- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄358759 > LC72345 (Sanyo Electric Co.,Ltd.) Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip DC-DC Converter PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LC72345 |
| 廠商: | Sanyo Electric Co.,Ltd. |
| 元件分類: | DC/DC變換器 |
| 英文描述: | Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip DC-DC Converter |
| 中文描述: | 低電壓東突控制器的片上DC - DC變換器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/13頁 |
| 文件大小: | 90K |
| 代理商: | LC72345 |
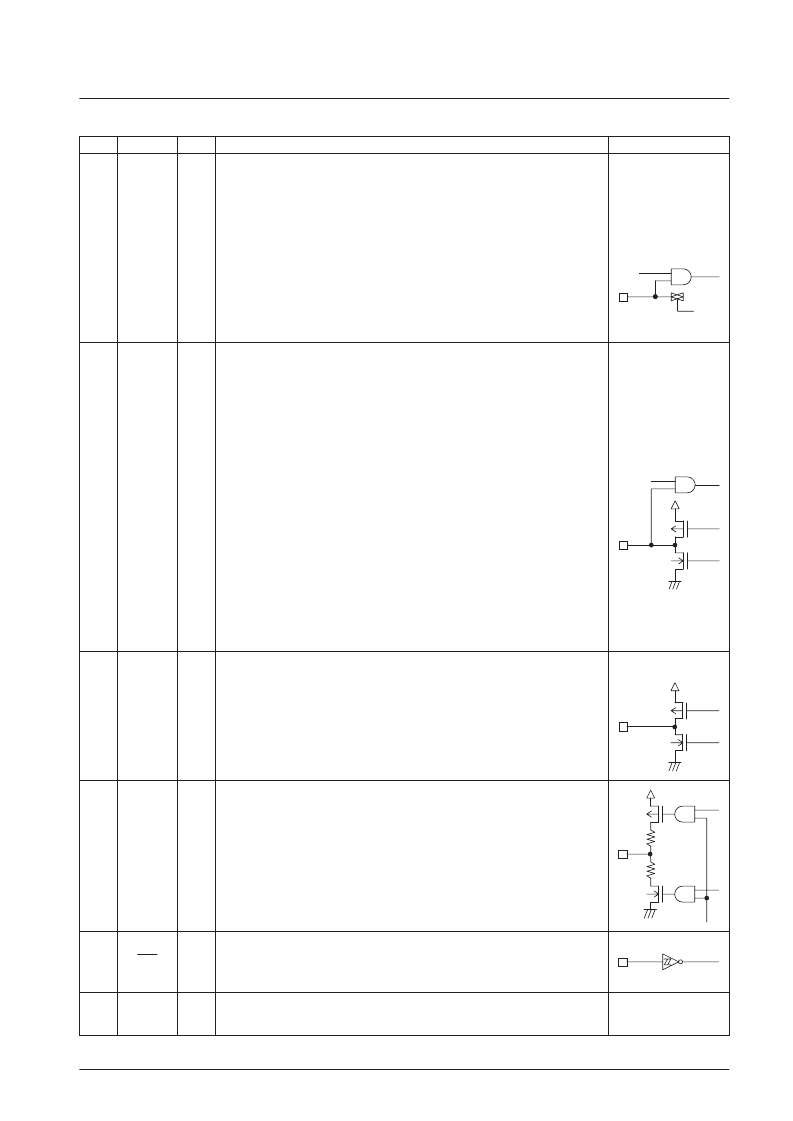
No. 6171-8/13
LC72344W, 72345W
Continued from preceding page.
Pin No.
Pin
I/O
Function
I/O circuit
General-purpose input and A/D converter input shared function ports.
The IOS instruction (Pwn = FH) is used to switch between the general-purpose input and A/D
converter port functions. The general-purpose input and A/D converter port functions can be
switched in a bit units, with 0 specifying general-purpose input, and 1 specifying the A/D
converter input function. To select the A/D converter function, set up the A/D converter pin
with an IOS instruction with Pwn set to 1. The A/D converter is started with the UCC
instruction (b3 = 1, b2 = 1). The ADCE flag is set when the conversion completes. The INR
instruction is used to read in the data.
*
: If an input instruction is executed for one of these pins which is set up for analog input, the
read in data will be at the low level since CMOS input is disabled. In backup mode these pins
go to the input disabled high-impedance state. These ports are set to their general-purpose
input port function after a reset. The A/D converter is a 5-bit successive approximation type
converter, and features a conversion time of 1.28 ms. Note that the full-scale A/D converter
voltage (1FH) is (63/96) times VDC3.
23
22
PF0/ADI0
PF1/ADI1
I
CMOS input/analog input
LCD driver segment output and general-purpose I/O shared function ports.
The IOS instruction
*
is used for switching both between the segment output and general-
purpose I/O functions and between input and output for the general-purpose I/O port function.
When used as segment output ports
The general-purpose I/O port function is selected with the IOS instruction (Pwn = 8).
b0 = S16 to 19/PG0 to 3 (0: Segment output, 1: PG0 to 3)
The general-purpose I/O port function is selected with the IOS instruction (Pwn = 9).
b0 = S12 to 15/PH0 to 3 (0: Segment output, 1: PH0 to 3)
When used as general-purpose I/O ports
The IOS instruction (Pwn = 6,7) is used to select input or output. Note that the mode can
be set in a bit units.
b0 = PG0
b1 = PG1
b2 = PG2
b3 = PG3
b0 = PH0
b1 = PH1
b2 = PH2
b3 = PH3
0: Input
1: Output
0: Input
1: Output
In backup mode, these pins go to the input disabled high-impedance state if set up as
general-purpose outputs, and are fixed at the low level if set up as segment outputs. These
ports are set up as segment outputs after a reset.
Although the general-purpose port/LCD port setting is a mask option, the IOS instruction
must be used as described above to set up the port function.
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
PG3/S19
PG2/S18
PG1/S17
PG0/S16
PH3/S15
PH2/S14
PH1/S13
PH0/S12
(
*
)
(
)
(
)
O
CMOS push-pull output
LCD driver segment output pins.
A 1/4-duty 1/2-bias drive technique is used.
The frame frequency is 75 Hz.
In backup mode, these outputs are fixed at the low level.
After a reset, these outputs are fixed at the low level.
39 to 49
S11 to S1
O
CMOS push-pull output
LCD driver common output pins.
A 1/4-duty 1/2-bias drive technique is used.
The frame frequency is 75 Hz.
In backup mode, these outputs are fixed at the low level.
After a reset, these outputs are fixed at the low level.
50
51
52
53
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
O
System reset input.
In CPU operating mode or halt mode, applications must apply a low level for at least one full
machine cycle to reset the system and restart execution with the PC set to location 0. This
pin is connected in parallel with the internal power on reset circuit.
54
RES
I
Battery presence/absence discrimination.
The internal clock oscillator starts when a high level is input to this pin.
The IN instruction can be used to determine whether or not a battery is present.
21
BATT
I
Continued on next page.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LC72346 | Ultralow-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
| LC72346W | Ultralow-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
| LC72349 | Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
| LC72349W | Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
| LC72349G | Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LC72345W | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Low-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip DC-DC Converter |
| LC72346 | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Ultralow-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
| LC723461W | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述: |
| LC723462W | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述: |
| LC72346W | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Ultralow-Voltage ETR Controller with On-Chip LCD Driver |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。