- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄180538 > MAX6723UTRYD2-T (MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC) Analog IC PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MAX6723UTRYD2-T |
| 廠商: | MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 電源管理 |
| 英文描述: | Analog IC |
| 中文描述: | 3-CHANNEL POWER SUPPLY MANAGEMENT CKT, PDSO6 |
| 封裝: | SOT-23, 6 PIN |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/19頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 324K |
| 代理商: | MAX6723UTRYD2-T |
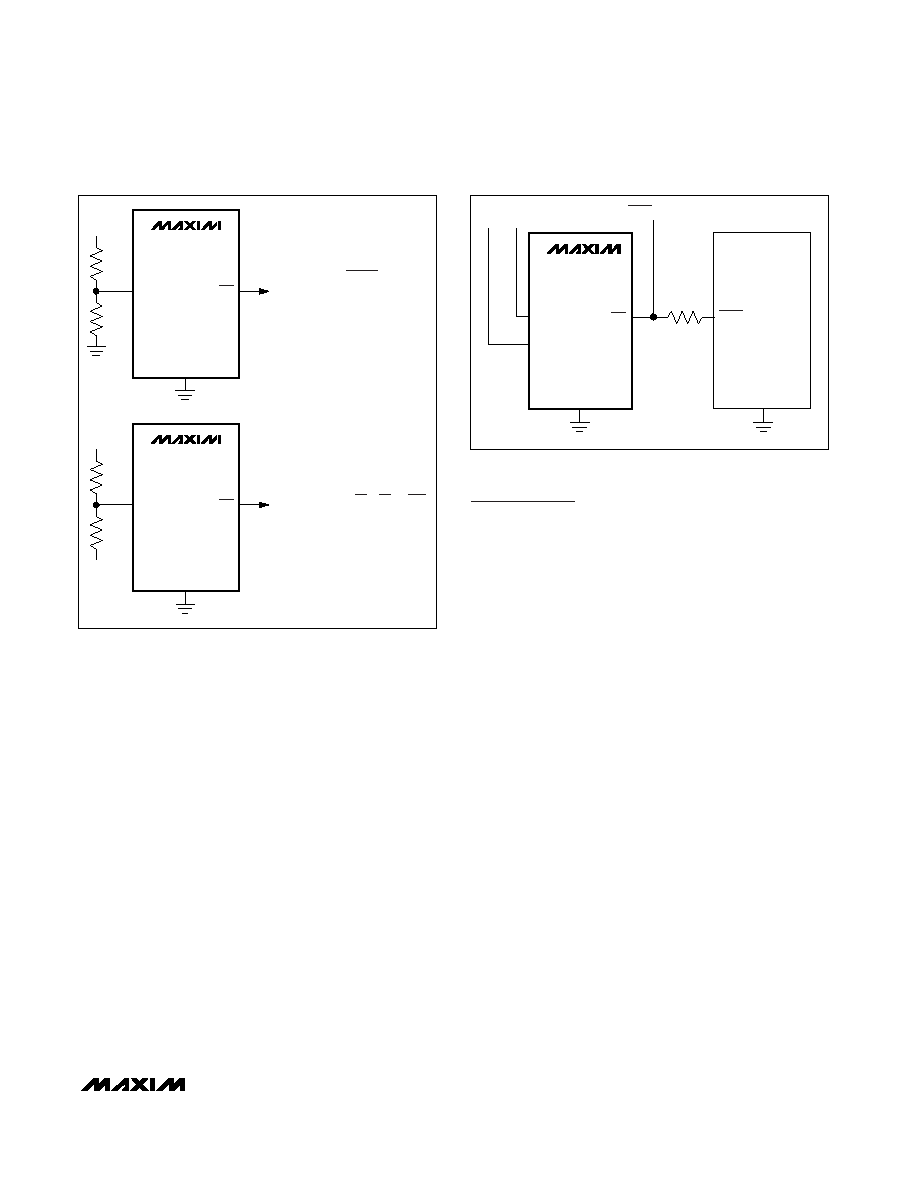
providing an early power-fail warning so software can
conduct an orderly system shutdown. It can also be
used to monitor supplies other than VCC1 or VCC2 by
setting the power-fail threshold with a resistor-divider, as
shown in Figure 3. PFI is the input to the power-fail com-
parator. The typical comparator delay is 2s from PFI to
PFO. Connect PFI to ground of VCC1 if unused.
Ensuring a Valid Reset Output
Down to VCC = 0
The MAX6715–MAX6729 are guaranteed to operate
properly down to VCC = 0.8V. In applications that
require valid reset levels down to VCC = 0 use a pull-
down resistor at RST to ground. The resistor value used
is not critical, but it must be large enough not to load
the reset output when VCC is above the reset threshold.
For most applications, 100k
is adequate. This config-
uration does not work for the open-drain outputs of the
MAX6715/MAX6717/MAX6719/MAX6721/MAX6723/
MAX6725/MAX6727/MAX6728. For push-pull, active-
high RST output connect the external resistor as a
pullup from RST to VCC1.
Applications Information
Interfacing to Ps with Bidirectional
Reset Pins
Most microprocessors with bidirectional reset pins can
interface directly to open-drain RST output options.
Systems simultaneously requiring a push-pull RST out-
put and a bidirectional reset interface can be in logic
contention. To prevent contention, connect a 4.7k
resistor between RST and the P’s reset I/O port as
shown in Figure 4.
Adding Hysteresis to the Power-Fail
Comparator
The power-fail comparator has a typical input hysteresis
of 3mV. This is sufficient for most applications where a
power-supply line is being monitored through an external
voltage-divider (see the Power-Fail Comparator section).
If additional noise margin is desired, connect a resistor
between PFO and PFI as shown in Figure 5. Select the
values of R1, R2, and R3 so PFI sees VPFI (626mV) when
VEXT falls to its power-fail trip point (VFAIL) and when VIN
rises to its power-good trip point (VGOOD). The hysteresis
window extends between the specified VFAIL and VGOOD
thresholds. R3 adds the additional hysteresis by sinking
current from the R1/R2 divider network when PFO is logic
low and sourcing current into the network when PFO is
logic high. R3 is typically an order of magnitude greater
than R1 or R2.
The current through R2 should be at least 2.5A to
ensure that the 25nA (max) PFI input current does not
significantly shift the trip points. Therefore, R2 <
VPFI/2.5A < 248k
for most applications. R3 will provide
additional hysteresis for PFO push-pull (VOH = VCC1) or
open-drain (VOH = VPULLUP) applications.
MAX6715–MAX6729
Dual/Triple Ultra-Low-Voltage SOT23 P
Supervisory Circuits
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
MAX6728/
MAX6729
R1
R2
PFI
GND
VIN
PFO
VTRIP = VPFI
R1 + R2
R2
()
MAX6728/
MAX6729
R1
R2
PFI
GND
VCC
VIN
PFO
VTRIP = R2 (VPFI)
1
R1
1
R2
+-
VCC
R1
[]
()
VPFI = 626.5mV
A
B
Figure 3. Using Power-Fail Input to Monitor an Additional
Power-Supply a) VIN is Positive b) VIN is Negative
MAX6715–
MAX6729
GND
VCC1VCC2
VCC2
VCC1
RST
RESET TO OTHER SYSTEM COMPONENTS
RESET
P
4.7k
Figure 4. Interfacing to Ps with Bidirectional Reset I/O
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX6723UTRYD4-T | Analog IC |
| MAX6723UTRYD5-T | ADS7861 Evaluation Module |
| MAX6723UTRYD6-T | Analog IC |
| MAX6723UTYVD4-T | Analog IC |
| MAX6723UTYVD5-T | Dual/Triple Ultra-Low-Voltage SOT23 µ.P Supervisory Circuits |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX6723UTRYD3 | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:- Rail/Tube |
| MAX6723UTRYD3+T | 功能描述:監(jiān)控電路 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 監(jiān)測電壓數(shù): 監(jiān)測電壓: 欠電壓閾值: 過電壓閾值: 輸出類型:Active Low, Open Drain 人工復位:Resettable 監(jiān)視器:No Watchdog 電池備用開關(guān):No Backup 上電復位延遲(典型值):10 s 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:UDFN-6 封裝:Reel |
| MAX6723UTRYD3-T | 功能描述:監(jiān)控電路 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 監(jiān)測電壓數(shù): 監(jiān)測電壓: 欠電壓閾值: 過電壓閾值: 輸出類型:Active Low, Open Drain 人工復位:Resettable 監(jiān)視器:No Watchdog 電池備用開關(guān):No Backup 上電復位延遲(典型值):10 s 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:UDFN-6 封裝:Reel |
| MAX6723UTRYD4 | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:- Rail/Tube |
| MAX6723UTRYD4+T | 功能描述:監(jiān)控電路 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 監(jiān)測電壓數(shù): 監(jiān)測電壓: 欠電壓閾值: 過電壓閾值: 輸出類型:Active Low, Open Drain 人工復位:Resettable 監(jiān)視器:No Watchdog 電池備用開關(guān):No Backup 上電復位延遲(典型值):10 s 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:UDFN-6 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。