- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄24774 > 935084930112 (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) TELEPHONE SPEECH CKT, PDIP20 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 935084930112 |
| 廠商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | 無繩電話/電話 |
| 英文描述: | TELEPHONE SPEECH CKT, PDIP20 |
| 封裝: | 0.300 INCH, PLASTIC, SOT-146, DIP-20 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/38頁 |
| 文件大小: | 303K |
| 代理商: | 935084930112 |
第1頁第2頁當(dāng)前第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁
March 1994
11
Philips Semiconductors
Product specication
Low voltage versatile telephone transmission circuit
with dialler interface and transmit level dynamic limiting
TEA1064A
Microphone inputs MIC
+ and MIC and gain pins
GAS1 and GAS2
The TEA1064A has symmetrical microphone inputs, its
input impedance is 64 k
(2 × 32 k) and its voltage
amplification is typ. 52 dB with R7 = 68 k
. Either
dynamic, magnetic or piezo-electric microphones can be
used, or an electret microphone with a built-in FET buffer.
Arrangements for the microphone types are shown in
Fig.12.
The gain of the microphone amplifier is proportional to
external resistor R7 connected between GAS1 and GAS2
and with this it can be adjusted between 44 dB and 52 dB
to suit the sensitivity of the transducer.
An external 100 pF capacitor (C6) is required between
GAS1 and SLPE to ensure stability. A larger value of C6
may be chosen to obtain a first-order low-pass filter with a
cut-off frequency corresponding to the time constant
R7
× C6.
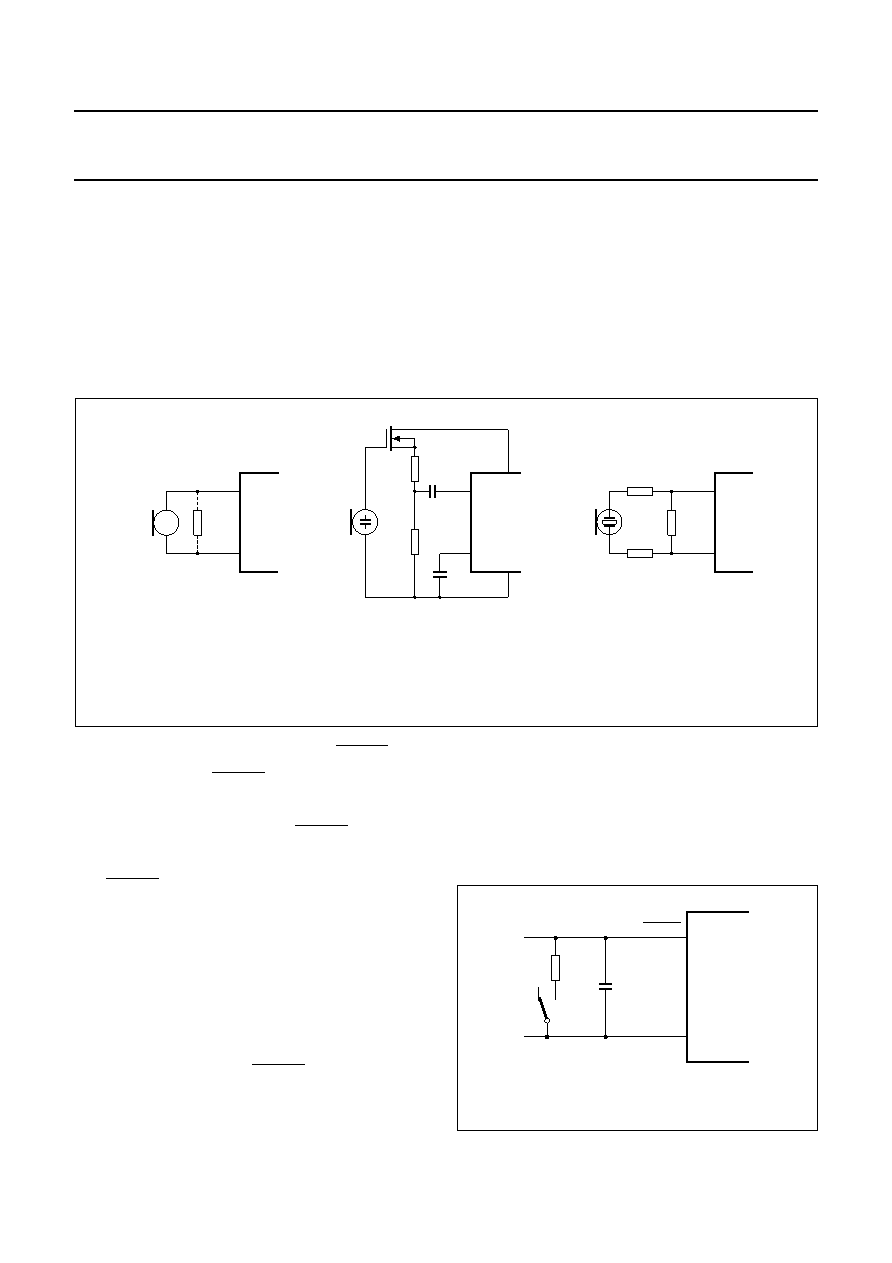
Fig.12 Microphone arrangements: a) magnetic or dynamic microphone, the resistor (1) may be connected to
reduce the terminating impedance, or for sensitive types a resistive attenuator can be used to prevent
overloading the microphone inputs; b) electret microphone; c) piezo-electric microphone.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGR067
VEE
VCC1
16
8
9
11
9
8
(1)
(a)
(b)
(c)
MIC
+
MIC
MIC
MIC
+
9
8
MIC
MIC
+
Dynamic limiter (microphone) pin DLS/MMUTE
A low level at the DLS/MMUTE pin inhibits the microphone
inputs MIC
+ and MIC but has no influence on the
receiving and DTMF amplifiers.
Removing the low level at the DLS/MMUTE pin provides
the normal function of the microphone amplifier after a
short time determined by the capacitor connected to
DLS/MMUTE pin. The microphone mute function can be
realised by a simple switch as shown in Fig.13.
To prevent distortion of the transmitted signal, the gain of
the sending amplifier is reduced rapidly when peaks of the
signal on the line exceed an internally-determined
threshold. The time in which gain reduction is effected
(attack time) is very short. The circuit stays in the
gain-reduced condition until the peaks of the sending
signal remain below the threshold level. The sending gain
then returns to normal after a time determined by the
capacitor connected to DLS/MMUTE (release time).
The internal threshold adapts automatically to the DC
voltage setting of the circuit (voltage VLN-SLPE). This
means that the maximum output swing on the line will be
higher if the DC voltage dropped across the circuit is
increased.
Fig.14 shows the maximum possible output swing on the
line as a function of the DC voltage drop (VLN-SLPE) with
Iline Ip as a parameter.
Fig.13 Microphone-mute function.
handbook, halfpage
MGR068
R17
3.3 k
7
11
DLS/MMUTE
VEE
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 0672.400 | Circular Connector; MIL SPEC:MIL-C-26482, Series I, Solder; Body Material:Aluminum; Series:PT06; Number of Contacts:55; Connector Shell Size:22; Connecting Termination:Solder; Circular Shell Style:Straight Plug; Body Style:Straight |
| 0672.500 | Circular Connector; No. of Contacts:61; Series:; Body Material:Aluminum; Connecting Termination:Solder; Connector Shell Size:24; Circular Contact Gender:Pin; Circular Shell Style:Straight Plug; Insert Arrangement:24-61 |
| 935085450112 | F/FAST SERIES, DUAL POSITIVE EDGE TRIGGERED D FLIP-FLOP, COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT, PDSO14 |
| 935007650118 | F/FAST SERIES, DUAL POSITIVE EDGE TRIGGERED D FLIP-FLOP, COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT, PDSO14 |
| 935007640602 | F/FAST SERIES, DUAL POSITIVE EDGE TRIGGERED D FLIP-FLOP, COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT, PDIP14 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 935087-000 | 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:301A511-51-05/164-0 - Bulk |
| 935087N001 | 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:301A511-51-05/164-CS7092 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:301A511-51-05/164-CS7092 - Bulk |
| 9350DC-200-0GZZZA | 制造商:Siemens 功能描述: |
| 9350DC-200-0ZZZTA | 制造商:Siemens 功能描述: |
| 9350DC-200-0ZZZZA | 制造商:Siemens 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。