- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄378405 > AND8090 (ON SEMICONDUCTOR) AC Characteristics of ECL Devices PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | AND8090 |
| 廠商: | ON SEMICONDUCTOR |
| 英文描述: | AC Characteristics of ECL Devices |
| 中文描述: | 交流特性的ECL裝置 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/20頁 |
| 文件大小: | 896K |
| 代理商: | AND8090 |
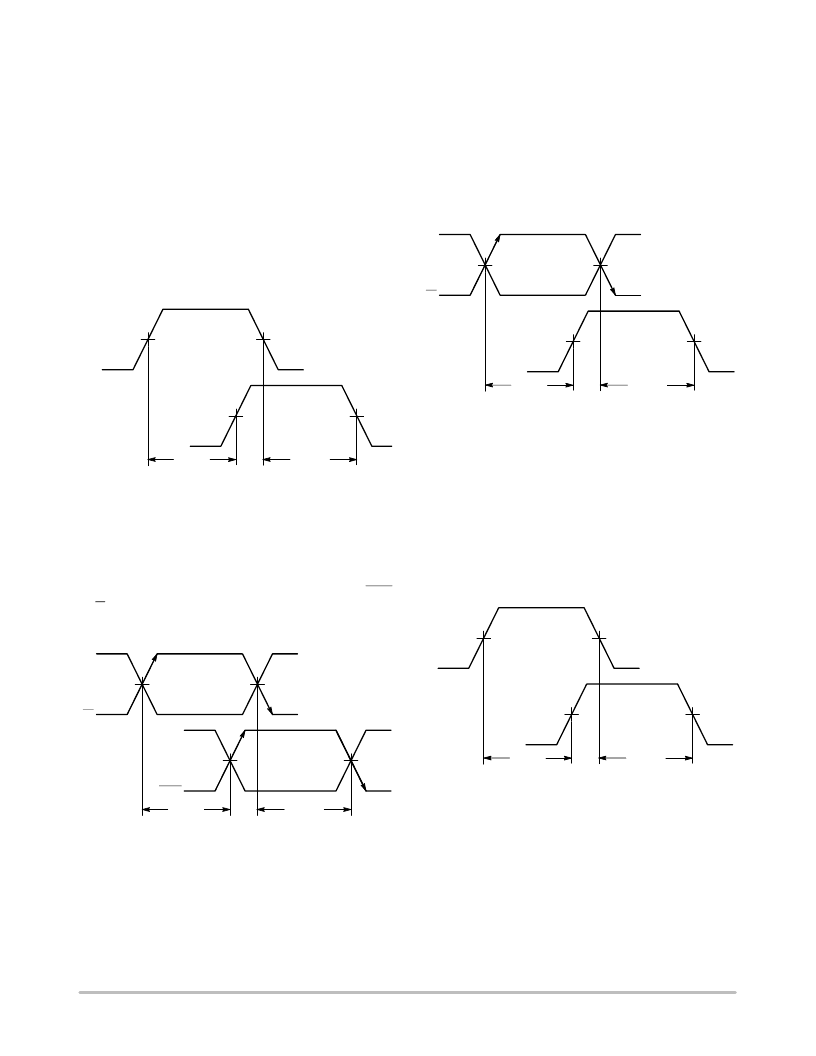
AND8090/D
http://onsemi.com
10
Propagation Delay
Rising Edge Propagation
– The rising edge (LOW
toHIGH transition) propagation delay (t
PLH
or t
P++
) is the
time needed to propagate an input rising edge to the output.
Falling Edge Propagation
– The falling edge (HIGH
toLOW transition) propagation delay (t
PHL
or t
P
) is the
time needed to propagate an input falling edge to the output.
SingleEnded ECL Devices
– Singleended propagation
delay is measured between the 50% point of the input rising
or falling edge, and the 50% point of the identical output
edge. There are many types of singleended propagation
delays such as a clock input to data output (CLK to Q)
propagation delay. Singleended output propagation delay
is shown in Figure 23.
t
PLH
IN
50%
OUT
50%
50%
50%
Figure 23. SingleEnded Propagation Delay
t
PHL
Differential ECL Devices
– Differential propagation
delay is measured between the crosspoint of the input rising
or falling edge, and the crosspoint of the identical output
edge. There are many types of differential input/output pairs
such as inverted clock inputs to inverted data outputs (CLK
to Q). Differential output propagation delay is shown in
Figure 24.
IN
X
pt
X
pt
Figure 24. Differential Propagation Delay
t
PLH
OUT
t
PHL
OUT
X
pt
X
pt
IN
ECL Inputs and NonECL Outputs
– Refer to the
device data sheet as several methods are used to measure the
output propagation delays. One method specifies the output
propagation delays from an ECL input crosspoint to a
nonECL fixed output voltage. For example, the output
propagation delays for the MC100ELT21 PECL to TTL
translator are specified between the ECL input crosspoint
and a TTL output fixed voltage equal to 1.5 V as shown in
Figure 25.
Figure 25. TTL Output Propagation Delay
t
PLH
OUT
1.5 V
1.5 V
t
PHL
IN
IN
X
pt
X
pt
NonECL Input and ECL Outputs
– Refer to the device
data sheet as several methods are used to measure the output
propagation delays. One method specifies the output
propagation delays from a nonECL input fixed voltage to
an ECL output 50% point. For example, the output
propagation delays for the MC10H352 CMOS to PECL
translator are specified between a CMOS input fixed voltage
equal to V
CC
/2 and the ECL output 50% point as shown in
Figure 26.
Figure 26. CMOS Input Propagation Delay
t
PLH
IN
V
CC
/2
OUT
50%
50%
t
PHL
V
CC
/2
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AND8090D | AC Characteristics of ECL Devices |
| AND8094 | Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching |
| AND8094D | Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching |
| AND8098 | Low-Cost 100 mA High-Voltage Buck and Buck-Boost Using NCP1052 |
| AND8099 | 5.0 V, 2.0 A Flyback Converter |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AND8090D | 制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全稱:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:AC Characteristics of ECL Devices |
| AND8094 | 制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全稱:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching |
| AND8094D | 制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全稱:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching |
| AND8098 | 制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全稱:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:Low-Cost 100 mA High-Voltage Buck and Buck-Boost Using NCP1052 |
| AND8099 | 制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全稱:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:5.0 V, 2.0 A Flyback Converter |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。