- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370725 > HV3-2405E-5 (INTERSIL CORP) PT 21C 21#16 SKT PLUG PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HV3-2405E-5 |
| 廠商: | INTERSIL CORP |
| 元件分類: | 基準(zhǔn)電壓源/電流源 |
| 英文描述: | PT 21C 21#16 SKT PLUG |
| 中文描述: | 5 V-24 V ADJUSTABLE POSITIVE REGULATOR, PDIP8 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, DIP-8 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 13/14頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 573K |
| 代理商: | HV3-2405E-5 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)當(dāng)前第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)
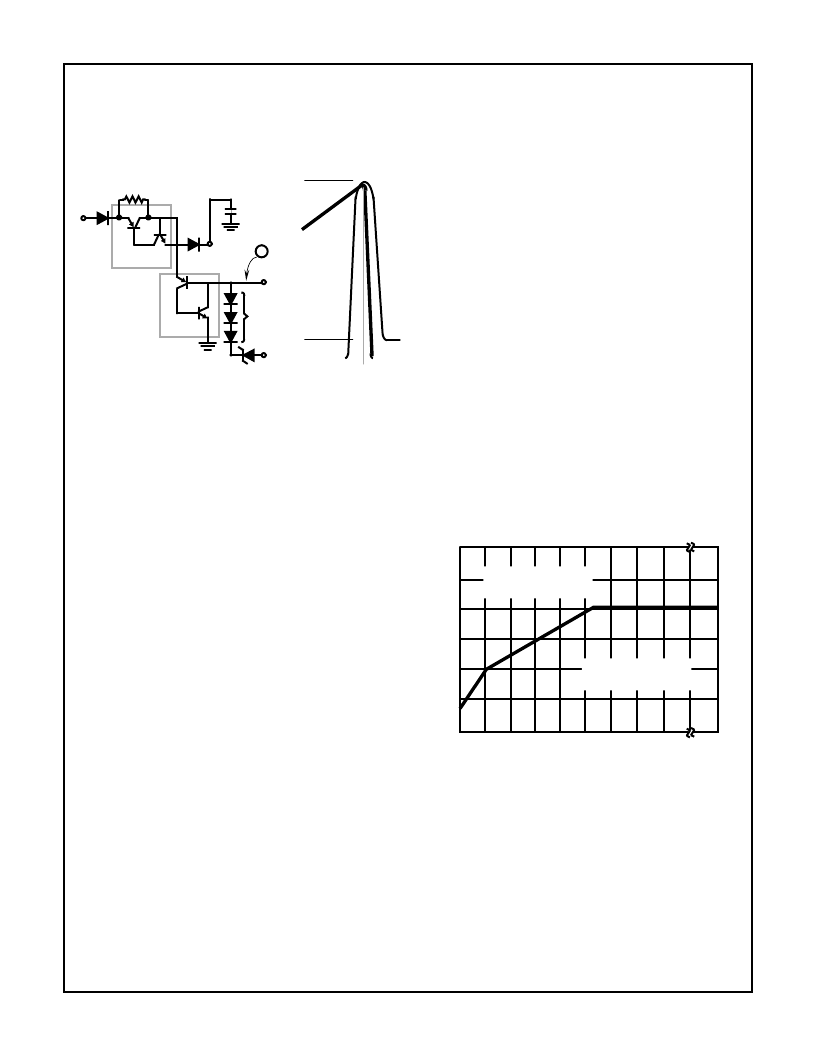
5-27
HV-2405E
Assume that SA1 is on and the current path is from pin 8 to
pin 2. If a small current is pulled out of the base of SA2s pnp
(point 1, Figure 17A) SA2 will turn on. When SA2 turns on
the collector current of SA1s pnp no longer provides base
drive to its npn and SA1 turns off. Figure 17(B) shows the
current relationships for both SCRs.
FIGURE 17 (A) (B). SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF SCRs
In order for current to be pulled out of the base of SA2s pnp
the voltage on the pnps emitter will have to be more positive
than the voltage on the base. The voltage on the base is ref-
erenced 7.5V above the output voltage by the zener diode
stack between pin 4 and pin 6. When the voltage on pin 2
reaches 6.8V (7.5V-1Vbe) above the output voltage, current
flows and SA2 is gated on. With 6.8V above the output volt-
age on C2, there is a sufficient voltage across SA2 to turn off
SA1 by sinking 100% of SA1s anode current.
SA2 could be triggered on before C2s voltage is sufficient to
ensure that SA2 can sink 100% of SA1s current, by noise on
pin 8. In this case SA1 goes into a high impedance state but
does not turn off. This condition can exist if switch arcing trig-
gers enough current through the inhibit capacitor to prema-
turely turn on SA2.
The
S
afe
O
perating
A
rea (SOA) of the HV-2405E is defined
by the voltage on C2 and the magnitude of the input current.
Figure 18 shows the safe operating area of the HV-2405E.
Under normal operating conditions the HV-2405E does not
turn off the input current until the voltage on C2 is well above
5V. Input currents larger than the safe turn off value in Figure
10 do not present any problems as long as the HV-2405E
does not attempt to interrupt them.
(B)
SA2
SA1
TURN OFF
SA1
SA2
(A)
PIN 8
RA4
DA2
PIN 2
C2
STORAGE
CAP
PIN 4
INHIBIT
PIN
PIN 6
OUTPUT
5.4V
1
2A
0.002
During start up operation, power line noise, typically gener-
ated by switch bounce/arcing, may accidently initiate input
current turn off before C2 is charged. The application circuit
shown in Figure 1 never permits the HV-2405E to operate
outside the safe turn off current region so any false turn off
signals have no effect. Also, once the capacitor is charged,
noise causes no problems.
For applications where there is little noise during start up, the
external transistor and associated resistors are not needed.
A 150pF capacitor connected to pin 4 helps keep the HV-
2405E turned off until any switching noise dies out. Also the
input resistor R1 may have to be increased to limit the input
current to the allowable maximum.
Some applications inherently have little start-up noise. EMI
filters between the power switch and the HV-2405E greatly
attenuate switch bounce noise. Likewise, the presences of
large capacitors connected through bridge rectifiers act as
filters. Solid-state relays that close at the line zero crossing
generate little noise. Also, there is no problem if power is
applied during the negative part of the line cycle. [The user is
cautioned to verify the suitability of his application circuit.
Contact Harris Applications for specific questions.]
If the safe turn off current is exceeded, SA1 will fail as a
short circuit. However, SA2 will continue to act, temporarily,
as shunt regulator to keep the voltage on pin 2 from exceed-
ing the safe limit of the post regulator. The voltage at pin 6
will not change. Failure to use a properly rated fuse may
cause R1 to reach dangerously high temperatures or cause
the HV-2405E to crack or explode.
FIGURE 18. HV-2405E SAFE INTERRUPT CURRENT vs PIN 2
VOLTAGE
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
30
I
SAFE AREA
OF OPERATION
ELECTRICAL
OVERSTRESS
PIN 2 (V)
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HV3-2405E-9 | World-WideSingle Chip Power Supply |
| HV341C | Interface IC |
| HV341MC | Interface IC |
| HV341MWG | Interface IC |
| HV341P | Interface IC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HV3-2405E-9 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:World-WideSingle Chip Power Supply |
| HV3-2405E-9 DIE | 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| HV33 | 制造商:WELWYN 制造商全稱:Welwyn Components Limited 功能描述:High Voltage Thick film Resistors |
| HV3304DJ | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Interface IC |
| HV3304PJ | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Interface IC |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。