- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98144 > ST72311N4T6/XXX (STMICROELECTRONICS) 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | ST72311N4T6/XXX |
| 廠商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, TQFP-64 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 60/92頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 624K |
| 代理商: | ST72311N4T6/XXX |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁當(dāng)前第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁
63/92
ST72311
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d)
4.5.4.3 Data Transfer Format
During an SPI transfer, data is simultaneously
transmitted (shifted out serially) and received
(shifted in serially). The serial clock is used to syn-
chronize the data transfer during a sequence of
eight clock pulses.
The SS pin allows individual selection of a slave
device; the other slave devices that are not select-
ed do not interfere with the SPI transfer.
Clock Phase and Clock Polarity
Four possible timing relationships may be chosen
by software, using the CPOL and CPHA bits.
The CPOL (clock polarity) bit controls the steady
state value of the clock when no data is being
transferred. This bit affects both master and slave
modes.
The combination between the CPOL and CPHA
(clock phase) bits selects the data capture clock
edge.
Figure 39, shows an SPI transfer with the four
combinations of the CPHA and CPOL bits. The di-
agram may be interpreted as a master or slave
timing diagram where the SCK pin, the MISO pin,
the MOSI pin are directly connected between the
master and the slave device.
The SS pin is the slave device select input and can
be driven by the master device.
The master device applies data to its MOSI pin-
clock edge before the capture clock edge.
CPHA bit is set
The second edge on the SCK pin (falling edge if
the CPOL bit is reset, rising edge if the CPOL bit is
set) is the MSBit capture strobe. Data is latched on
the occurrence of the first clock transition.
No write collision should occur even if the SS pin
stays low during a transfer of several bytes (see
Figure 38).
CPHA bit is reset
The first edge on the SCK pin (falling edge if CPOL
bit is set, rising edge if CPOL bit is reset) is the
MSBit capture strobe. Data is latched on the oc-
currence of the second clock transition.
This pin must be toggled high and low between
each byte transmitted (see Figure 38).
To protect the transmission from a write collision a
low value on the SS pin of a slave device freezes
the data in its DR register and does not allow it to
be altered. Therefore the SS pin must be high to
write a new data byte in the DR without producing
a write collision.
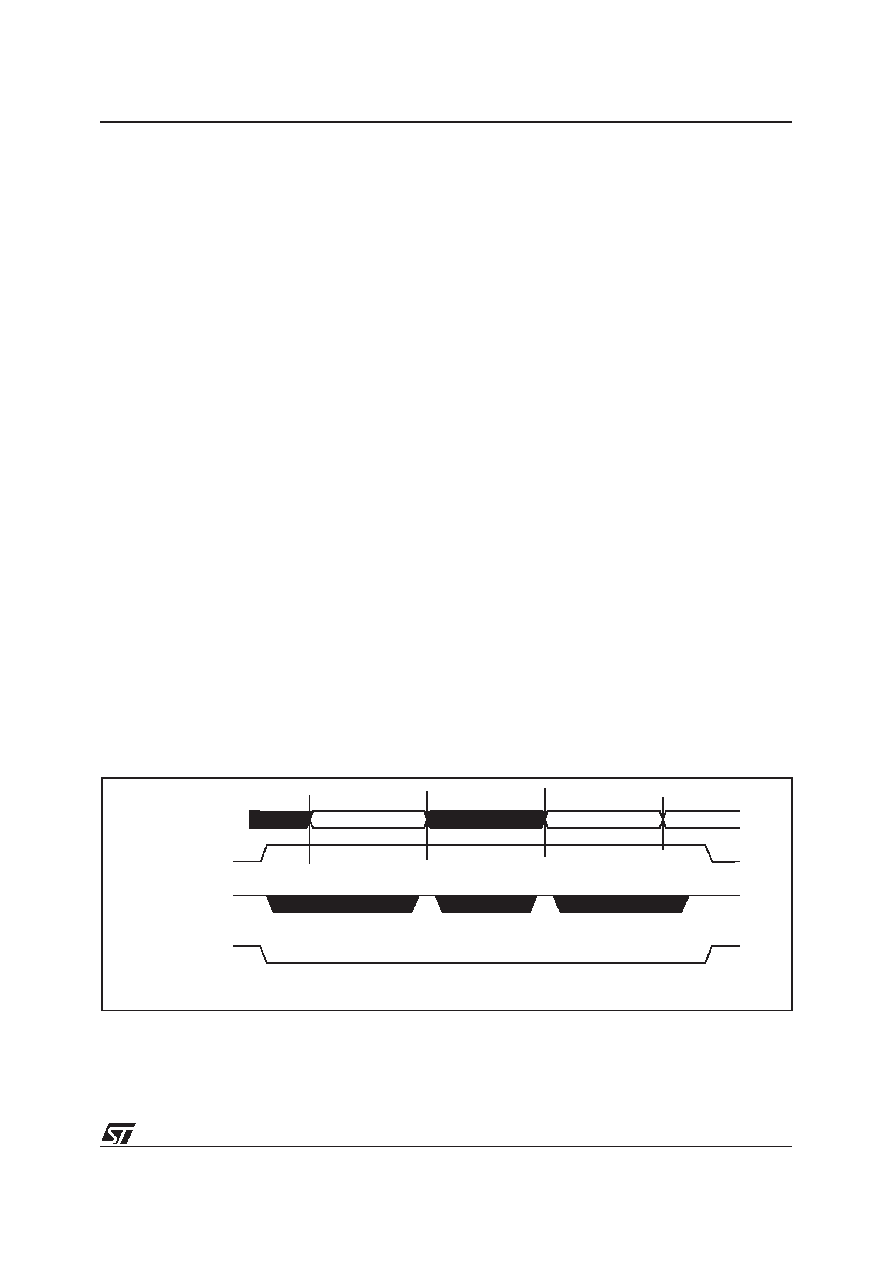
Figure 38. CPHA / SS Timing Diagram
MOSI/MISO
Master SS
Slave SS
(CPHA=0)
Slave SS
(CPHA=1)
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
VR02131C
63
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ST72311J2B6/XXX | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP42 |
| ST72311N2T3/XXX | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| ST72321BAR7T6 | MICROCONTROLLER, QFP64 |
| ST72321BR7T3 | MICROCONTROLLER, QFP64 |
| ST72321M9T3/XXX | 8-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| ST72311N5B6 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
| ST72311N6B6 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
| ST72311R | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:8-BIT MCU WITH NESTED INTERRUPTS, EEPROM, ADC, 16-BIT TIMERS, 8-BIT PWM ART, SPI, SCI, CAN INTERFACES |
| ST72311R4Q6 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
| ST72311R5Q6 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。