(Spartan-XL)
Both
Legend:
X
__/
SR
0*
1*
Don
’
t care
Rising edge (clock not inverted)
Set or Reset value. Reset is default.
Input is Low or unconnected (default value)
Input is High or unconnected (default value)
Figure 3: CLB Flip-Flop Functional Block Diagram
D
Q
SD
RD
SR
GND
D
EC
CK
Q
Multiplexer Controlled
by Configuration Program
Rev 1.1
Vcc
GSR
Powered by ICminer.com Electronic-Library Service CopyRight 2003
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XCS05-3CS256I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS280C | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS280I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS84C | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS84I | Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCS05-3CS256I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS280C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS280I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS84C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCS05-3CS84I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan and Spartan-XL Families Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。