- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄45341 > MPC5604BF1VLQ6R (FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC) MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | MPC5604BF1VLQ6R |
| 廠商: | FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| 封裝: | 20 X 20 MM, 1.40 MM HEIGHT, 0.50 MM PITCH, LQFP-144 |
| 文件頁數: | 61/104頁 |
| 文件大小: | 953K |
| 代理商: | MPC5604BF1VLQ6R |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁當前第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁
MPC5604B/C Microcontroller Data Sheet, Rev. 9
Block diagram
Freescale Semiconductor
6
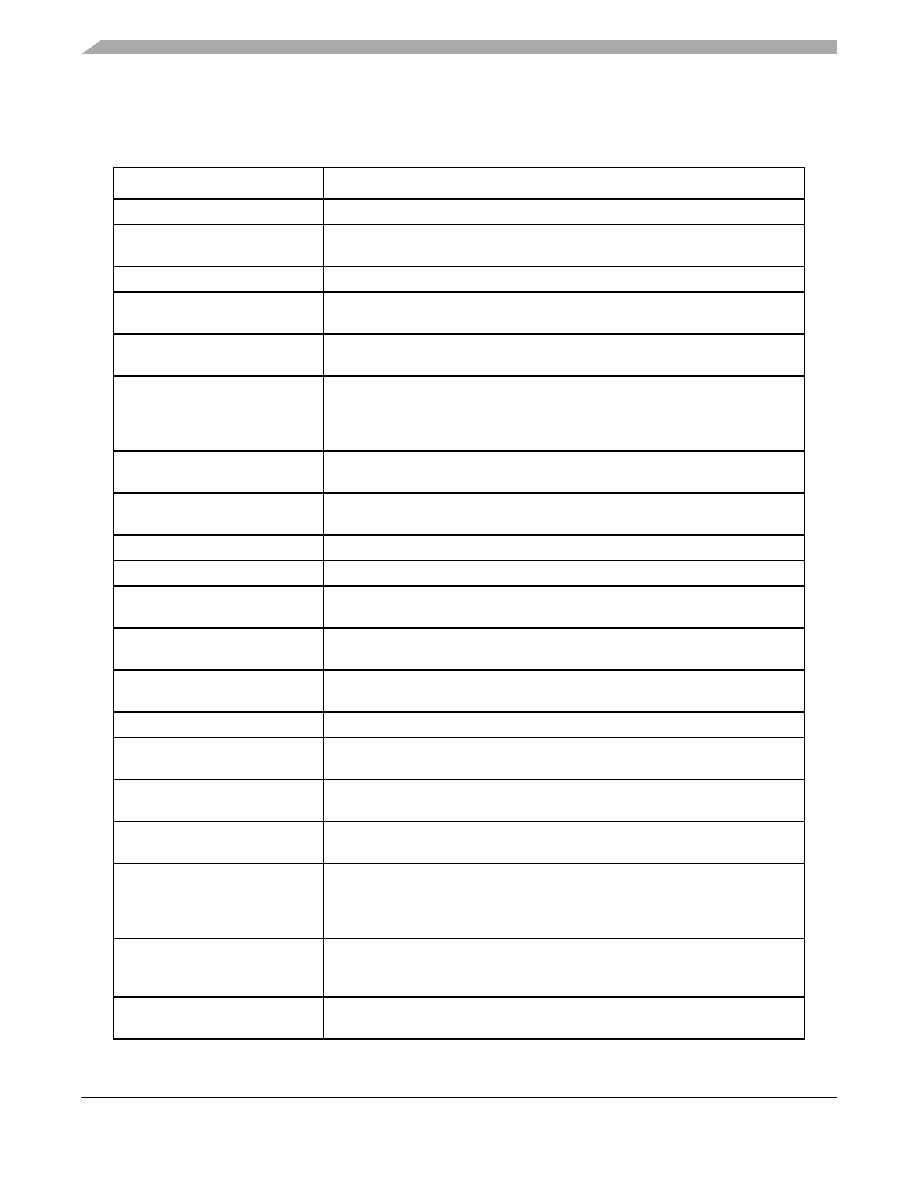
Table 2 summarizes the functions of all blocks present in the MPC5604B/C series of microcontrollers. Please note that the
presence and number of blocks vary by device and package.
Table 2. MPC5604B/C series block summary
Block
Function
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) Multi-channel, 10-bit analog-to-digital converter
Boot assist module (BAM)
A block of read-only memory containing VLE code which is executed according
to the boot mode of the device
Clock monitor unit (CMU)
Monitors clock source (internal and external) integrity
Cross triggering unit (CTU)
Enables synchronization of ADC conversions with a timer event from the eMIOS
or from the PIT
Deserial serial peripheral interface
(DSPI)
Provides a synchronous serial interface for communication with external devices
Error Correction Status Module
(ECSM)
Provides a myriad of miscellaneous control functions for the device including
program-visible information about configuration and revision levels, a reset status
register, wakeup control for exiting sleep modes, and optional features such as
information on memory errors reported by error-correcting codes
Enhanced Direct Memory Access
(eDMA)
Performs complex data transfers with minimal intervention from a host processor
via “
n” programmable channels.
Enhanced modular input output
system (eMIOS)
Provides the functionality to generate or measure events
Flash memory
Provides non-volatile storage for program code, constants and variables
FlexCAN (controller area network) Supports the standard CAN communications protocol
Frequency-modulated
phase-locked loop (FMPLL)
Generates high-speed system clocks and supports programmable frequency
modulation
Internal multiplexer (IMUX) SIU
subblock
Allows flexible mapping of peripheral interface on the different pins of the device
Inter-integrated circuit (I2C) bus A two wire bidirectional serial bus that provides a simple and efficient method of
data exchange between devices
Interrupt controller (INTC)
Provides priority-based preemptive scheduling of interrupt requests
JTAG controller
Provides the means to test chip functionality and connectivity while remaining
transparent to system logic when not in test mode
LINFlex controller
Manages a high number of LIN (Local Interconnect Network protocol) messages
efficiently with a minimum of CPU load
Clock generation module
(MC_CGM)
Provides logic and control required for the generation of system and peripheral
clocks
Mode entry module (MC_ME)
Provides a mechanism for controlling the device operational mode and mode
transition sequences in all functional states; also manages the power control unit,
reset generation module and clock generation module, and holds the
configuration, control and status registers accessible for applications
Power control unit (MC_PCU)
Reduces the overall power consumption by disconnecting parts of the device
from the power supply via a power switching device; device components are
grouped into sections called “power domains” which are controlled by the PCU
Reset generation module
(MC_RGM)
Centralizes reset sources and manages the device reset sequence of the device
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MPC5604BF1VMG4 | MICROCONTROLLER, PBGA208 |
| MPC5604BF1MLL4R | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| MPC5604CF1MLH4R | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| MPC5604CF1MLH4 | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| MPC5604BF1VLH4 | MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| MPC5604BMLL4R | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:MPC5604B/C Microcontroller |
| MPC5604C | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:MPC5604B/C Microcontroller Data Sheet |
| MPC5604CECLQ | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontroller |
| MPC5604CECLU | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontroller |
| MPC5604CECMG | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontroller |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。