- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄358734 > LA70001 (Sanyo Electric Co.,Ltd.) Record/Playback Amplifiers for VHS Format VCRs PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LA70001 |
| 廠商: | Sanyo Electric Co.,Ltd. |
| 英文描述: | Record/Playback Amplifiers for VHS Format VCRs |
| 中文描述: | 記錄/回放放大器適合于VHS格式錄像機(jī) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 2/8頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 134K |
| 代理商: | LA70001 |
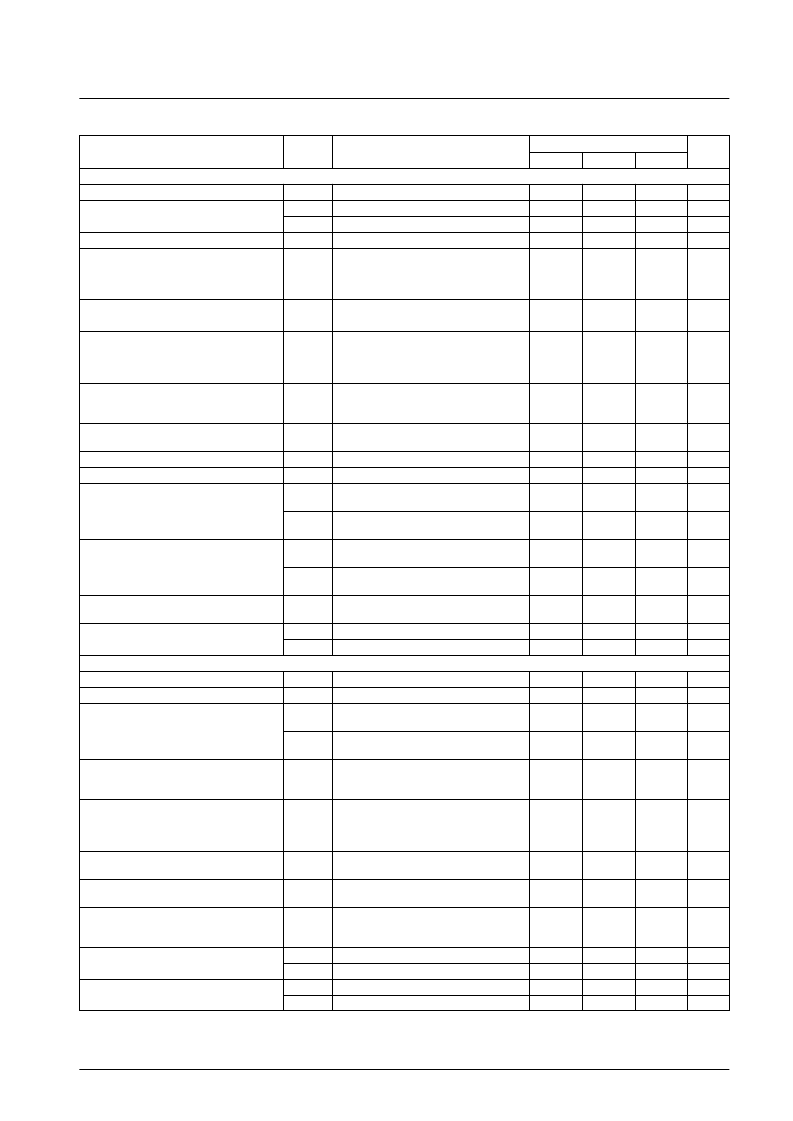
No. 5709-2/8
LA70001, 70001M
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min
typ
max
[Playback Mode]
Current drain
I
CCP
G
VP
1
G
VP
2
G
VP
1
The pin 13 inflow current.
23
29
35
mA
Voltage gain
CH1
V
IN
= 38 m Vp-p, f = 1 MHz
56
59
62
dB
CH2
56
59
62
dB
Voltage gain difference 1
G
VP
1—G
VP
2
With the same conditions as for the voltage
gain, the ratio of the output passed through a
1.1-MHz low-pass filter and the output with no
input signal.
–1
0
+1
dB
Equivalent input noise voltage
CH1
CH2
V
NIN
1
V
NIN
2
1.0
1.5
μVrms
Frequency characteristics
CH1
V
fp
1
V
fp
2
The ratio of the output for V
IN
= 38 mVp-p,
f = 7 MHz and G
VP
1, 2, 3, and 4.
With V
IN
= 38 mVp-p, f = 4 MHz, the ratio of
the 8-MHz output component (second
harmonic) and the 4-MHz component (the
fundamental).
CH2
–2.5
0
dB
Second harmonic distortion
CH1
CH2
V
HDP
1
V
HDP
2
–40
–35
dB
CH1
CH2
V
OMP
1
V
OMP
2
At f = 1 MHz, the output level when the ratio
of the 3-MHz output (third harmonic) and the
1-MHz output (fundamental) is –30 dB.
Maximum output level
1.0
1.2
Vp-p
Crosstalk SP
V
CR
1
The ratio of the V
IN
= 38 mVp-p, f = 4 MHz
output and G
VP
1.
CH1 – CH2
–40
–35
dB
Output DC offset
V
ODC
1
V
ENV
–100
0
+100
mV
Envelope detector output pin voltage
The T6 DC level when there is no input signal.
0
0.8
1.3
V
V
ENVSP
1
With a f = 4 MHz input, the T6 DC level when
the T7A output level becomes 175 mVp-p.
2.0
2.5
3.0
V
Envelope detector output pin voltage SP1
V
ENVSP
2
With a f = 4 MHz input, the T6 DC level when
the T7A output level becomes 400 mVp-p.
3.5
4.0
4.5
V
V
ENVEP
1
With a f = 4 MHz input, the T6 DC level when
the T7A output level becomes 125 mVp-p.
2.0
2.5
3.0
V
Envelope detector output pin voltage EP
V
ENVEP
2
With a f = 4 MHz input, the T6 DC level when
the T7A output level becomes 300 mVp-p.
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
Switch transistor on resistance in playback
mode
R
PON
18
Measure the difference in the DC levels with
a 1-mA and a 2-mA inflow current.
Lch
→
Hch
*
1
Hch
→
Lch
4
6
SW30 threshold level
SW30-1
1.2
5.0
V
SW30-2
0.0
0.8
V
[Record Mode]
Current drain
I
CCR
V
RSP
The pin 13 inflow current.
43
50
57
mA
Record AGC amplifier output level
The output level when V
IN
= 400 mVp-p, f = 4 MHz.
At f = 4 MHz, when V
IN
= 700 mVp-p: the
output level /VRSP, EP
105
112
119
mVp-p
V
AGC
1-SP
0.5
1.0
dB
Record AGC amplifier control
characteristics
V
AGC
2-SP
At f = 4 MHz, when V
IN
= 100 mVp-p: the
output level /VRSP, EP
–1.0
–0.5
dB
Record AGC amplifier frequency
characteristics
At V
IN
= 400 mVp-p, the ratio of the outputs
when f is 1 MHz and 7 MHz, i.e. the ratio of
the 7-MHz value to the 1-MHz value.
*
2.
V
FRS
–1
0
+1
dB
With V
IN
= 400 mVp-p, f = 4 MHz, the ratio
of the 8-MHz output component (second
harmonic) and the 4-MHz component (the
fundamental).
Record AGC amplifier second harmonic
distortion
V
HDRS
–45
–40
dB
Record AGC amplifier maximum output level
V
MOSP
At f = 4 MHz, the output level at which the
second harmonic goes to –35 dB.
*
3
20
22
mAp-p
Record AGC amplifier muting attenuation
V
MRS
When V
IN
= 400 mVp-p and f = 4 MHz, the
output level/VRSP, EP
–45
–40
dB
Record AGC amplifier cross modulation
relative level
T9A: V
IN
= 400 mVp-p, f = 4 MHz
T10A: V
IN
= 2.4 Vp-p, f = 629 kHz
The ratio of the (4 MHz ± 629 kHz) and the 4-MHz outputs.
MUTE OFF
→
MUTE ON
*
1
MUTE ON
→
MUTE OFF
PB
→
REC
*
1
REC
→
PB
V
CYS
–45
–40
dB
Record muting threshold level
MUTE-1
1.2
2.8
V
MUTE-2
3.2
5.0
V
Record mode to playback mode threshold level
PB-REC
1.2
5.0
V
REC-PB
0.0
0.8
V
Electrical Characteristics
at Ta = 25°C
Notes:Use a resistor with an accuracy of 1.0% for the resistor between pins 13 and 14.
*
1. This is the voltage application point
*
2. Here, fix the AGC amplifier gain by applying a 1.8-V DC level to the AGC detector filter pin (pin 15).
*
3. Here, adjust the output level by applying a DC voltage to the REC-CUR-Adj pin (pin 12).
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LA70001M | Record/Playback Amplifiers for VHS Format VCRs |
| LA70011 | Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
| LA70011M | Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
| LA70020 | Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
| LA70020M | Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LA70001M | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Record/Playback Amplifiers for VHS Format VCRs |
| LA7000S | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述: |
| LA70011 | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
| LA70011M | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
| LA70020 | 制造商:SANYO 制造商全稱:Sanyo Semicon Device 功能描述:Recording/Playback Amplifier for VHS VCRs |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。