- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45017 > M30620MAA-XXXFP 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M30620MAA-XXXFP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| 封裝: | 14 X 20 MM, 0.65 MM PITCH, PLASTIC, QFP-100 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/40頁 |
| 文件大小: | 3893K |
| 代理商: | M30620MAA-XXXFP |
第1頁第2頁當(dāng)前第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M16C / 62A Group
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
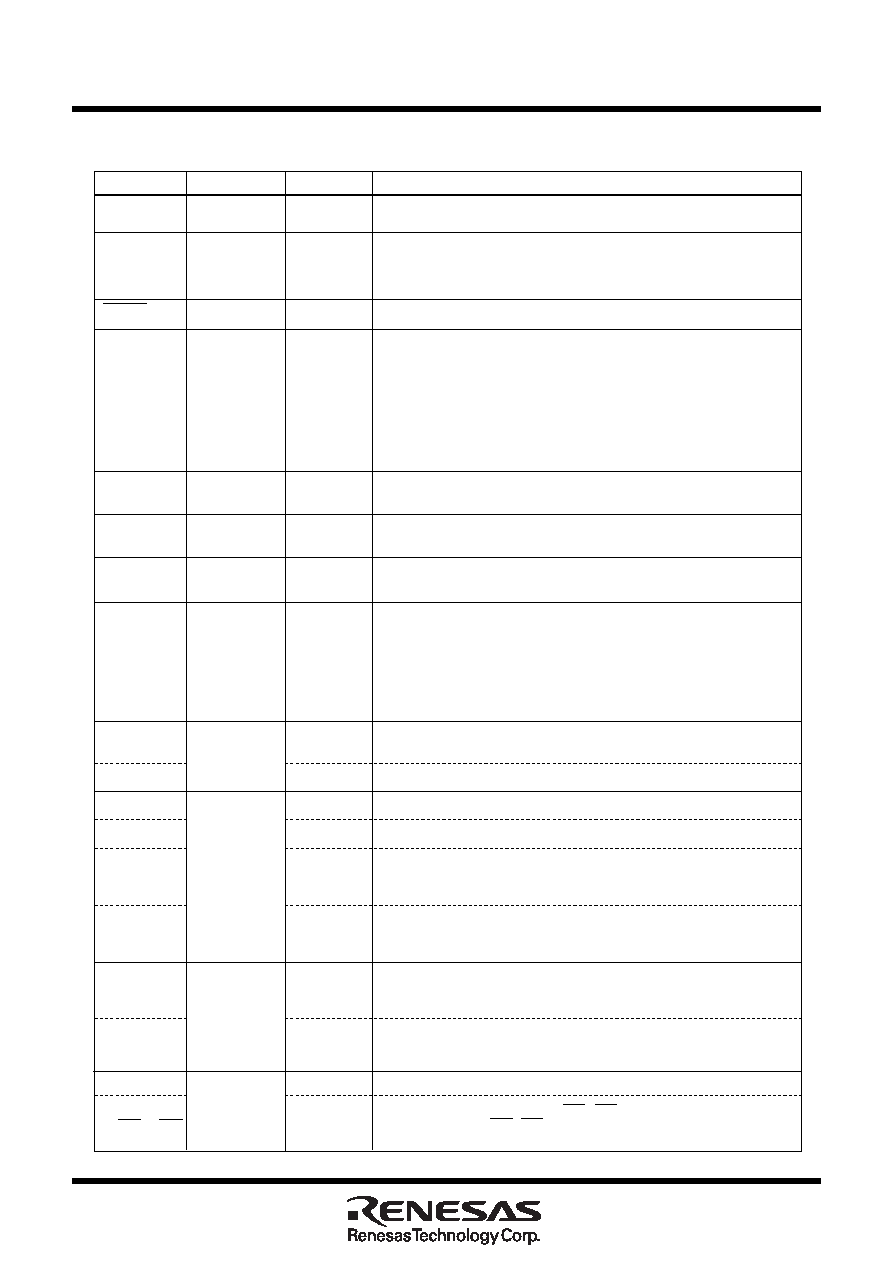
Pin Description
8
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
XIN
XOUT
BYTE
AVCC
AVSS
VREF
P00 to P07
D0 to D7
P10 to P17
D8 to D15
P20 to P27
A0 to A7
A0/D0 to
A7/D7
A0
A1/D0
to A7/D6
P30 to P37
A8 to A15
A8/D7,
A9 to A15
P40 to P47
Signal name
Power supply
input
CNVSS
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
External data
bus width
select input
Analog power
supply input
Reference
voltage input
I/O port P0
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
I/O port P3
I/O port P4
Supply 2.7V to 5.5 V to the VCC pin. Supply 0 V to the VSS pin.
Function
This pin switches between processor modes. Connect this pin to the
VSS pin when after a reset you want to start operation in single-chip
mode (memory expansion mode) or the VCC pin when starting
operation in microprocessor mode.
A “L” on this input resets the microcomputer.
These pins are provided for the main clock generating circuit.Connect
a ceramic resonator or crystal between the XIN and the XOUT pins. To
use an externally derived clock, input it to the XIN pin and leave the
XOUT pin open.
This pin selects the width of an external data bus. A 16-bit width is
selected when this input is “L”; an 8-bit width is selected when this
input is “H”. This input must be fixed to either “H” or “L”. Connect this
pin to the VSS pin when not using external data bus.
This pin is a power supply input for the A-D converter. Connect this
pin to VCC.
This pin is a power supply input for the A-D converter. Connect this
pin to VSS.
This pin is a reference voltage input for the A-D converter.
This is an 8-bit CMOS I/O port. It has an input/output port direction
register that allows the user to set each pin for input or output
individually. When used for input in single-chip mode, the port can be
set to have or not have a pull-up resistor in units of four bits by
software. In memory expansion and microprocessor modes, selection
of the internal pull-resistor is not available.
When set as a separate bus, these pins input and output data (D0–D7).
This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P0. P15 to P17 also function as
external interrupt pins as selected by software.
When set as a separate bus, these pins input and output data (D8–D15).
This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P0.
These pins output 8 low-order address bits (A0–A7).
If the external bus is set as an 8-bit wide multiplexed bus, these pins
input and output data (D0–D7) and output 8 low-order address bits
(A0–A7) separated in time by multiplexing.
If the external bus is set as a 16-bit wide multiplexed bus, these pins
input and output data (D0–D6) and output address (A1–A7) separated
in time by multiplexing. They also output address (A0).
This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P0.
These pins output 8 middle-order address bits (A8–A15).
If the external bus is set as a 16-bit wide multiplexed bus, these pins
input and output data (D7) and output address (A8) separated in time
by multiplexing. They also output address (A9–A15).
This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P0.
Pin name
Input
Output
Input
Input/output
I/O type
Analog power
supply input
Input/output
Output
Input/output
Output
Input/output
Output
Input/output
Output
Input/output
Output
A16 to A19,
CS0 to CS3
These pins output A16–A19 and CS0–CS3 signals. A16–A19 are 4 high-
order address bits. CS0–CS3 are chip select signals used to specify an
access space.
RESET
Pin Description
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M30620MCA-XXXGP | 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M30622M4A-XXXGP | 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M30622SAGP | 16-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M30622M4A-XXXFP | 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M30620SAGP | 16-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M30620MAA-XXXGP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30620MA-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:16-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER M16C FAMILY |
| M30620MA-XXXGP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:16-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER M16C FAMILY |
| M30620MC-2F2FP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30620MC-311FP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。