- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370451 > HCPL-3700 AC/DC to Logic Interface Optocouplers(AC/DC邏輯接口光耦合器) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | HCPL-3700 |
| 英文描述: | AC/DC to Logic Interface Optocouplers(AC/DC邏輯接口光耦合器) |
| 中文描述: | AC / DC的邏輯接口光電耦合器(交流/直流邏輯接口光耦合器) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 12/12頁 |
| 文件大小: | 241K |
| 代理商: | HCPL-3700 |
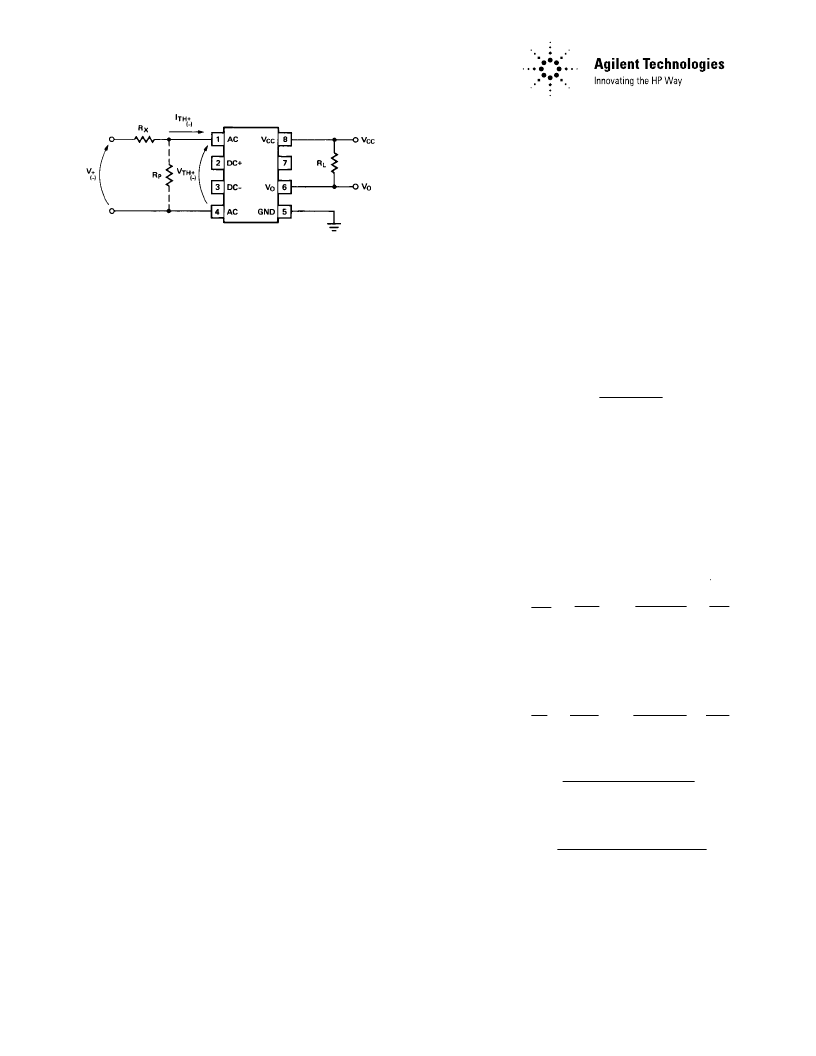
Electrical Considerations
The HCPL-3700/3760 optocoup-
lers have internal temperature
compensated, predictable voltage
and current threshold points
which allow selection of an
external resistor, R
X
, to determine
larger external threshold voltage
levels. For a desired external
threshold voltage, V
±
, a corre-
sponding typical value of R
X
can
be obtained from Figure 12.
Specific calculation of R
X
can be
obtained from Equation (1).
Specification of both V
+
and V
-
voltage threshold levels simul-
taneously can be obtained by the
use of R
X
and R
P
as shown in
Figure 13 and determined by
Equations (2) and (3).
R
X
can provide over-current
transient protection by limiting
input current during a transient
condition. For monitoring con-
tacts of a relay or switch, the
HCPL-3700/3760 in combination
with R
X
and R
P
can be used to
allow a specific current to be
conducted through the contacts
for cleaning purposes (wetting
current).
The choice of which input voltage
clamp level to choose depends
upon the application of this
device (see Figure 1). It is recom-
mended that the low clamp
condition be used when possible.
The low clamp condition in
conjunction with the low input
current feature will ensure
extremely low input power
dissipation.
In applications where dV
CM
/dt
may be extremely large (such as
static discharge), a series resistor,
R
CC
, should be connected in
series with V
CC
and Pin 8 to pro-
tect the detector IC from destruc-
tively high surge currents. See
Note 13 for determination of R
CC
.
In addition, it is recommended
that a ceramic disc bypass
capacitor of 0.01
μ
F be placed
between Pins 8 and 5 to reduce
the effect of power supply noise.
For interfacing ac signals to TTL
systems, output low pass filtering
can be performed with a pullup
resistor of 1.5 k
and 20
μ
F
capacitor. This application
requires a Schmitt trigger gate to
avoid slow rise time chatter
problems. For ac input applica-
tions, a filter capacitor can be
placed across the dc input
terminals for either signal or
transient filtering.
Either ac (Pins 1, 4) or dc
(Pins 2, 3) input can be used to
determine external threshold
levels.
V
- V
TH+
(-)
(-)
R
X
=
(1)
I
TH+
(-)
For two specifically selected
external threshold voltage levels,
V
+
and V
-
, the use of R
X
and R
P
will permit this selection via
equations (2), (3) provided the
following conditions are met. If
the denominator of equation (2)
is positive, then
V
+
V
-
V
TH+
V
TH-
V
+
- V
TH+
V
-
- V
TH-
I
TH+
I
TH-
≥
and
<
Conversely, if the denominator of
equation (2) is negative, then
V
+
V
-
V
TH+
V
TH-
V
+
- V
TH+
V
-
- V
TH-
I
TH+
I
TH-
≤
and
>
V
TH-
(V
+
) - V
TH+
(V
-
)
R
X
=
(2)
I
TH+
(V
TH-
) - I
TH-
(V
TH+
)
V
TH-
(V
+
) - V
TH+
(V
-
)
R
P
=
(3)
I
TH+
(V
-
-V
TH-
)+I
TH-
(V
TH+
-V
+
)
Figure 13. External Threshold Voltage Level Selection.
For one specifically selected
external threshold voltage level
V
+
or V
-
, R
X
can be determined
without use of R
P
via
www.semiconductor.agilent.com
Data subject to change.
Copyright 1999 Agilent Technologies
Obsoletes 5091-9668E
5965-3582E (11/99)
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HCPL-4100300 | Optically Coupled 20 mA Current Loop Transmitter |
| HCPL-4100500 | Optically Coupled 20 mA Current Loop Transmitter |
| HCPL4100 | Optically Coupled 20 mA Current Loop Transmitter |
| HCPL-4100 | Optically Coupled 20 mA Optically Coupled 20 mA |
| HCPL-4534 | Dual Channel, High Speed Optocouplers |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HCPL-3700#010 | 制造商:Hewlett Packard Co 功能描述: |
| HCPL-3700#300 | 功能描述:邏輯輸出光電耦合器 AC/DC to Logic RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 絕緣電壓:4243 Vrms 輸出類型:Push-Pull 最大傳播延遲時(shí)間:500 ns 最大正向二極管電壓: 最大反向二極管電壓: 最大正向二極管電流: 最大連續(xù)輸出電流:2.5 A 最大功率耗散:100 mW 最大工作溫度:+ 100 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16 封裝:Tube |
| HCPL-3700#500 | 功能描述:邏輯輸出光電耦合器 AC/DC to Logic RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 絕緣電壓:4243 Vrms 輸出類型:Push-Pull 最大傳播延遲時(shí)間:500 ns 最大正向二極管電壓: 最大反向二極管電壓: 最大正向二極管電流: 最大連續(xù)輸出電流:2.5 A 最大功率耗散:100 mW 最大工作溫度:+ 100 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16 封裝:Tube |
| HCPL-3700 | 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation 功能描述:Optocoupler |
| HCPL-3700.SD | 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation 功能描述:TAPE REEL / AC/DC HI-SPEED LOGIC, SURFACE MOUNT LEAD BEND, T&R |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。