- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄16275 > MAX6495EVKIT (Maxim Integrated Products)EVAL KIT MAX6495 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MAX6495EVKIT |
| 廠商: | Maxim Integrated Products |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 2/16頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | EVAL KIT MAX6495 |
| 標準包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | * |
MAX6495–MAX6499
72V, Overvoltage-Protection Switches/
Limiter Controllers with an External MOSFET
10
Maxim Integrated
where IGATE is GATE’s 100A sourcing current, ILOAD
is the load current at startup, and COUT is the output
capacitor.
MOSFET Selection
Select external MOSFETs according to the application
current level. The MOSFET’s on-resistance (RDS(ON))
should be chosen low enough to have a minimum volt-
age drop at full load to limit the MOSFET power dissipa-
tion. Determine the device power rating to
accommodate an overvoltage fault when operating the
MAX6495/MAX6496/MAX6499 in overvoltage-limit mode.
During normal operation, the external MOSFET dissi-
pates little power. The power dissipated in the MOSFET
during normal operation is:
P= ILOAD2 x RDS(ON)
where P is the power dissipated in the MOSFET, ILOAD
is the output load current, and RDS(ON) is the drain-to-
source resistance of the MOSFET.
Most power dissipation in the MOSFET occurs during a
prolonged overvoltage event when operating the
MAX6495/MAX6496/MAX6499 in voltage-limiter mode.
The power dissipated across the MOSFET is as follows
(see the
Thermal Shutdown in Overvoltage-Limiter
Mode section):
P = VDS x ILOAD
where VDS is the voltage across the MOSFET’s drain
and source.
Thermal Shutdown
The MAX6495–MAX6499 thermal-shutdown feature
turns off GATE if it exceeds the maximum allowable
thermal dissipation. Thermal shutdown also monitors
the PC board temperature of the external n-channel
MOSFET when the devices sit on the same thermal
island. Good thermal contact between the MAX6495–
MAX6499 and the external n-channel MOSFET is essen-
tial for the thermal-shutdown feature to operate effec-
tively. Place the n-channel MOSFET as close to
possible to OUTFB.
When the junction temperature exceeds TJ = +160°C,
the thermal sensor signals the shutdown logic, turning
off the GATE output and allowing the device to cool.
The thermal sensor turns the GATE on again after the
IC’s junction temperature cools by 20°C. Thermal-over-
load protection is designed to protect the MAX6495–
MAX6499 and the external MOSFET in the event of cur-
rent-limit fault conditions. For continuous operation, do
not exceed the absolute maximum junction-temperature
rating of TJ = +150°C.
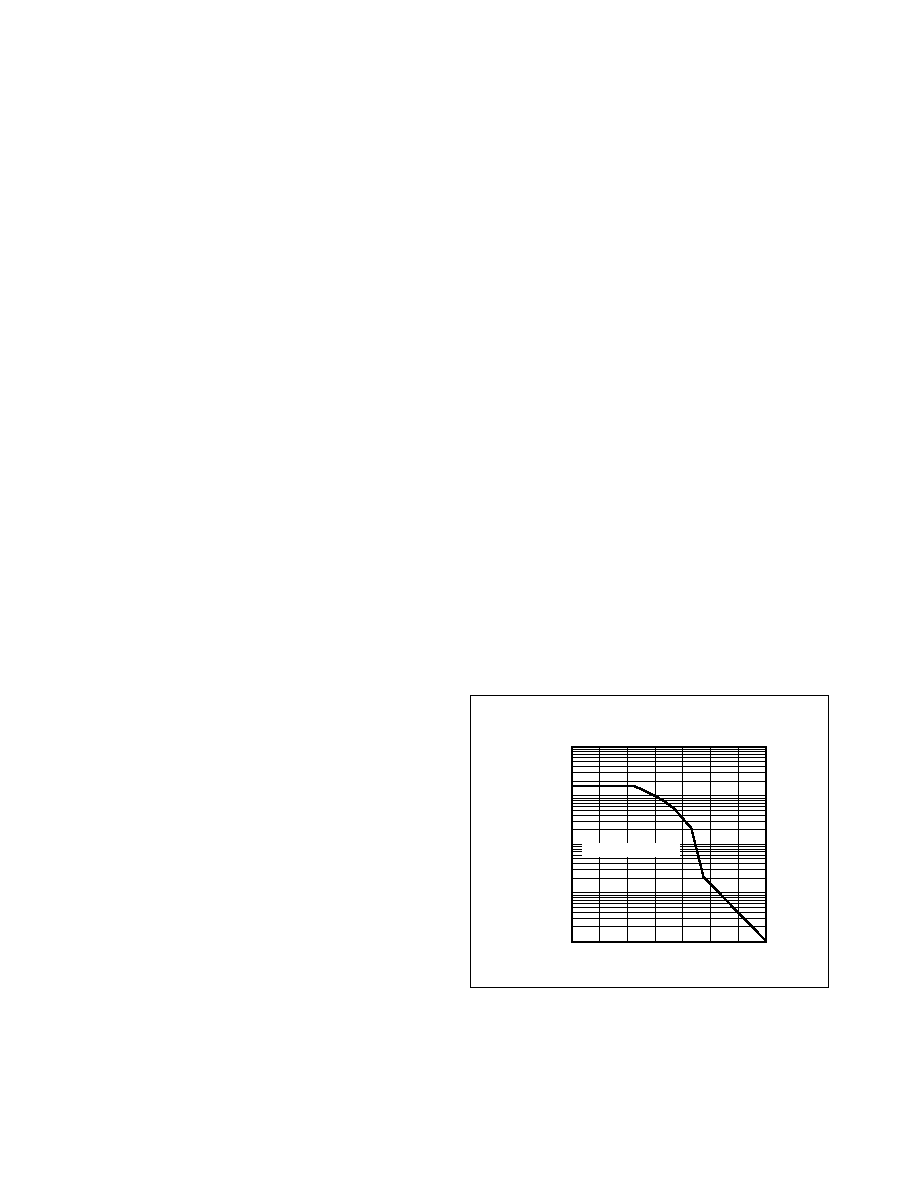
Peak Power-Dissipation Limit
The MAX6495–MAX6499 activate an internal 100mA
pulldown on GATE when
SHDN goes low, OVSET
exceeds its threshold or UVSET falls below its threshold.
Once the voltage on GATE falls below the OUTFB volt-
age, current begins to flow from OUTFB to the 100mA
pulldown through the internal clamp diode, discharging
the output capacitors.
Depending on the output capacitance and the initial volt-
age, a significant amount of energy may be dissipated
by the internal 100mA pulldown. To prevent damage to
the device ensure that for a given overvoltage threshold,
the output capacitance does not exceed the limit provid-
ed in Figure 4. This output capacitance represents the
sum of all capacitors connected to OUTFB, including
reservoir capacitors and DC-DC input filter capacitors.
Thermal Shutdown in Overvoltage-Limiter Mode
When operating the MAX6495/MAX6496/MAX6499 in
overvoltage-limit mode for a prolonged period of time, a
thermal shutdown is possible. The thermal shutdown is
dependent on a number of different factors:
The device’s ambient temperature
The output capacitor (COUT)
The output load current (IOUT)
The overvoltage threshold limit (VOV)
MAXIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE
vs. OVERVOLTAGE THRESHOLD
MAX6495
fig04
OVERVOLTAGE THRESHOLD (V)
MAXIMUM
OUTPUT
CAPACITANCE
(μ
F)
60
50
40
30
20
10
100
1000
10,000
100,000
10
070
SAFE OPERATING AREA
Figure 4. Safe Operating Area for 100mA Pulldown.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| H3WWH-4036G | IDC CABLE - HPL40H/AE40G/HPL40H |
| A3BBH-5036G | IDC CABLE - ASR50H/AE50G/ASR50H |
| CM453232-102JL | INDUCTOR 1MH 30MA SMD |
| M3CWK-2406J | IDC CABLE - MKC24K/MC24G/MPL24K |
| M3CKK-2406J | IDC CABLE - MKC24K/MC24G/MPK24K |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX6495EVKIT+ | 功能描述:電源管理IC開發(fā)工具 MAX6495 Eval Kit RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 產(chǎn)品:Evaluation Kits 類型:Battery Management 工具用于評估:MAX17710GB 輸入電壓: 輸出電壓:1.8 V |
| MAX6496ATA+ | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:OVERVOLT PROT CNTRLR 8TDFN EP - Rail/Tube |
| MAX6496ATA+T | 功能描述:電流和電力監(jiān)控器、調(diào)節(jié)器 72V Over V Protect Switch/Limiter RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:Current Regulators 電源電壓-最大:48 V 電源電壓-最小:5.5 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 150 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HPSO-8 封裝:Reel |
| MAX6496EVKIT+ | 功能描述:電源管理IC開發(fā)工具 MAX6496 Eval Kit RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 產(chǎn)品:Evaluation Kits 類型:Battery Management 工具用于評估:MAX17710GB 輸入電壓: 輸出電壓:1.8 V |
| MAX6497ATA+ | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:OVERVOLT PROT CNTRLR 8TDFN EP - Rail/Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。