- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370425 > HAL574 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HAL574 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family |
| 中文描述: | 雙線(xiàn)霍爾效應(yīng)傳感器系列 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 4/20頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 185K |
| 代理商: | HAL574 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)當(dāng)前第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)
HAL57x, HAL58x
ADVANCE INFORMATION
4
Micronas
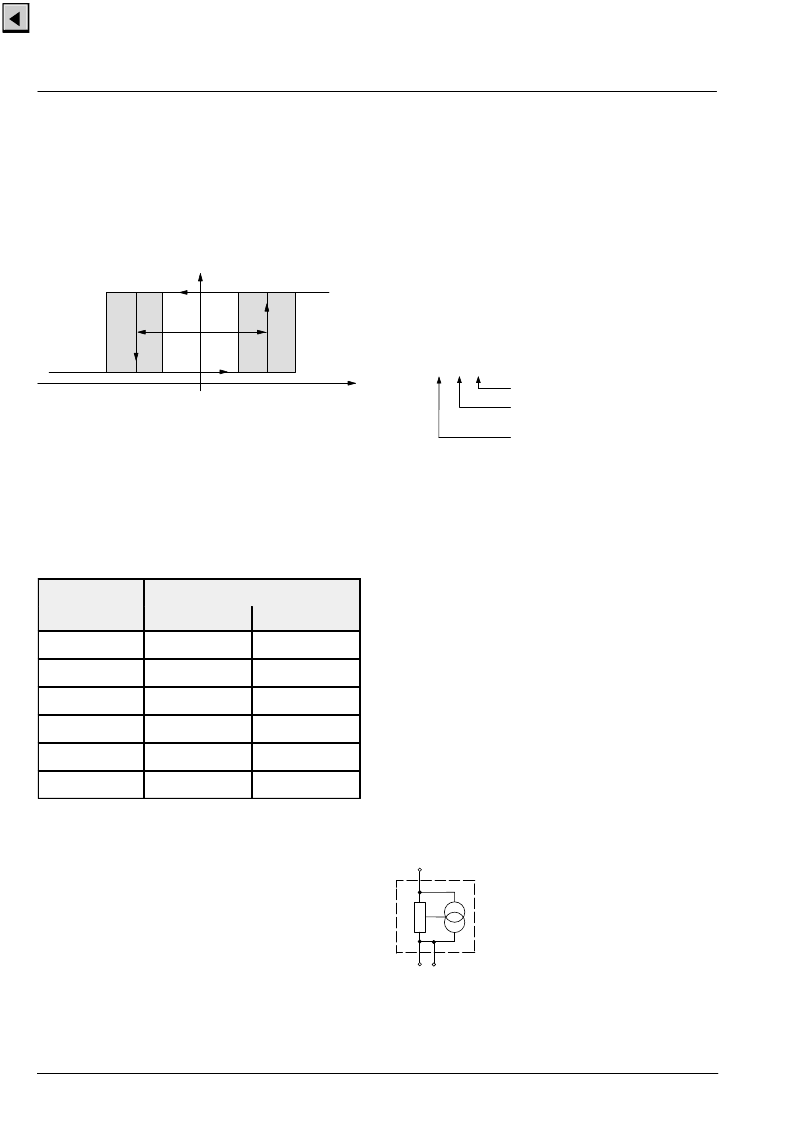
Latching Sensors:
The sensor turns to high current consumption with the
magnetic south pole on the branded side of the package
and turns to low consumption with the magnetic north
pole on the branded side. The current consumption does
not change if the magnetic field is removed. For chang-
ing the current consumption, the opposite magnetic field
polarity must be applied.
B
HYS
Current consumption
0
B
ON
B
OFF
I
DDlow
B
Fig. 1–3:
Latching Sensor
I
DDhigh
1.3. Marking Code
All Hall sensors have a marking on the package surface
(branded side). This marking includes the name of the
sensor and the temperature range.
Type
Temperature Range
K
E
HAL571
571K
571E
HAL573
573K
573E
HAL574
574K
574E
HAL575
575K
575E
HAL581
581K
581E
HAL584
584K
584E
1.4. Operating Junction Temperature Range
The Hall sensors from Micronas are specified to the chip
temperature (junction temperature T
J
).
K:
T
J
= –40
°
C to +140
°
C
E:
T
J
= –40
°
C to +100
°
C
Note:
Due to the high power dissipation at high current
consumption, there is a difference between the ambient
temperature (T
A
) and junction temperature. Please refer
section 5.4. on page 19 for details.
1.5. Hall Sensor Package Codes
Type: 57x or 58x
HALXXXPA-T
Temperature Range: K or E
Package: SF for SOT-89B
UA for TO-92UA
→
Type: 581
→
Package: TO-92UA
→
Temperature Range: T
J
= –40
°
C to +100
°
C
Example:
HAL581UA-E
Hall sensors are available in a wide variety of packaging
versions and quantities. For more detailed information,
please refer to the brochure: “Ordering Codes for Hall
Sensors”.
1.6. Solderability
all packages: according to IEC68-2-58
During soldering reflow processing and manual rework-
ing, a component body temperature of 260
°
C should not
be exceeded.
Components stored in the original packaging should
provide a shelf life of at least 12 months, starting from the
date code printed on the labels, even in environments as
extreme as 40
°
C and 90% relative humidity.
Fig. 1–4:
Pin configuration
GND
2
1V
DD
3
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HAL575 | Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL581 | Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL584 | Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL700 | Dual Hall-Effect Sensor with Independent Outputs |
| HAL700SF-E | Dual Hall-Effect Sensor with Independent Outputs |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HAL574SF-E | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱(chēng):MICRONAS 功能描述:Two-Wire Hall-Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL574SF-K | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱(chēng):MICRONAS 功能描述:Two-Wire Hall-Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL574UA-E | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱(chēng):MICRONAS 功能描述:Two-Wire Hall-Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL574UA-K | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱(chēng):MICRONAS 功能描述:Two-Wire Hall-Effect Sensor Family |
| HAL575 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:Two-Wire Hall Effect Sensor Family |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。