- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄375916 > FS7M0680YDTU (FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | FS7M0680YDTU |
| 廠商: | FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) |
| 中文描述: | 24 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, PZFM5 |
| 封裝: | TO-3P, 5 PIN |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/16頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1598K |
| 代理商: | FS7M0680YDTU |
FS7M0680
7
Then, Vfb continues increasing and the preset maximum
current flows through the primary side until the over load
protection circuit is activated. Since maximum current is
transferred to the secondary side, the secondary side voltage
becomes much higher than the rated voltage. If there is no
protection circuit against over voltage, the devices in the
secondary side will be damaged. In order to prevent this sit-
uation, the FPS has an over voltage protection circuit (pro-
tection against feedback circuit abnormalities). In general,
Vcc is proportional to the output voltage and FPS uses Vcc
instead of directly monitoring the output voltage to detect
over voltage situation. If V
CC
exceeds 24 V, the FPS acti-
vates the OVP circuit. Therefore, V
CC
should be properly
designed to be below 24V during normal operation to avoid
the undesired activation of OVP.
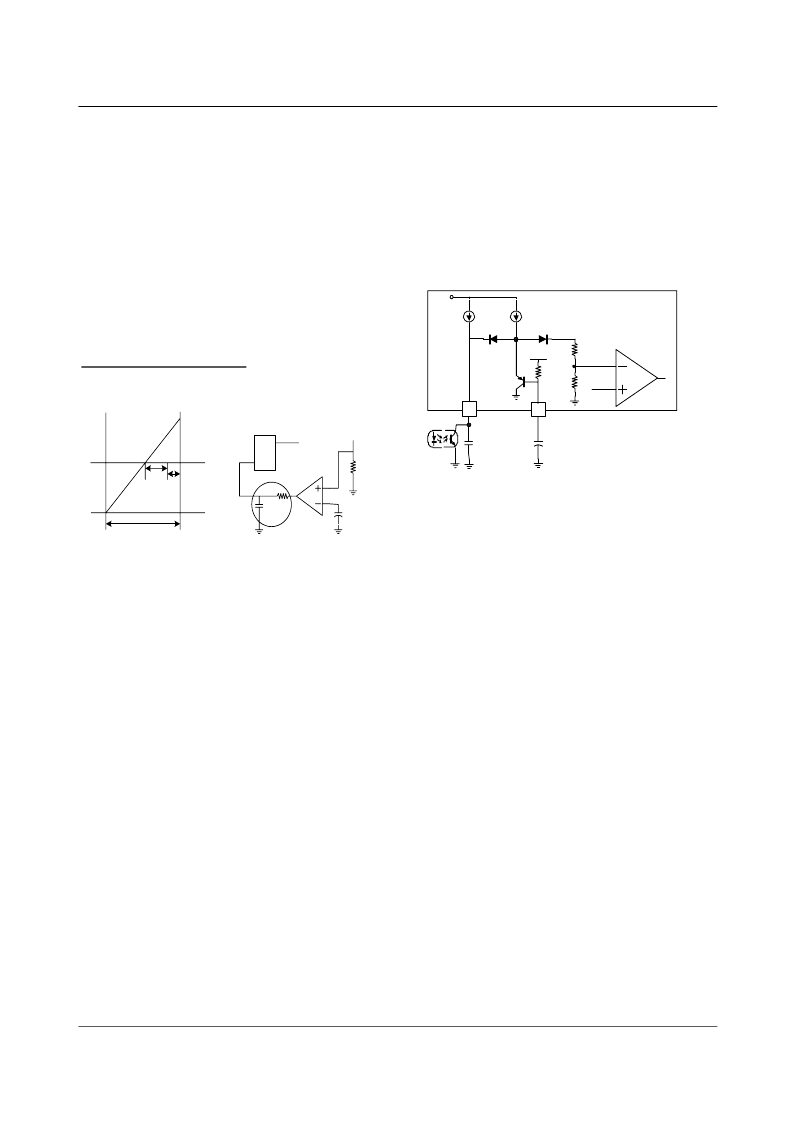
OCP (Over Current Protection)
Even though the FPS has OLP (Over Load Protection) and
pulse by pulse current limiting feature, these are not enough
to protect FPS when a secondary side diode short or load
short occurs. Therefore, FPS has internal OCP (Over Cur-
rent Protection) circuit as shown in figure 4. When the gate
turn-on signal is applied to the power MOSFET, the OCP
block is enabled and monitors the current through the sens-
ing resistor for 1us. The voltage across the resistor is com-
pared with the preset OCP level. If the sensing resistor
voltage is greater than the OCP level for longer than 200ns
within the allowed comparison time of 1us, the reset signal
is applied to the latch, resulting in the shutdown of SMPS.
Here, the additional delay of 100ns after the 200ns delay is
the time required for the operation of the protection circuit.
Soft start operation
At startup, the voltage of the PWM comparator inverting
input is saturated to its maximum value. In that case, the
power MOSFET current is at its maximum value and maxi-
mum allowable power is delivered to the secondary side
until the output voltage is established. It should be noted
that when the SMPS delivers maximum power to the sec-
ondary side during the startup, the entire circuit is seriously
stressed. By using a soft start function, such stresses can be
alleviated. Figure 5 shows how the soft-start circuit is
implemented. When it starts up, the soft start capacitor Cs
on pin 5 begins to be charged through the internal resistor
(Rss), which forces the comparator inverting input voltage
to increase slowly, also increasing the duty ratio slowly.
When the voltage of C
S
reaches about 3.2V, PNP transistor
is turned off and Cs continues being charged up to 5V
through Rss. Then, the voltage of the comparator inverting
input follows the feedback voltage of pin 4 instead of follow-
ing the voltage of C
S
. When the SMPS is shut down by the
protection circuits, C
S
is discharged through the internal
resistor allowing C
S
to be charged from 0V when the SMPS
starts up again.
S
R
Q
Latch signal
OCP time
R
C
OCP Level
Rsense
200ns
100ns delay
Minimum Turn-on Time
OCP Operating
Fiqure 4. OCP Function & Block
Figure 5. Soft Start Circuit
PWM
Comparator
5 V
18.5K
#4
#5
Switch(FPS)
Fairchild Power
10V
5uA
0.9mA
C S
D1
D2
Vfb
Cfb
R
ss
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| FS7M0880 | Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) |
| FS7M0880TU | Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) |
| FS7M0880YDTU | Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) |
| FS7SM-12 | HIGH-SPEED SWITCHING USE |
| FS7SM-16 | HIGH-SPEED SWITCHING USE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| FS7M0880 | 制造商:FAIRCHILD 制造商全稱:Fairchild Semiconductor 功能描述:Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) |
| FS7M0880TU | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 8a/800V Power Switch 70kHz RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| FS7M0880TU | 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation 功能描述:Power Supply IC |
| FS7M0880YDTU | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 8a/800V Power Switch 70kHz RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| FS7SM12 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:TRANSISTOR | MOSFET | N-CHANNEL | 600V V(BR)DSS | 7A I(D) | TO-247VAR |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。