- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371200 > X24256BI-2.5 75V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a TO-262 package; Similar to IRF2907ZL with Lead-Free Packaging PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | X24256BI-2.5 |
| 英文描述: | 75V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a TO-262 package; Similar to IRF2907ZL with Lead-Free Packaging |
| 中文描述: | I2C串行EEPROM的 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/18頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 144K |
| 代理商: | X24256BI-2.5 |
X24256
Characteristics subject to change without notice.
8 of 18
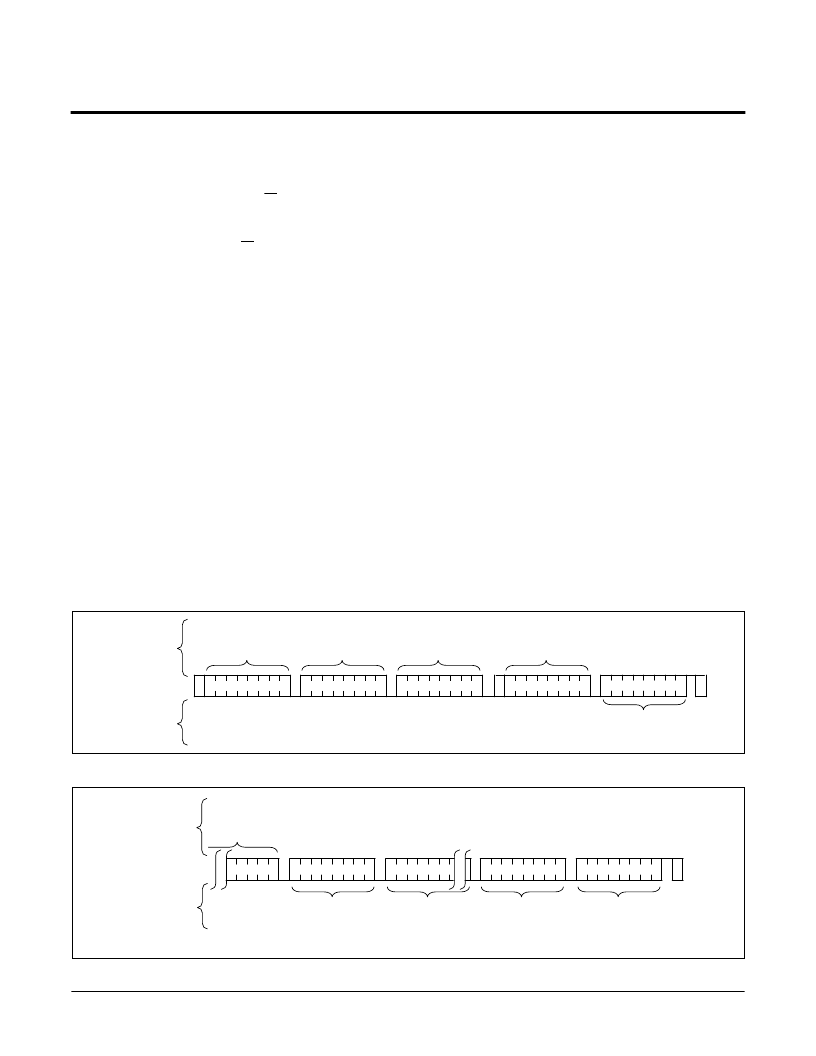
Random Read
Random read operation allows the master to access
any memory location in the array. Prior to issuing the
Slave Address Byte with the R/W bit set to one, the
master must first perform a “Dummy” write operation.
The master issues the start condition and the Slave
Address Byte with the R/W bit low, receives an
acknowledge, then issues the Word Address Byte 1,
receives another acknowledge, then issues the Word
Address Byte 0. After the device acknowledges receipt
of the Word Address Byte 0, the master issues another
start condition and the Slave Address Byte with the R/
W bit set to one. This is followed by an acknowledge
and then eight bits of data from the device. The master
terminates the read operation by not responding with
an acknowledge and then issuing a stop condition.
Refer to Figure 9 for the address, acknowledge, and
data transfer sequence.
The device will perform a similar operation called “Set
Current Address” if a stop is issued instead of the
second start shown in Figure 9. The device will go into
standby mode after the stop and all bus activity will be
ignored until a start is detected. The effect of this oper-
ation is that the new address is loaded into the
address counter, but no data is output by the device.
The next Current Address Read operation will read
from the newly loaded address.
Sequential Read
Sequential reads can be initiated as either a current
address read or random read. The first Data Byte is
transmitted as with the other modes; however, the
master now responds with an acknowledge, indicating
it requires additional data. The device continues to out-
put data for each acknowledge received. The master
terminates the read operation by not responding with an
acknowledge and then issuing a stop condition.
The data output is sequential, with the data from
address n followed by the data from address n + 1.
The address counter for read operations increments
through all byte addresses, allowing the entire memory
contents to be read during one operation. At the end of
the address space the counter “rolls over” to address
0000h and the device continues to output data for
each acknowledge received. Refer to Figure 10 for the
acknowledge and data transfer sequence.
Figure 9. Random Read Sequence
Figure 10. Sequential Read Sequence
SIGNALS
FROMTHE
MASTER
SDA BUS
SIGNALS
FROMTHE
SLAVE
S
T
A
R
T
S
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
WORDADDRESS
BYTE 1
SLAVE
ADDRESS
0
WORD ADDRESS
BYTE 0
S
T
A
R
T
S
1
DATA
A
C
K
1 0 1 0 0
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA
(1)
DATA
(2)
SIGNALS
FROM THE
MASTER
SDA BUS
SIGNALS
FROM THE
SLAVE
DATA
(n–1)
DATA
(n)
1
(n is any integer greater than 1)
Powered by ICminer.com Electronic-Library Service CopyRight 2003
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| X24256S8 | 20V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a SO-8 package; Similar to IRF7459 with lead free packaging. |
| X24256S8-1.8 | 20V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-Pak package; A IRF1302S with Standard Packaging |
| X24256S8-2.5 | 60V Single N-Channel HEXFET Power MOSFET in a D2-Pak package; A IRFS3306PBF with Standard Packaging |
| X24256S8I | EEPROM |
| X24256S8I-1.8 | EEPROM |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| X24256S8 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM |
| X24256S8-1.8 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM |
| X24256S8-2.5 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:I2C Serial EEPROM |
| X24256S8I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM |
| X24256S8I-1.8 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。